[OD16] End-of-life vehicles 

Key message

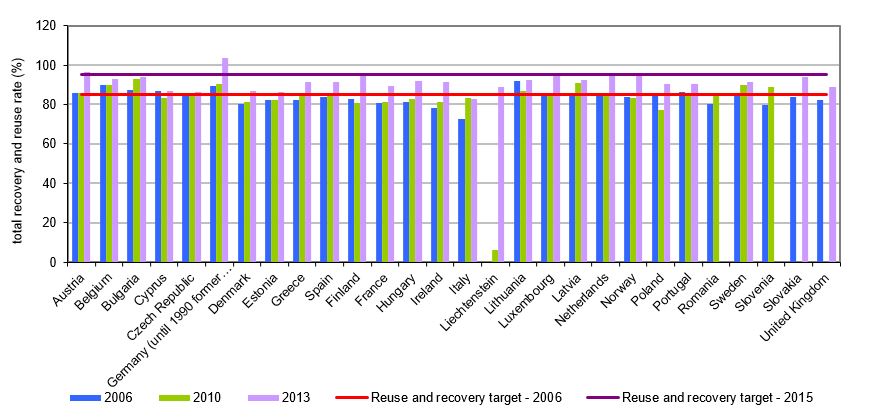
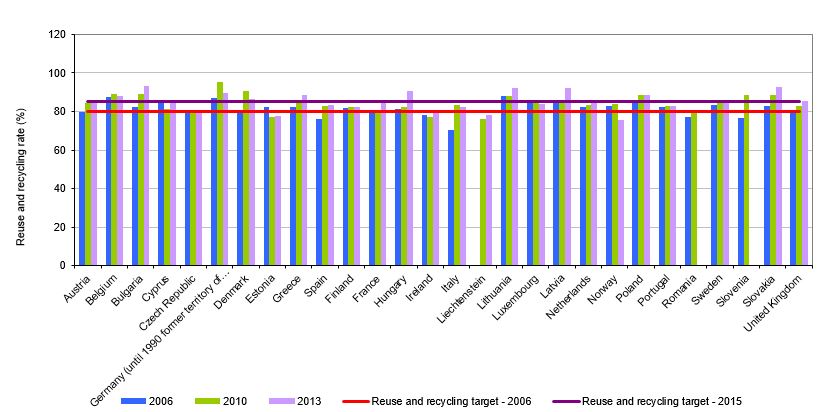
The number of end-of-life motor vehicles is increasing in line with the increasing number of newly registered vehicles. End-of-life motor vehicles qualify as hazardous waste due to the substances they contain. The dismantling system was established in 2004, creating conditions to meet the targets set at 80% of reuse and recycling, and 85% of reuse and recovery, which are being met by Slovenia. Nevertheless, the coverage of ELVs is lower than expected.
Definition
This indicator shows the number of end-of-life vehicles (ELVs) in Slovenia, the rates of reuse and recovery of ELVs in EU countries in 2006 and 2013 and the rates of reuse and recycling of ELVs in EU countries in 2006 and 2013.
An end-of life vehicle is a vehicle (passenger vehicles with up to eight seats excluding a driver's seat, cargo vehicles with a mass of up to 3.5 tonnes and three-wheeled motor vehicles, except three-wheeled motorcycles) that is considered to be waste, pursuant to the act governing environmental protection.
Because of hazardous substances (lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, oils, antifreeze liquids, brake fluids, fuel, batteries and other substances) in end-of-life vehicles, they are classified as hazardous waste.
The management of end-of-life vehicles is regulated by the Decree on end-of-life vehicles (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, Nos. 32/11, 45/11-amended and 26/12). Instead of public utility services responsible for the management of end-of-life vehicles (which used to be regulated by the Rules of the management of end-of-life motor vehicles [Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, No. 118/04]), the Decree introduced the Principle of Extended Producer Responsibility.
Charts
Concessionaire Reports - SARA - Internet application on end-of-life vehicles decomposition, Ministry of the Environment and Spatial Planning, 2014
| 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| old burden | number | 6381 | 3811 | 1314 | 1755 | 1802 | 1169 | 1476 |
| decommissioning Certificate | number | 4886 | 1886 | 8104 | 6654 | 4974 | 5874 | 5331 |
| total | number | 11267 | 5697 | 9418 | 8409 | 6776 | 7043 | 6807 |
EUROSTAT, End of life vehicles, 2014
| Cyprus | Poland | Finland | France | Ireland | Denmark | United Kingdom | Hungary | Luxembourg | Lithuania | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | % | 86.6 | 85.8 | 83 | 81 | 78.1 | 80 | 82.3 | 81.5 | 85.8 | 92 |
| 2007 | % | 83.4 | 77 | 81 | 81.5 | 81.3 | 81.2 | 83.1 | 82.8 | 85.2 | 86.7 |
| 2008 | % | 79.8 | 80.1 | 81 | 81.4 | 81.8 | 82.9 | 84 | 84.4 | 85 | 85 |
| Reuse and recovery target - 2006 | % | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 |
| Reuse and recovery target - 2015 | % | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 |
| Netherlands | Spain | Greece | Czech Republic | Romania | Bulgaria | Italy | Portugal | Slovakia | Latvia | ||
| 2006 | % | 85.2 | 84 | 82.3 | 85.1 | 80.3 | 87.2 | 72.7 | 86.1 | 83.6 | 86 |
| 2007 | % | 85.3 | 85.1 | 84.1 | 85.1 | 85.7 | 92.7 | 83.1 | 85.7 | 88.6 | 91 |
| 2008 | % | 85.6 | 85.7 | 85.7 | 86 | 86.5 | 86.7 | 87.1 | 87.2 | 88.8 | 89 |
| Reuse and recovery target - 2006 | % | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 |
| Reuse and recovery target - 2015 | % | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 |
| Slovenia | Belgium | Sweden | Estonia | Germany | Austria | ||||||
| 2006 | % | 79.6 | 90 | 85 | 82.5 | 89.5 | 86 | ||||
| 2007 | % | 88.7 | 90.1 | 90 | 82.2 | 90.4 | 86 | ||||
| 2008 | % | 89.7 | 90.2 | 91 | 92.7 | 92.9 | 96.1 | ||||
| Reuse and recovery target - 2006 | % | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | ||||
| Reuse and recovery target - 2015 | % | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 |
EUROSTAT, End of life vehicles, 2014
| Ireland | Cyprus | Poland | France | Czech Republic | Portugal | Bulgaria | Finland | Spain | United Kingdom | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | % | 78.1 | 85.4 | 84.7 | 79.6 | 79 | 82.2 | 82.4 | 82 | 76 | 81 |
| 2007 | % | 81.3 | 83.7 | 72.8 | 79.8 | 79 | 81.7 | 89.5 | 81 | 81.9 | 81.8 |
| 2008 | % | 75.9 | 78.3 | 79.5 | 79.9 | 80.1 | 80.8 | 81 | 81 | 82.5 | 82.5 |
| Reuse and recycling target - 2006 | % | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| Reuse and recycling target - 2015 | % | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 |
| Denmark | Hungary | Sweden | Austria | Romania | Luxembourg | Italy | Netherlands | Lithuania | Greece | ||
| 2006 | % | 80 | 81.2 | 83.4 | 80 | 77.1 | 85.1 | 70.3 | 82.5 | 88 | 82.3 |
| 2007 | % | 81 | 81.6 | 83 | 80 | 83.7 | 83 | 82.3 | 83.1 | 86.4 | 84.1 |
| 2008 | % | 82.7 | 83 | 83 | 83.7 | 83.7 | 84 | 84.3 | 84.4 | 85 | 85.7 |
| Reuse and recycling target - 2006 | % | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| Reuse and recycling target - 2015 | % | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 |
| Latvia | Slovenia | Belgium | Slovakia | Germany | Estonia | ||||||
| 2006 | % | 86 | 76.8 | 87.7 | 82.8 | 86.8 | 82.5 | ||||
| 2007 | % | 88 | 87.2 | 87.9 | 88 | 88.1 | 82.2 | ||||
| 2008 | % | 87 | 87.6 | 88 | 88.4 | 89.2 | 92.4 | ||||
| Reuse and recycling target - 2006 | % | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | ||||
| Reuse and recycling target - 2015 | % | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 |
Goals
· to ensure a unified system of collecting end-of-life vehicles on the entire territory of the Republic of Slovenia and 100% collection of end-of-life vehicles;
· to achieve target percentages of reuse and recovery (85% by the end of 2014 and 95% by the end of 2015);
· to achieve target percentages of reuse and recycling (80% by the end of 2014 and 85% by the end of 2015);
· to eliminate old burdens;
· to provide proper treatment of hazardous substances generated in the process of dismantling ELVs.
Comment
In the Republic of Slovenia, the number of newly registered passenger cars has increased to around 100,000 in recent years. The upward trend of registered passenger cars is similar; from around 700,000 in the middle of the 1990s, the number has grown to almost 1,130,000 in recent years.
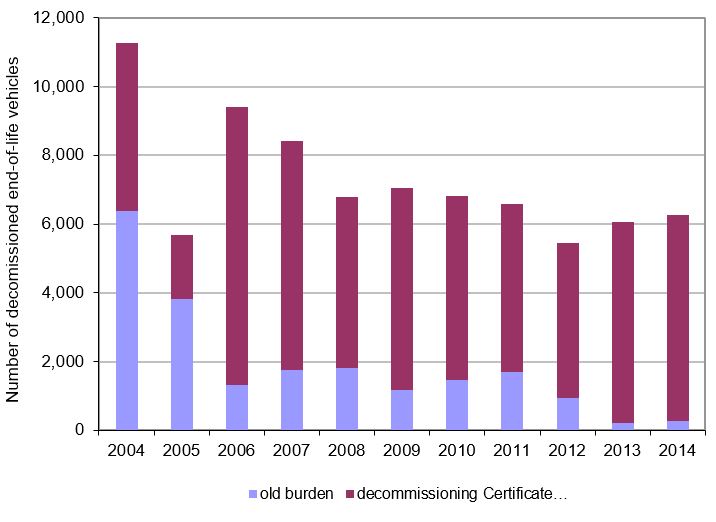
Between May 2004 and the end of 2014, approximately 72,000 tonnes of ELVs were dried and dismantled in recovery centres, In 2014, slightly less than 6,300 cars were dismantled in Slovenia.
Until 2011, the system of end-of-life vehicles management was provided by public utility services. One essential measure for the functioning of the system was the introduction of the “dismantling certificate”. Upon deregistration of a vehicle, the last owner of a vehicle qualifying as an end-of-life vehicle pursuant to regulations governing environmental protection and end-of-life vehicle management was obliged to present a certificate of vehicle destruction. The service of dismantling is free of charge for the last owner of a vehicle. Since its establishment in April 2004, the public utility service providers have dismantled 72,590 ELVs.
According to the most recent estimates, at least 30,000 end-of-life vehicles are generated in Slovenia each year. The actual number of dismantled ELVs differs considerably from these estimates largely due to abuse of the instrument of deregistration of vehicles. Vehicle location statements are being abused in such a way that the last owners are using them to deregister vehicles that are later being illegally dismantled. In view of the large number of vehicle location statements that are issued in Slovenia (approximately 15,000 annually), it impossible to efficiently carry out control of vehicles that are deregistered in this way.
With the adoption of a new regulation introducing extended producer responsibility, end-of-life vehicle management has become more transparent. In Slovenia there are currently 47 collection points for end-of-life vehicles that collect ELVs under the authorisation of three dismantling facilities operating within the framework of the extended producer responsibility system. In addition, 16 independent facilities for ELV dismantling operate. For the last owner, recovery of an end-of-life vehicle is rendered free of charge. Upon handing over an end-of-life vehicle for dismantling, the owner is issued a certificate of destruction.
The target ELV reuse and recovery rate for 2015 was 95%, while the target reuse and recycling rate for the same year was 85%. In 2013, target ELV reuse and recovery rates for 2015 were achieved by 6 countries, while target ELV reuse and recycling rates for 2015 were achieved by 16 countries. Slovenia achieved both targets.