[NV02] Protected areas 

Key message

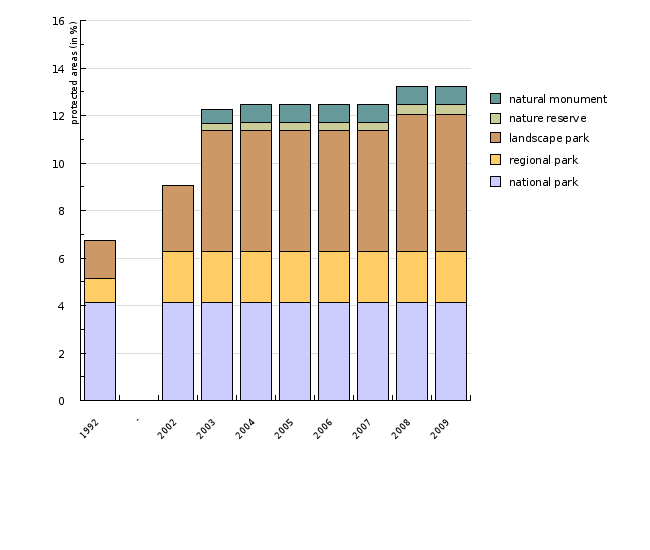
Protected areas are a national measure aimed at preserving valuable natural features and in-situ biodiversity. The proportion of protected areas increased by ca. 3.4% in 2002 and 2003 because of the foundation of the Notranjska Regional Park and the Goričko Landscape Park, followed by the foundation of the Ljubljansko barje Landscape Park in 2008, adding another 0.7% of the Slovenian territory into the category of protected areas; protected areas now cover just over 13% of the Slovenian territory.
Definition
The indicator shows the surface area of protected areas in Slovenia with regard to the type of protection and the category in accordance with the criteria of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). We differentiate among large (national, regional, landscape parks) and small (strict nature reserves, nature reserves and natural monuments) protected areas where prescribed protection regimes apply. Currently, 1 national park, 3 regional parks, 44 landscape parks, 1 strict nature reserve, 58 nature reserves and 1185 natural monuments in Slovenia are protected by state or municipal acts.
Charts
Register of protected areas, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2009.
| 1992 | - | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| national park | % | 4.13 | 4.13 | 4.13 | 4.13 | 4.13 | 4.13 | 4.13 | 4.13 | 4.13 | |
| regional park | % | 1.02 | 2.14 | 2.14 | 2.14 | 2.14 | 2.14 | 2.14 | 2.14 | 2.14 | |
| landscape park | % | 1.6 | 2.8 | 5.08 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 5.77 | 5.77 | |
| nature reserve | % | np | np | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | |
| natural monument | % | np | np | 0.6 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.73 | |
| total | % | 6.75 | 9.07 | 12.26 | 12.45 | 12.45 | 12.45 | 12.45 | 13.21 | 13.21 |
Goals
To increase the proportion of protected areas of various categories by between 5% (Resolution on National Programme of Environmental Protection Plan 2005-2012; OG of the RS, No. 2/06) and 17% of the Slovenian surface area.
Comment
Slovenia is rich with an exceptionally variegated landscape, varied plant and animal diversity and most of all, with people who foster a lasting relationship with nature and who long ago came to the fundamental realisation and awareness of the inevitable co-dependence between man and nature. Designated protected areas are among the most important (and oldest) mechanisms for preserving plant and animal species and their habitats.
Data for the period up until 2004 shows a continued increase in the share of protected areas. An important portion of these areas is covered by the Triglav National Park, the only national park in Slovenia, declared in its current size in 1981. The increase in the protected surface area in recent years has mostly been due to the proclamation of three larger parks, namely the Notranjska Regional Park in 2002, the Goričko Landscape Park in 2003 and the Ljubljansko barje Landscape Park in 2008.
According to data by the Ministry of Environment and Spatial Planning, two further parks are in the final phase of establishment, namely the Regional Park of Kamniško-Savinjske Alpe and the Radensko polje Landscape Park, so as to preserve the favourable condition of rare and threatened species and ecosystems as well as to ensure further sustainable development of the area by connecting and directing various activities, i.e. by actively managing the area.
The proclamation of both parks (probably in 2010) will lead to an increase of protected areas in Slovenia by another one percent.
Protected areas partially overlap with Natura 2000 protection areas. They encompass a smaller surface area than the Natura 2000 sites; they are, however, organised to a higher level with elaborated management plans and appointed managers.
Methodology
Data on Slovenia:
Data on protected areas is managed in the database Register of protected areas by the Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, the Nature Conservation Sector, on the basis of Article 111 of the Nature Conservation Act (ZON-UPB2, Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, No. 96/04).
Objectives summarized by: the Resolution on National Environmental Action Plan 2005-2012 (ReNPVO. Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, 2/06)
Source database or source: Register of protected areas
Data administrator: Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, the Nature Conservation Sector
Data acquisition date for this indicator: 4 November 2009
Methodology and frequency of data collection for the indicator: Data is collected upon designation of new areas or when corrections are made to eliminate errors or deficiencies found.
Data processing methodology: Data is presented in ratios to provide more insight and clarity.
Information concerning data quality:
- Advantages and disadvantages of the indicator: Data is considered official even though the maintenance of the Register of protected areas is not regulated by law. In particular, data on older protected sites is not reliable.
- Relevance, accuracy, robustness, uncertainty:
Reliability of the indicator (archive data): Graphical data is insufficient and inaccurate.
Uncertainty of the indicator (scenarios/projections): Not applicable to the indicator.
- Overall assessment (1 = without comments, 3 = data with reservations)
Relevance: 2
Accuracy: 2
Completeness over time: 2
Completeness over space: 2