[PR21] Introducing new technologies in transport

Key message

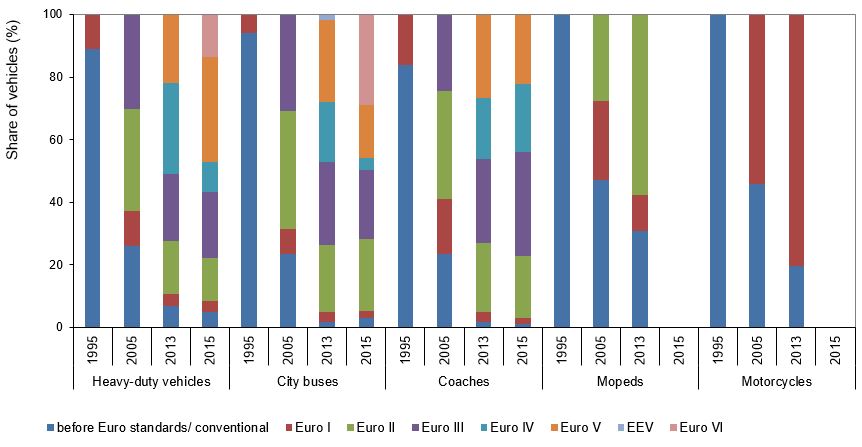
In Slovenia, as well as in other European countries, the proportion of the vehicle fleet that complies with the latest and most stringent emissions standards increased sharply in the period 2011–2015 in all categories of vehicles. The penetration rate of new technology is highest in the category of diesel cars. In Slovenia, the penetration rate of new technologies and introduction of the latest EURO emission standards is lowest in the category of two-wheelers (i.e. mopeds and motorcycles), while it is highest in the category of city buses and heavy-duty vehicles.
Definition
This indicator shows the share of vehicles that comply with EURO V, EURO IV, EURO III, EURO II, EURO I and EEV (Energy Efficient Vehicle) standards or pre-EURO standards and conventionally powered vehicles.
Standards EURO V, EURO IV, EURO III, EURO II, EURO I and EEV are defined in EU legislation. They set limit values for gases (NOx – nitrogen oxides, THC – total hydrocarbon, NHMC– non-methane hydrocarbons, CO – carbon oxide) and particulates in exhaust gases from vehicles. The data is shown by category of vehicles (diesel-powered passenger cars, petro-powered passenger cars, gas-powered passenger cars, petrol-powered light commercial vehicles, diesel-powered light commercial vehicles, heavy-duty vehicles, city buses, other buses, mopeds and motorcycles). Categories of vehicles are defined by Directives 2001/116/EC and 2002/24/EC.
The data for Slovenia are presented for the years 1995, 2005, 2013 and 2015, while the data or an estimated share of vehicles that comply with EURO V, EURO IV, EURO III, EURO II and EURO I standards and pre-EURO standards in the EEA-30 Member States (EU-27 countries plus Norway, Switzerland and Turkey) are presented for the years 1995, 2005 and 2011.
Charts
Record of registered motor vehicles and trailers in the Republic of Slovenia, Ministry of the Interior, 2015; Vehicle registration records - section of the state, national interoperability framework ( NIO ), the Ministry of Infrastructure, 2016
Record of registered motor vehicles and trailers in the Republic of Slovenia, Ministry of the Interior, 2015; Vehicle registration records - section of the state, national interoperability framework (NIO ), the Ministry of Infrastructure, 2016
*Note to image PR21-2: Data on the share of mopeds and motorcycles belonging to a particular Euro standard are not available for 2015.
Vehicle category split in technology classes, 1995-2011 from TREMOVE v3.3.1; cv: EEA, 2015.
| 1995-Gassoline passenger cars | 2005-Gassoline passenger cars | 2011-Gassoline passenger cars | 1995-Diesel passenger cars | 2005-Diesel passenger cars | 2011-Diesel passenger cars | 1995-Gasoline light-duty vehicles | 2005-Gasoline light-duty vehicles | 2011-Gasoline light-duty vehicles | 1995-Diesel light-duty vehicles | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| before Euro standards/ conventional | število | 104574551 | 32548755 | 14189595 | 15849128 | 4724729 | 2025947 | 6703578 | 3030222 | 1810427 | 10679944 |
| Euro I | število | 45681870 | 35877364 | 18927258 | 9177307 | 7328051 | 3231653 | 199395 | 774906 | 572101 | 1091395 |
| Euro II | število | 103552 | 47908464 | 34890613 | 0 | 15561242 | 11142085 | 0 | 850174 | 552445 | 0 |
| Euro III | število | 0 | 49226026 | 42407674 | 0 | 33736121 | 29760454 | 0 | 1545071 | 1820143 | 0 |
| Euro IV | število | 0 | 415701 | 21770752 | 0 | 217341 | 20829486 | 0 | 0 | 1220531 | 0 |
| Euro V | število | 0 | 0 | 26184684 | 0 | 0 | 23576210 | 0 | 0 | 2223408 | 0 |
| Total | število | 150359973 | 165976310 | 158370576 | 25026436 | 61567484 | 90565835 | 6902973 | 6200374 | 8199054 | 11771338 |
| before Euro standards/ conventional | % | 70 | 20 | 9 | 63 | 8 | 2 | 97 | 49 | 22 | 91 |
| Euro I | % | 30 | 22 | 12 | 37 | 12 | 4 | 3 | 12 | 7 | 9 |
| Euro II | % | 0 | 29 | 22 | 0 | 25 | 12 | 0 | 14 | 7 | 0 |
| Euro III | % | 0 | 30 | 27 | 0 | 55 | 33 | 0 | 25 | 22 | 0 |
| Euro IV | % | 0 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| Euro V | % | 0 | 0 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 26 | 0 | 0 | 27 | 0 |
| 2005-Diesel light-duty vehicles | 2011-Diesel light-duty vehicles | ||||||||||
| before Euro standards/ conventional | število | 4534759 | 2213731 | ||||||||
| Euro I | število | 2511998 | 1100547 | ||||||||
| Euro II | število | 6531200 | 4237747 | ||||||||
| Euro III | število | 8205218 | 7976417 | ||||||||
| Euro IV | število | 0 | 2460651 | ||||||||
| Euro V | število | 0 | 4029271 | ||||||||
| Total | število | 21783175 | 22018365 | ||||||||
| before Euro standards/ conventional | % | 21 | 10 | ||||||||
| Euro I | % | 12 | 5 | ||||||||
| Euro II | % | 30 | 19 | ||||||||
| Euro III | % | 38 | 36 | ||||||||
| Euro IV | % | 0 | 11 | ||||||||
| Euro V | % | 0 | 18 |
Vehicle category split in technology classes, 1995-2011 from TREMOVE v3.3.1; cv: EEA, 2015.
| 1995-Heavy duty vehicles | 2005-Heavy duty vehicles | 2011-Heavy duty vehicles | 1995-Buses and Coaches | 2005-Buses and Coaches | 2011-Buses and Coaches | 1995-Mopeds | 2005-Mopeds | 2011-Mopeds | 1995-Motorcycles | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| before Euro standards/ conventional | število | 5265863 | 2122603 | 1133330 | 999814 | 543257 | 0 | 16310461 | 8173438 | 4957632 | 11140931 |
| Euro I | število | 696871 | 556201 | 289990 | 77946 | 95079 | 48195 | 0 | 3970973 | 2308821 | 0 |
| Euro II | število | 7708 | 2005167 | 1195873 | 0 | 314171 | 519501 | 0 | 4095697 | 3015389 | 0 |
| Euro III | število | 0 | 2291879 | 2278592 | 0 | 430686 | 510501 | 0 | 0 | 8306791 | 0 |
| Euro IV | število | 0 | 590 | 1732296 | 0 | 0 | 181662 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Euro V | število | 0 | 236 | 1306493 | 0 | 0 | 127444 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | število | 5970442 | 6976677 | 7936575 | 1077759 | 1383193 | 1387304 | 16310461 | 16240108 | 18588634 | 11140931 |
| before Euro standards/ conventional | % | 88 | 30 | 14 | 93 | 39 | 0 | 100 | 50 | 27 | 100 |
| Euro I | % | 12 | 8 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 24 | 12 | 0 |
| Euro II | % | 0 | 29 | 15 | 0 | 23 | 37 | 0 | 25 | 16 | 0 |
| Euro III | % | 0 | 33 | 29 | 0 | 31 | 37 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 0 |
| Euro IV | % | 0 | 0 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Euro V | % | 0 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2005-Motorcycles | 2011-Motorcycles | ||||||||||
| before Euro standards/ conventional | število | 8679954 | 4399415 | ||||||||
| Euro I | število | 4700042 | 3789110 | ||||||||
| Euro II | število | 4156929 | 3712672 | ||||||||
| Euro III | število | 0 | 7410916 | ||||||||
| Euro IV | število | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Euro V | število | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Total | število | 17536924 | 19312113 | ||||||||
| before Euro standards/ conventional | % | 49 | 23 | ||||||||
| Euro I | % | 27 | 20 | ||||||||
| Euro II | % | 24 | 19 | ||||||||
| Euro III | % | 0 | 38 | ||||||||
| Euro IV | % | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Euro V | % | 0 | 0 |
Goals
A common goal of Slovenia and the EU is to improve the age structure of the vehicle fleet and to replace old vehicles, which present a greater environmental burden, with newer, more environmentally friendly vehicles. For this purpose, the EU adopted a legislation framework setting the limit values for emissions in exhaust gases from vehicles. The EURO standards were introduced in order to regulate and promote the use of new technologies to reduce emissions from transport.
Each EURO standard sets limit values for emissions of certain gases and particulates, as follows:
- The EURO I standard was introduced in 1993 by Directive 91/441/EEC. It sets the following emission limit values (for diesel-powered vehicles only): CO – 2.72g/km; HC+ NOx – 0.97 g/km; PM – 0.14 g/km.
- The EURO II standard was introduced in 1996. Limit values were set by Directive 94/12/EC, separately for diesel- and petrol-powered vehicles: for petrol-powered vehicles: CO – 2.2 g/km; HC (hydrocarbons) + NOx – 0.5 g/km; for diesel-powered vehicles: CO – 1.0 g/km; HC (hydrocarbons) + NOx – 0.7 g/km; PM – 0.08 g/km.
- The EURO III standard was introduced by Directive 98/69/EC. Limit values for petrol-powered vehicles: CO – 2.3 g/km; HC (hydrocarbons) – 0.20 g/km; NOx – 0.15 g/km. Limit values for diesel-powered vehicles: CO – 0.64 g/km; HC (hydrocarbons) + NOx – 0.56 g/km; NOx – 0.50 g/km; PM – 0.05 g/km.
- The EURO IV standard was introduced in 2005 by the same Directive as the EURO III standard (98/69/EC). Limit values for petrol-powered vehicles: CO – 1.0 g/km; HC (hydrocarbons) – 0.10 g/km; NOx – 0.08 g/km. Limit values for diesel-powered vehicles: CO – 0.50 g/km; HC (hydrocarbons) + NOx – 0.30 g/km; NOx – 0.25 g/km; PM – 0.025 g/km.
- The EURO V standard was introduced by Regulation 715/2007/EC. Limit values for petrol-powered vehicles: CO – 1.0 g/km; HC (hydrocarbons) – 0.10 g/km; NOx – 0.06 g/km; PM – 0.005 g/km. Limit values for diesel-powered vehicles: CO – 0.50 g/km; HC (hydrocarbons) + NOx – 0.23 g/km; NOx – 0.18 g/km; PM – 0.005 g/km.
- The EURO VI standard was introduced in 2014 by Regulation (EC) No. 715/2007 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 June 2007 and is dependant on approval of motor vehicle type with respect to emissions from light passenger and commercial vehicles (Euro 5 and Euro 6) and on access to vehicle repair and maintenance information. The standard sets emission limit values for light passenger and commercial vehicles (categories M, N1 and N2). Limit values for petrol-powered vehicles of category M: CO – 1.9 g/km; HC (hydrocarbons) – 0.10 g/km; NOx - 0.06 g/km; PM - 0.005 g/km. Limit values for diesel-powered vehicles of category M: 0.5 g/km; HC (hydrocarbons) + NOx – 0.17 g/km; NOx – 0.08 g/km; PM – 0.005 g/km.
- The EEV (Energy Efficient Vehicle) standard for city buses, which is not obligatory, has also been introduced. Limit values: NOx – 2g/kWh; PM - 0.002 g/kWh.
At the EU level, measures and regulations have been adopted to reduce emissions from transport, including greenhouse gases. Accordingly, GHG emissions are planned to be reduced by at least 20% by 2020 compared to the baseline year (1990) and by at least 60% by 2050 (again with regard to 1990). The meeting of these targets is regulated by Regulation 443/2009, setting the limit for CO2 emissions from new passenger cars sold in the European Union to an average of 130g/km by 2015. Further, a longer-term CO2 emissions target of 95g/km was specified for 2020.
Comment
The introduction of new technologies should be followed by the monitoring of compliance with EURO standards set by EU legislation.
In 2013, buses were the category in which the highest share of vehicles complied with the EURO V standard (27%), while in 2015, the share of heavy-duty cargo vehicles compliant with the standard was 34%. In most categories, compliance with the EURO V standard increased between 2013 and 2015. The increase by category was as follows: petrol-powered passenger cars from 11% to 17%, diesel-powered passenger cars from 15% to 27%, petrol-powered light commercial vehicles from 10% to 11% and petrol-powered light commercial vehicles from 19% to 26%. Compared to other categories, city buses and heavy-duty cargo vehicles have a higher share of vehicles complying with the EURO VI standard (city buses 29% and heavy duty cargo vehicles 13% in 2015). In 2013, 1.6% city buses complied with the EEV standard, which served as an upgrade to the EURO V standard. In 2013, mopeds were the category with the highest share (31%) of vehicles that failed to comply even with the EURO I standard. In other categories, the share was between 0.9% (other buses) and 4.9% (heavy-duty cargo vehicles).
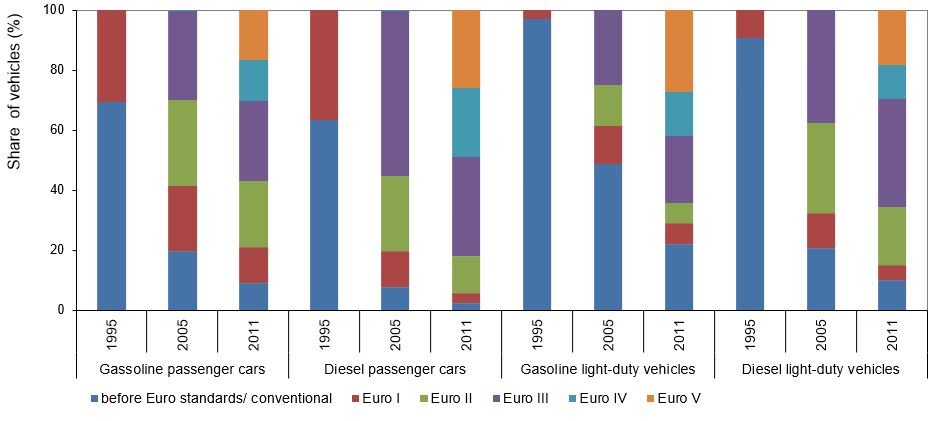
In Slovenia, diesel-powered passenger cars and light commercial vehicles are more environmentally friendly than petro-powered ones. Generally, passenger cars are slightly more environmentally friendly than light commercial vehicles. In 2015, 27% of passenger cars and 26% of light commercial vehicles complied with the EURO V standard. In the same year, 3% of passenger cars and only 0.9% of light commercial vehicles complied with the EURO VI standard. In the same year, 22% of petrol-powered passenger cars, 14% of petrol-powered light commercial vehicles and only 6% of diesel-powered passenger cars and 7% of light commercial vehicles complied with the EURO II standard. In the group of gas-powered vehicles, 34% complied with the EURO III standard in 2015, 26% complied with the EURO IV standard and 25.3% complied with the EURO IV standard. Slightly more than 5% of gas-powered vehicles complied with the EURO V standard.
The comparison of estimated effectiveness of the introduction of new technologies and compliance with EURO standards between different categories of vehicles in the years 1995, 2005 and 2013 in Slovenia and in the years 1995, 2005 and 2011 in the EEA-30 Member States (EU-27 countries + Norway, Switzerland and Turkey) shows the following picture:
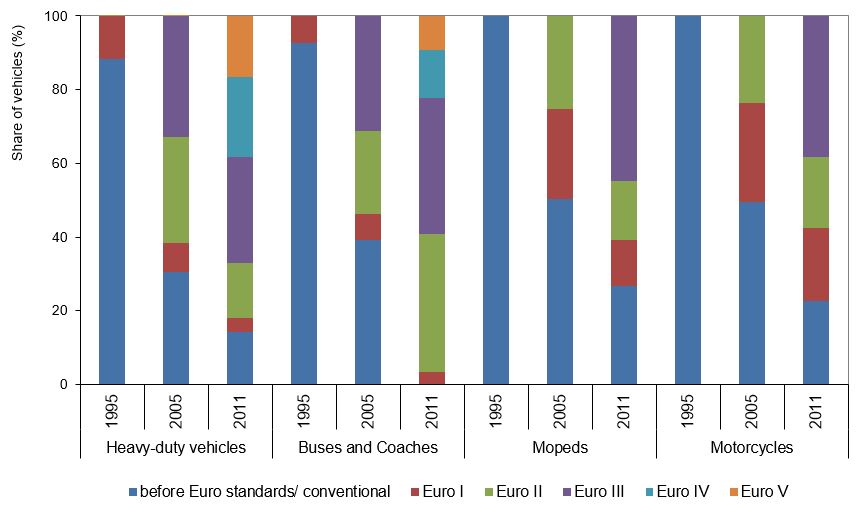
- In 1995, Slovenia had a relatively high share of petrol-powered passenger cars complying with the EURO I standard (65% compared to EEA-30 member countries, with a 30% share). Conversely, the share of diesel-powered passenger cars complying with the EURO I standard was higher in the EEA-30 countries than in Slovenia in the same year (37% compared to 10% in Slovenia). Introduction of new technologies and compliance with EURO standards increased considerably by 2011 in European countries and by 2013 in Slovenia. In European countries in 2011, 17% of petro-powered passenger cars and 26% of diesel-powered passenger cars complied with the EURO V standard, while the number of cars complying with only the EURO I or ‘pre-EURO’ standards decreased considerably. In Slovenia, 11% of petrol-powered and 15% of diesel-powered passenger cars complied with the EURO V standard in 2013. On the other hand, the share of (petrol-powered, in particular) passenger cars complying with only the EURO I or ‘pre-EURO’ standards was considerably lower than in European countries in 2011.
- Greater differences between Slovenia and European countries exist when it comes to light commercial vehicles. In 1995, almost 27% of petrol-powered light commercial vehicles and almost 22% of diesel-powered light commercial vehicles in Slovenia complied with the EURO I standard. In European countries, only 2.5% of petrol-powered and 9% of diesel-powered light commercial vehicles complied with the EURO I standard. In 2011, the share of light commercial vehicles complying with the EURO V standard was much higher in European countries than in Slovenia in 2013. The share of petrol-powered light commercial vehicles complying with the EURO V standard was more than 27% in European countries in 2011 and slightly more than 10% in Slovenia in 2013. The differences in the share of diesel-powered light commercial vehicles complying with the EURO V standard between European countries in 2011 and Slovenia in 2013 were smaller.
- The situation as regards the introduction of new technologies and compliance with EURO standards was similar when it comes to heavy-duty cargo vehicles. In 1995, 11% of heavy-duty cargo vehicles in Slovenia complied with the EURO I standard, while the compliance in European countries was above 11%. In 2011, almost 17% of heavy-duty cargo vehicles in European countries complied with the EURO V standard, while the level of compliance in Slovenia was almost 22% in 2013. In Slovenia in 2013, the average level of compliance of heavy-duty cargo vehicles with the EURO IV, EURO III and EURO II standards was higher than in EEA-30 member countries in 2011.
In Slovenia as well as in European countries, the introduction of new technologies and compliance with the EURO standards has been least effective in the categories of mopeds and motorcycles. In 2011, mopeds and motorcycles in European countries mostly complied with EURO III and EURO II standards. Almost 45% of mopeds and almost 39% of motorcycles complied with the EURO III standard, while 16% mopeds and 19% motorcycles complied with the EURO II standard. In Slovenia in 2013, mopeds and motorcycles only complied with EURO II and EURO I standards. In 2013, almost 58% mopeds complied with the EURO II standard and almost 61% of motorcycles complied with the EURO I standard. A considerable share of mopeds and motorcycles only complied with ‘pre-EURO’ standards, while these categories of vehicles did not comply with standards V and IV in Slovenia or in other European countries.
It needs to be pointed out that the standards for petrol-powered and diesel-powered vehicles are not the same and that standards for passenger cars and cargo vehicles also differ.