[ZD15] Dietary intake of certain metals

Key message

The estimated average long-term dietary intake of metals (lead, cadmium, and mercury) for the adult population of Slovenia does not exceed the corresponding reference points (BMDL) or health-based guidance values (tolerable daily/weekly intakes). However, for children, the average intake of lead, cadmium and mercury (fish consumers) may be exceeded, a situation similar to that in the EU. Continuous public awareness-raising on healthy nutrition is necessary, including the implementation of measures to reduce the intake of toxic metals, particularly in children and pregnant women, from both dietary and other environmental sources. Furthermore, the official monitoring of metal levels in foodstuffs on the Slovenian market must be continued.
Charts
Reports on the implementation of individual tasks related to official control performed by the competent authorities (from 2013 onwards The Administration for Food Safety, Veterinary Sector and Plant Protection of the Republic of Slovenia - UVHVVR) for the period 2011 ? 2016 (Kirinčič et al., 2019; EFSA, 2025). (2025)
| Slovenia[mg/kg] | EU[mg/kg] | |
|---|---|---|
| Special nutritional products | 0.38 | 0.28 |
| Meat and edible offal | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Fish and seafood | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| Sugar and confectionary | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| Vegetables and products | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| Herbs, spices and condiments | 0.02 | 0.16 |
| Grains and products | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Legumes, nuts, oilseeds | 0.02 | 0.09 |
| Fruit and vegetable juices | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Fruit and fruit products | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Food for children | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Alcoholic beverages | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Starchy roots and tubers | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Fats and oils | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Eggs and egg products | 0.01 | |
| Milk and dairy products | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| Drinking water | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Non-alcoholic beverages | 0.00 | |
| Composite food | 0.09 |
Reports on the implementation of individual tasks related to official control performed by the competent authorities (from 2013 onwards The Administration for Food Safety, Veterinary Sector and Plant Protection of the Republic of Slovenia - UVHVVR) for the period 2011 ? 2023; EFSA 2012b. (2024)
| Food categories | Unit | Grains and products | Vegetables and products | Starchy roots and tubers | Legumes, nuts, oilseeds | Fruit and fruit products | Meat and edible offal | Fish and seafood | Milk and dairy products | Eggs and products | Sugar and confectionary | Fats and oils | Fruit and vegetable juices | Non-alcoholic beverages | Alcoholic beverages | Drinking water | Herbs, spices and condiments | Food for children | Special nutritional products | Composite food | Snacks, desserts, other foods |
| Slovenia | mg/kg | 0,038 | 0,025 | 0,037 | 0,046 | 0,006 | 0,087 | 0,117 | 0,001 | 0,042 | 0,00007 | 0,018 | 0,012 | 0,056 | |||||||
| EU | mg/kg | 0,027 | 0,051 | 0,020 | 0,192 | 0,004 | 0,137 | 0,105 | 0,006 | 0,003 | 0,030 | 0,005 | 0,004 | 0,002 | 0,001 | 0,00021 | 0,050 | 0,008 | 0,075 | 0,031 | 0,017 |
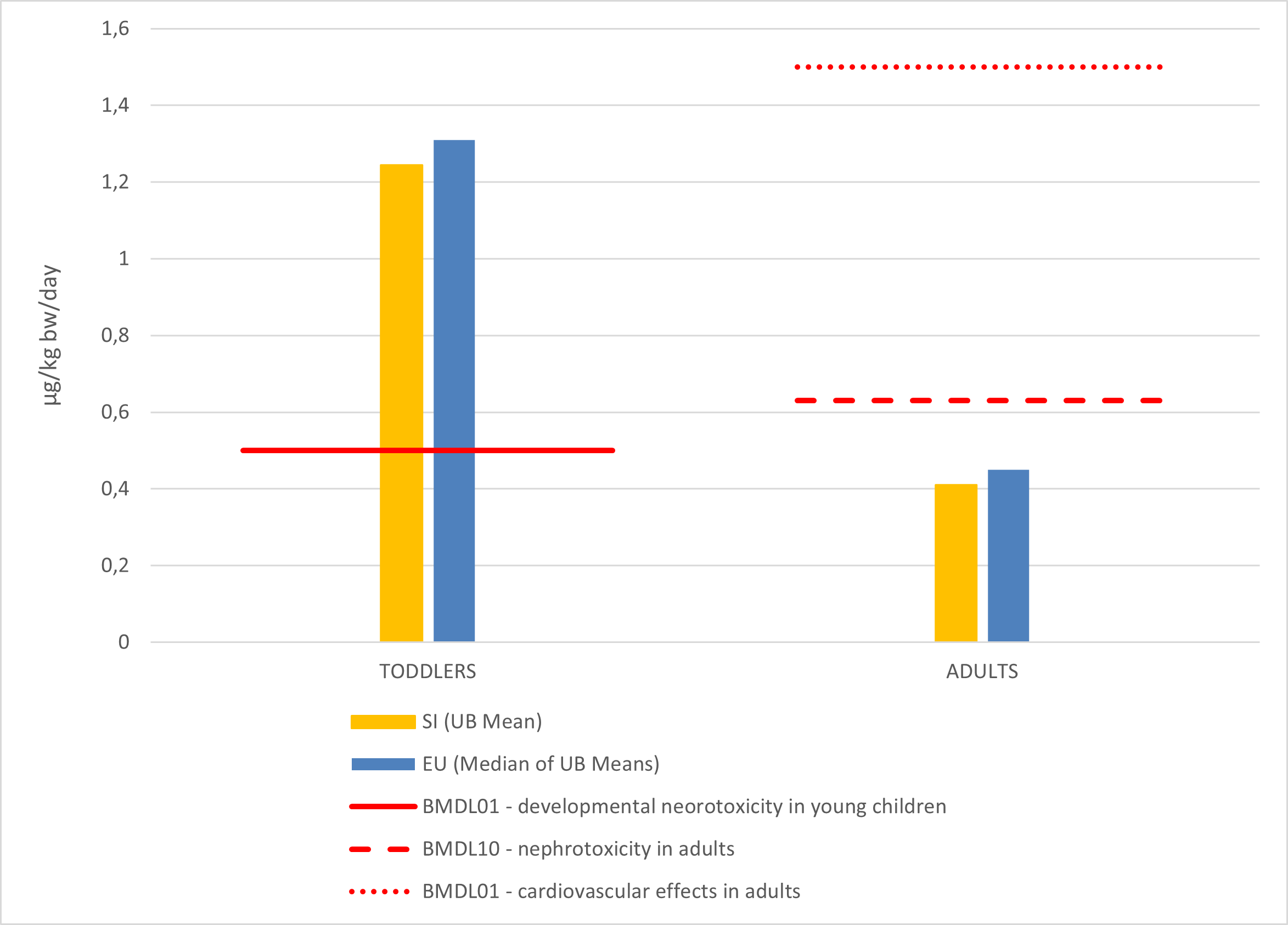
Reports on the implementation of individual tasks related to official control performed by the competent authorities for the period 2013 ̶ 2023 (EFSA, 2025).
| Slovenia[µg/kg bw/day] | EU[µg/kg bw/day] | BMDL01 - developmental neorotoxicity in young children[µg/kg bw/day] | BMDL10 - nephrotoxicity in adults[µg/kg bw/day] | BMDL01 - cardiovascular effects in adults[µg/kg bw/day] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TODDLERS | 1,24448008604634 | 1,31 | 0.50 | ||
| ADULTS | 0,411392058070442 | 0,45 | 0.63 | 1.50 |
Reports on the implementation of individual tasks related to official control performed by the competent authorities (from 2013 onwards The Administration for Food Safety, Veterinary Sector and Plant Protection of the Republic of Slovenia - UVHVVR) for the period 2011 ? 2023; EFSA, 2012a. (2024)
| Slovenia (UB Mean)[µg/kg bw/week] | EU (UB Mean)[µg/kg bw/week] | |
|---|---|---|
| TODDLERS | 5.75 | 5.90 |
| ADULTS | 1.58 | 1.98 |
Reports on the implementation of individual tasks related to official control performed by the competent authorities for the period 2013 - 2023 (EFSA, 2025)
| Other[%] | Water and water-based beverages[%] | Milk and dairy products[%] | Fruit and fruit products[%] | Vegetables and vegetable products[%] | Grains and grain-based products[%] | Meat and meat products[%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TODDLERS | 32.21 | 8.52 | 10.38 | 11.11 | 18.25 | 19.53 | |
| ADULTS | 28.17 | 4.06 | 6.05 | 12.90 | 21.09 | 27.73 |
Reports on the implementation of individual tasks related to official control performed by the competent authorities (from 2013 onwards The Administration for Food Safety, Veterinary Sector and Plant Protection of the Republic of Slovenia - UVHVVR) for the period 2011 ? 2023; Kirinčič et al., 2019. (2019)
| Other[%] | Legumes, nuts, oilseeds and spices[%] | Meat and meat products[%] | Milk and dairy products[%] | Food for children[%] | Starchy roots and tubers[%] | Vegetables and vegetable products[%] | Grains and products[%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADULTS | 19.72 | 6.10 | 8.40 | 0 | 0 | 13.11 | 15.86 | 36.82 |
| TODDLERS | 27.92 | 0 | 0 | 18.42 | 11.79 | 13.10 | 9.65 | 19.12 |
Reports on the implementation of individual tasks related to official control performed by the competent authorities (from 2013 onwards The Administration for Food Safety, Veterinary Sector and Plant Protection of the Republic of Slovenia - UVHVVR) for the period 2011 - 2019; EFSA, 2012b.
*SI value EFSA 2012c; **EU general value for fish and other seafood
| Slovenia[mg/kg] | EU[mg/kg] | |
|---|---|---|
| Pike | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| Bluefish | 0.34 | 0.18 |
| Tuna | 0.33 | 0.29 |
| Milkfish | 0.28 | 0.18 |
| Ocean perch | 0.28 | 0.17 |
| Sea bream | 0.21 | 0.23 |
| Sole | 0.19 | 0.08 |
| Squids | 0.18 | 0.04 |
| Hakes | 0.17 | 0.14 |
| Cuttlefish | 0.17 | 0.04 |
| Octopus | 0.15 | 0.04 |
| Canned tunas and similar | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| Marine fishes not identified | 0.10 | 0.18 |
| Cod | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| Catfishes (freshwater) | 0.09 | 0.18 |
| Sea bass | 0.09 | 0.30 |
| Whitefishes or coregonus | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| Anchovies | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Canned sardines | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| Mackerel | 0.05 | 0.11 |
| Sardines and sardine-type fishes | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| Shrimps and prawns | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Canned mackerel | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| Fish fingers breaded | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Fish paste or surimi | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Herrings | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Salmons | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Tilapias and similar | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Trout | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| Smoked salmon | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| Mussels | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| Alaska pollock | 0.01 | 0.18 |
| Canned salmon | 0.01 | 0.03 |
Reports on the implementation of individual tasks related to official control performed by the competent authorities (from 2013 onwards The Administration for Food Safety, Veterinary Sector and Plant Protection of the Republic of Slovenia - UVHVVR) for the period 2011 ? 2018; EFSA, 2012c. (3. 09. 2020)
| Age group | Unit | TODDLERS | ADULTS |
| Slovenia | μg/kg bw/week | 0,19 | 0,27 |
| EU | μg/kg bw/week | 0,07 | 0,24 |
| TWI - developmental neurotoxicity | μg/kg bw/week | 1,3 | 1,3 |
Reports on the implementation of individual tasks related to official control performed by the competent authorities (from 2013 onwards The Administration for Food Safety, Veterinary Sector and Plant Protection of the Republic of Slovenia - UVHVVR) for the period 2011 ̶ 2019. Individual consumption data of Slovenian population (SI.MENU-2018).
| Hake [%] | Canned tuna and the like [%] | Salmon [%] | (Whitefishes) [%] | Bream [%] | Squid [%] | Sea bass [%] | Fish pate or surimi [%] | Pike [%] | Bluefish [%] | Other [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toddlers (childredn) | 47.29 | 5.94 | 9.42 | 4.29 | 3.98 | 5.72 | 23.37 | ||||
| Adults | 19.94 | 38.81 | 6.78 | 7.39 | 1.73 | 12.07 | 13.28 |