[NV04] Valuable natural features 

Key message

14,901 valuable elements of nature on the Slovenian territory have been given the status of a valuable natural feature, 8,382 of which are subterranean caves. Interventions to and activities on valuable natural features may only be executed in the absence of other spatial or technical possibilities.
Definition
Valuable natural features include all natural heritage on the territory of the Republic of Slovenia.
A valuable natural feature is a rare, valuable or well-known natural phenomenon as well as any other valuable phenomenon, part of living and non-living nature, a natural area or part of a natural area, an ecosystem, landscape or designed landscape. This includes geological phenomena, minerals and fossils as well as their sites, surface and subterranean Karst phenomena, subterranean caves, gorges and narrows as well as other geomorphological phenomena, glaciers and glacial forms, springs, rapids, waterfalls, lakes, bogs, brooks and rivers with banks, the seashore, plant and animal species, their exceptional specimens and habitats, ecosystems, landscape and designed landscape.
The Rules on the designation and protection of valuable natural features (OG of the RS, Nos. 111/04 and 70/06, hereafter »the Rules«) gave 14,901 valuable elements of nature the status of a valuable natural feature of national or local importance. Valuable natural features of national importance comprise features which are of international or great national importance and which are under the jurisdiction of the state. The rest are of local importance and are protected by the local communities. All valuable natural features within protected areas established by the state are of national importance. Features of national importance are also all subterranean caves, which were given the status of a geomorphological valuable natural feature with the amendment of the Rules in 2006. 8,382 subterranean caves are maintained separately in the Register of subterranean caves, which forms part of the Register of valuable natural features. In this Register, detailed records of all valuable natural features are maintained by the Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia.
Interventions to and activities on valuable natural features may only be executed in the absence of other spatial or technical possibilities. They must be executed in a manner which ensures that the valuable natural feature is not ruined and which does not alter the characteristics due to which a part of nature has been recognized as a valuable natural feature. As a rule, current use of the valuable natural feature is preserved; however, sustainable use which does not threaten the existence of the valuable natural feature nor impede the protection thereof is also possible. The valuable natural feature and its immediate vicinity can be properly organised for public visits by stabilising the trails and panoramic spots, setting up resting places, setting fences, information and warning boards etc. Valuable features, which according to their importance are classified into valuable features of national and local importance, can subsequently be additionally protected by the state or the local community by means of protection measures which have been defined in the Nature Preservation act (contractual protection, custody, temporary or permanent protection as well as restoration).
Charts
The Register of valuable natural features, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2008.
| 2008 | ||
|---|---|---|
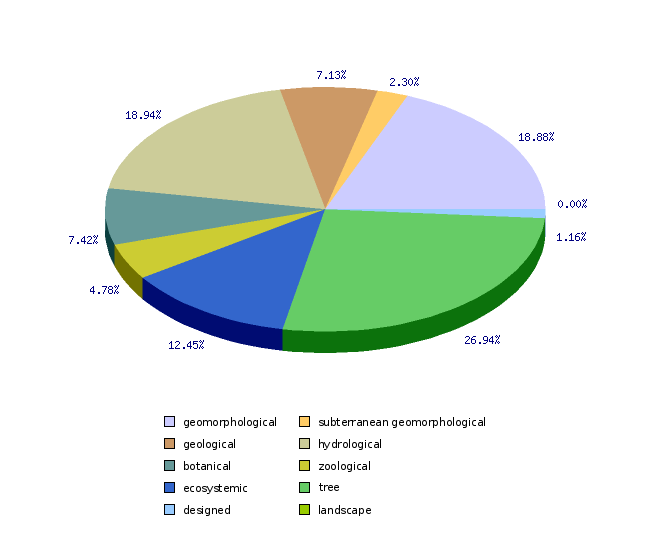
| geomorphological | number | 1817 |
| subterranean geomorphological | number | 221 |
| geological | number | 686 |
| hydrological | number | 1823 |
| botanical | number | 714 |
| zoological | number | 460 |
| ecosystemic | number | 1198 |
| tree | number | 2592 |
| designed | number | 112 |
| landscape | number | 0 |
| abiotic (geomorphological, geological, hydrological) | number | 4418 |
| biotic (botanical, zoological, ecosystemic ) | number | 5076 |
| valuable natural features without caves | number | 9494 |
| abiotic (geomorphological, geological, hydrological) | % | 46.53 |
| biotic (botanical, zoological, ecosystemic ) | % | 53.47 |
The Register of valuable natural features, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2008.
| 2008 | ||
|---|---|---|
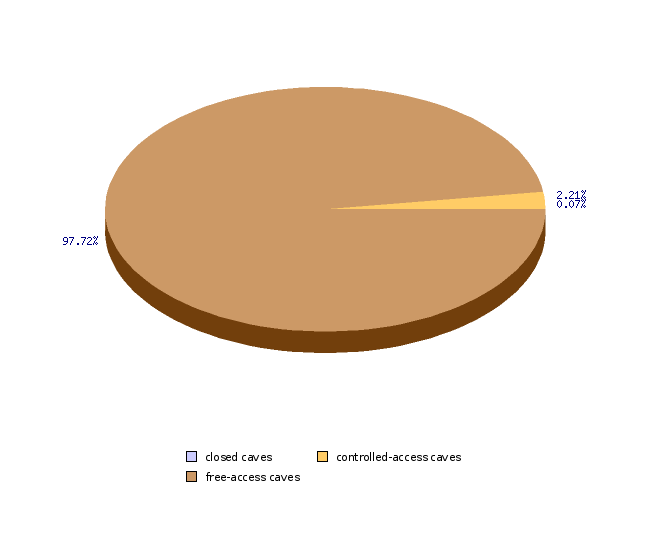
| closed caves | number | 6 |
| controlled-access caves | number | 185 |
| free-access caves | number | 8192 |
| closed caves | % | 0.06 |
| controlled-access caves | % | 2.21 |
| free-access caves | % | 97.73 |
Goals
The Resolution on National environmental action programme 2005-2012 (OG of the RS, No. 2/06) foresees the preparation and adoption of a valuable natural feature protection programme with the purpose of realizing the following goals:
• to preserve those characteristics due to which certain parts of nature have been designated as a valuable natural feature of a certain type, as well as to preserve all other characteristics as much as possible;
• to restore damaged or destroyed valuable natural features;
• to ensure the use of valuable natural features in a non-threatening way;
• to ensure ex-situ protection for those valuable natural features whose in-situ preservation is not possible.
Comment
14,901 valuable elements of nature have been given the status of a valuable natural feature, of which 6,519 are valuable natural features and 8,382 are subterranean caves. All subterranean caves are of national importance, while 2,092 (32,09%) of the remaining valuable natural features are of national importance and 4,427 (67,91%) are of local importance. In order to ensure uniform management, all valuable natural features established by the state are of national importance, regardless of the scientific criteria.
The density of valuable natural features for the entire country (20,273 km2 by taking into account planimetrically determined surface areas of the country sans sea surface areas) amounts to 0.32 per square kilometre or one valuable natural feature per 3.11 square kilometres. Valuable natural features include 4,085 objects (64,2%), spatially presented as points. 2830 (35,2%) objects contain both a point, which serves as the identity-holder, as well as a polygon delineating the area of the valuable natural feature.
The total surface area of all polygons amounts to 2,334.69 km2 or 11.52% of the country's territory. Polygons are predominantly small in size, as only 338 of them exceed 1 km2. In terms of the surface area, the largest geomorphological valuable natural features are the Pokljuka and Jelovica Plateaus, followed by the overthrust structure Nanos and the Karst edge.
In July 2006, the Rules amending the Rules on the designation and protection of valuable natural features gave 8,232 caves the status of a subterranean geomorphological valuable natural feature of national importance. This means that the density of caves – valuable features (20,273 km2 by taking into account planimetrically determined surface areas of the country sans sea surface areas) - amounts to 0.413 caves per square kilometre or one cave per 2.419 square kilometres.
The regulation also designates one of the three protection regimes in terms of access to each cave. According to the access regime caves are divided into closed caves, where the natural cave environment is vulnerable to such an extent that any entrance into the cave could damage or threaten it; controlled-access caves, where the natural cave environment is vulnerable to such an extent that any unsupervised entrance into the cave could damage or threaten it; and free-access caves, where unsupervised entrances, provided the general protection regime is respected, cannot damage them.
Ideally all 190 closed and controlled-access caves would have a gate at the entrance of the cave, which, coupled with custody, would ensure actual control over the cave. 72 caves are currently equipped with gates, 22 caves are defined as tourist caves. Even though no systematically gathered data concerning the pollution of caves for entire Slovenia are at hand, it can be estimated on the basis of available data that 15-20% caves in lowland Karst areas are polluted.
Methodology
The Register of valuable natural features, the Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2008 (state 30.6.2008).
The Register of valuable natural features is maintained by the Nature Conservation Sector of the Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia on the basis of the Article 39 of the Nature Conservation Act (NCA_OCT1, OG of the RS, No. 96/04) and Article 4 of the Rules on the designation and protection of valuable natural features (OG of the RS, Nos. 111/04).