[OD03] Hazardous waste

Definition
The indicator shows the quantity of generated hazardous waste and the manners of treatment of hazardous waste.
Hazardous waste has one or more hazardous properties which are harmful to health and/or the environment (e.g. flammability, irritancy, toxicity, mutagenicity, oxidizing properties, infectivity, etc.). The waste list is published in the Annex to the Rules on the Management of Waste, where hazardous wastes are marked with an asterisk next to the waste classification number.
Charts
Waste Management Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2006
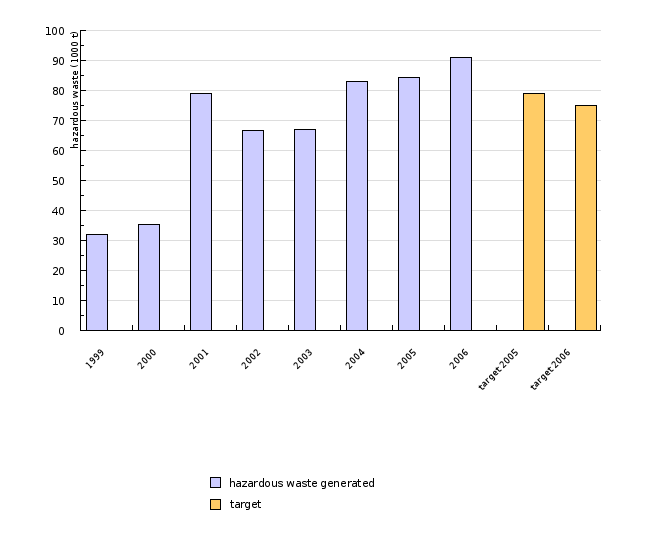
| 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | target 2005 | target 2006 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hazardous waste generated | 1000 t | 32 | 35.4 | 78.9 | 66.8 | 67.1 | 83.1 | 84.4 | 90.9 | ||
| target | 1000 t | 78.9 | 75 |
Waste Management Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2006
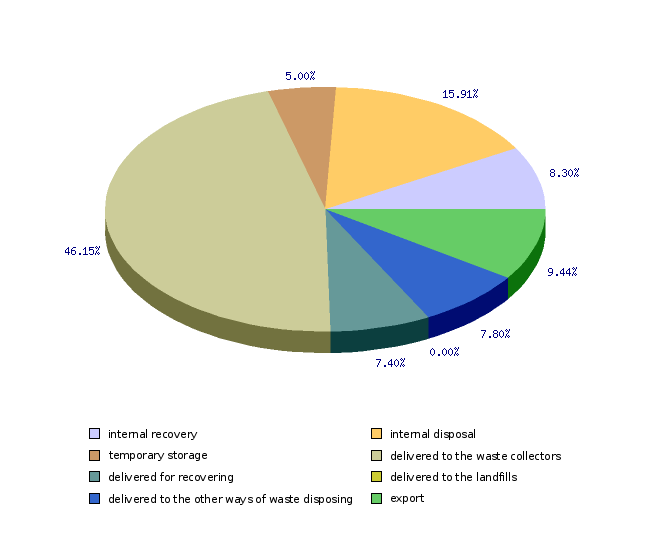
| 2005 | ||
|---|---|---|
| internal recovery | t | 7007 |
| internal disposal | t | 13431 |
| temporary storage | t | 4218 |
| delivered to the waste collectors | t | 38950 |
| delivered for recovering | t | 6245 |
| delivered to the landfills | t | 0 |
| delivered to the other ways of waste disposing | t | 6580 |
| export | t | 7966 |
| internal recovery | % | 8 |
| internal disposal | % | 16 |
| temporary storage | % | 5 |
| delivered to the waste collectors | % | 46 |
| delivered for recovering | % | 7 |
| delivered to the landfills | % | 0 |
| delivered to the other ways of waste disposing | % | 8 |
| export | % | 9 |
Goals
Continue the trend of reducing the generation of hazardous waste by 5 – 10% per year.
Comment
The annual quantities of hazardous waste are rising. The large increase in the generation of hazardous waste in 2001 compared to 2000, namely by 43,503 tonnes, was the result of an incident, i.e. the disposal of a large single quantity of hazardous waste. According to the data provided by waste generators, Slovenia produced 67,100 tonnes of hazardous waste in 2003. In 2003, generation of waste was reported by 1814 liable entities that generated 255 different types of hazardous waste. Compared to 2002, the number of entities that reported on hazardous waste has reduced, and the number of reported types of hazardous waste has increased.
Our estimate is that the annual quantity of generated hazardous waste has stabilised. According to the data submitted by the generators of waste, Slovenia produced 83,064 tonnes of hazardous waste in 2004. Compared to the previous year, the volume has increased by 1.46 times. There are several reasons for this increase; however, our estimate is that they are predominantly methodological in nature (collection of data related to hazardous waste):
• In 2003, the classification list of wastes was partially changed and some wastes were requalified from non-hazardous to hazardous.
• Separate collection of waste (including hazardous waste) has improved. A whole array of new regulations governing the management of this type of waste that were passed in 2003 and 2004 contributed to this improvement.
• The number of liable entities that submitted reports has increased; 2,945 of approximately 9,000 potential liable entities (i.e., entities who were given the form for their annual report on the generation of waste in production and service activities) submitted reports.
• The most significant growth in the quantity of hazardous waste can be observed in group 17 – construction and demolition waste (in 2003, a special regulation was passed on the treatment of construction waste; the waste under classification number 17 06 05 was requalified into 17 06 05* - construction material containing asbestos; and in 2004 the Operational programme on construction waste management for the period 2004-2008 was confirmed). The quantity of hazardous wastes in this group has increased by 25 index points.
• the greatest contribution to the total quantity of hazardous waste is made by waste belonging to group 07 – waste from organic chemical processes (the increase in the quantity of waste compared to 2003 is not significant in groups 9 and 10 – inorganic waste from thermal processes.)
In 2005, Slovenia produced 84,397 tonnes of hazardous waste. The reporting forms were sent to 8,640 liable entities and 7,421 forms were returned, which is 86% of all liable entities.
According to Eurostat, the volume of generated hazardous waste is growing in the majority of EU member states. Methodological problems with identifying the quantities of hazardous waste and comparability of data are also present at the international level.
Methodology
The Ministry of the Environment and Spatial Planning – the Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia has been monitoring the generation of hazardous waste since 1999. In 2000, liable entities reported on the generation of hazardous waste for the first time (report for 1999). The data are collected based on the Decree on waste management (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, nos. 34/08). (Up to 2008 data were gathered on Rules on the management of waste (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, nos. 84/98, 45/00, 20/01 and 13/03)), which stipulate that:
- the generator of waste who generates at least 5 kg of hazardous waste in one calendar year must deliver a report on the generated waste and its treatment for the previous calendar year;
- the collector must deliver a report on the collected hazardous waste for the previous calendar year;
- the waste treatment operator of hazardous waste must deliver a report on hazardous waste treatment in the previous calendar year.
The liable entities must send the above reports no later than 31st March of the current year on the form prescribed by the Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia.
The classification list of the waste, based on which the liable entities report on the quantities of a specific type of waste, has changed in accordance with the change in the European legislation in 2001. Some modifications were also made in 2003. The submitted reports are entered into the database. The Agency checks if all liable entities have submitted their reports. In case of irregularities or failure to report, the data are verified with each liable entity.