[KM21] Irrigation of agricultural land 

Key message

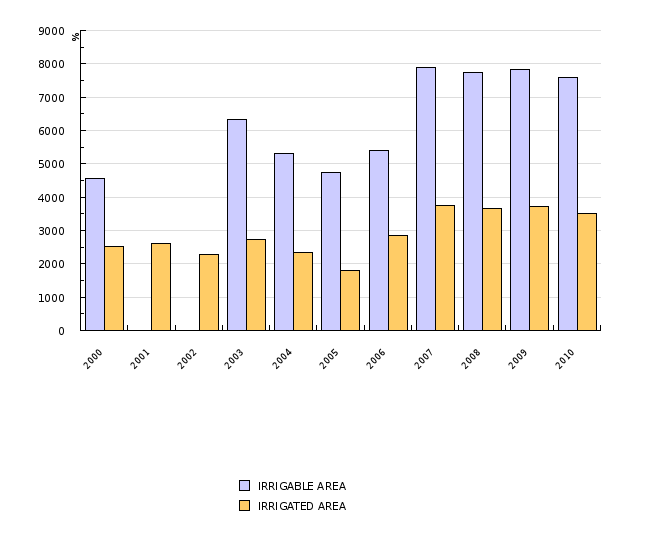
Land areas, prepared for irrigation, have increased from 4,554 ha to 9,695 ha in the period 2000-2008, and their share in total utilised agricultural area from 0.9 % to 2 %. The water consumption per hectare of land, prepared for irrigation, which strongly depends on weather conditions in each year, has decreased since 2000.
Definition
The indicator indicates land areas, prepared for irrigation, irrigated areas, and water use for irrigation in Slovenia in the period 2000-2008 and the share of irrigable area in total utilised agricultural area in the European Union (EU) in 2000 and 2007. The indicator does not provide direct information on environmental susceptibility of the irrigation, but indicates the pressure on the environment, related to irrigation.
Charts
Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia, 2009.
| 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRRIGABLE AREA | ha | 4554 | 6339 | 5303 | 4727 | 5395 | 7876 | 7732 | 7841 | ||
| Irrigable area - Sprinkling | ha | 6063 | 4947 | 4372 | 4967 | 7301 | 6890 | 5417 | |||
| Irrigable area - Drop by drop | ha | 276 | 356 | 355 | 428 | 575 | 842 | 2424 | |||
| Utilised agricultural area (UAA), total | ha | 508960 | 509624 | 505462 | 509709 | 490520 | 508759 | 490318 | 498467 | 492424 | 468496 |
| SHARE OF IRRIGABLE AREA IN TOTAL UAA | % | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.7 | ||
| IRRIGATED AREA | ha | 2535 | 2621 | 2292 | 2741 | 2329 | 1812 | 2837 | 3759 | 3651 | 3732 |
| Arable land | ha | 1825 | 1916 | 1624 | 2088 | 1713 | 1252 | 2228 | 3080 | 2842 | 2825 |
| Orchards, olive groves, nurseries | ha | 665 | 690 | 658 | 632 | 616 | 560 | 603 | 613 | 634 | 641 |
| Other | ha | 45 | 15 | 10 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 66 | 175 | 266 |
| WATER USE FOR IRRIGATION | 1000 m3 | 6569 | 8384 | 5257 | 6383 | 4553 | 2309 | 6344 | 4440 | 1728 | 1955 |
| IRRIGATION WATER ALLOCATION RATES | m3/ha | 1442.5 | 1006.9 | 858.6 | 488.5 | 1175.9 | 563.7 | 223.5 | 249.3 | ||
| 2010 | |||||||||||
| IRRIGABLE AREA | ha | 7604 | |||||||||
| Irrigable area - Sprinkling | ha | 5267 | |||||||||
| Irrigable area - Drop by drop | ha | 2337 | |||||||||
| Utilised agricultural area (UAA), total | ha | 482803 | |||||||||
| SHARE OF IRRIGABLE AREA IN TOTAL UAA | % | 1.6 | |||||||||
| IRRIGATED AREA | ha | 3501 | |||||||||
| Arable land | ha | 2541 | |||||||||
| Orchards, olive groves, nurseries | ha | 626 | |||||||||
| Other | ha | 334 | |||||||||
| WATER USE FOR IRRIGATION | 1000 m3 | 1608 | |||||||||
| IRRIGATION WATER ALLOCATION RATES | m3/ha | 211.5 |
Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia, 2009; EUROSTAT, 2009.
| Ireland | Luxembourg | Latvia | Lithuania | Poland | United Kingdom | Czech Republic | Slovenia | Belgium | Germany | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | % | 0 | 0 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 2.3 | 2.8 | ||||
| 2007 | % | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 1.7 | |
| Hungary | Finland | Bulgaria | Austria | Romania | Sweden | Slovakia | France | Spain | Denmark | ||
| 2000 | % | 4 | 2.8 | 4.4 | 8.9 | 13.3 | 16.9 | ||||
| 2007 | % | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.4 | 3.6 | 4.5 | 5.1 | 9.5 | 9.7 | 14.7 | 16.4 |
| Portugal | Netherlands | Malta | Italy | Cyprus | Greece | ||||||
| 2000 | % | 20.5 | 24.6 | 29.5 | 36.9 | ||||||
| 2007 | % | 16.8 | 23.9 | 31 | 31 | 31.4 | 38.2 |
Goals
- increasing the extent of irrigable agricultural area until 2013 by upgrading the existing and constructing new, technologically modern irrigation systems with more rational water consumption, which should not pose a threat to the water resources.
Comment
In conditions, when agriculture is more and more frequently faced with longer periods of drought, irrigation in key phases of growth enables effective increase of the quantity and quality of crops and thus contributes to lower dependence of agricultural production on natural conditions and to more stable income. At the same time, irrigation is associated to certain risks for the environment. The water consumption for irrigation may lead to excessive use of water resources, and greater risk for soil erosion, pollution of the waters with nitrates and pesticides, mineralization of soil and for other negative consequences for the environment (reduction of biodiversity, disappearance of habitats, reduction of natural, and landscape diversity). This risk can be decreased with the use of more modern and more rational technologies of irrigation and with the scope of irrigation that does not threat available water resources, which are also the demands of the EU Water Framework Directive. For all such interventions, besides the evaluation of impacts on the environment, and the nature protection consensus, an analysis of availability of water resources has to be carried out, and a water permit has to be issued.
In 2000, 4,554 ha or 0.9 % of all utilised agricultural area, was prepared for irrigation. Until 2008, this area grew to 9,695 ha, which is more than twice as much as in 2000 and represents 2.0 % of all utilised agricultural area. Particularly areas, prepared for drop by drop irrigation, grew considerably, which indicates changes towards the use of more modern and effective systems of irrigation. In 2008, 13.2 % of land was prepared for this kind of irrigation (in 2000 4.4 %), the rest of the land was prepared for sprinkling.
In the structure of land that was irrigated at least once, arable landprevailed (in 2008 83 %). Most frequently irrigated crops are hops, vegetables, fruit, and maize.
The water consumption for irrigation depends mainly on weather conditions in each year. In 2000, 2001, 2003 and 2006, which were the most dry years, between 6 and 8 million m3 of water a year (on average 6,920,000 m3 a year) was used for irrigation, and in the other years water consumption was lower (on average 3,819,000 m3 a year). Average water consumption per hectare of land, prepared for irrigation, in the period 2000-2008, was 820 m3 a year, from maximum 1,442 m3 in 2000 to minimum 241 m3 in 2008.
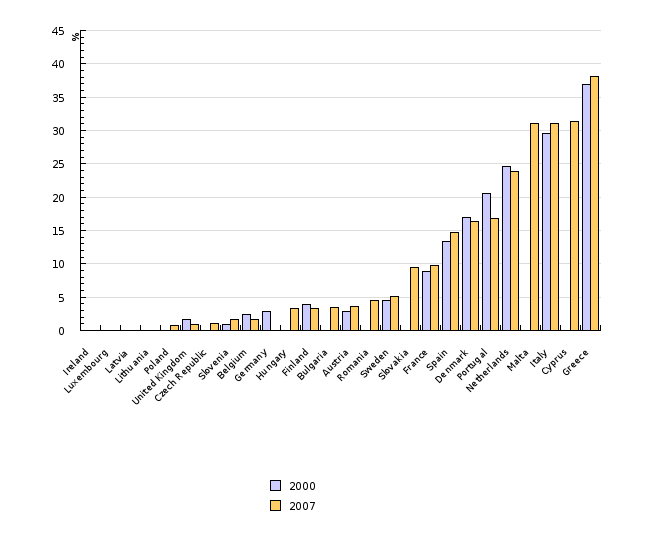
In Slovenia, the share of land, prepared for irrigation in total utilised agricultural area, is among the lowest within EU Member States. In 2007, this share was lower than in Slovenia (below 2 %) only in eight North European Member States. The greatest shares of land prepared for irrigation are in Greece, Cyprus, Italy, and Malta (over 30%), among Middle and North European countries the shares vary above in Slovakia (close to 10%), Denmark (a good 16%), and the Netherlands (24%).
Methodology
Data for Slovenia:
Objectives summarized by: the Rural development plan for the Republic of Slovenia for the period 2007-2013.
Source database or source: The Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia, SI-STAT data portal.
Data, used for the indicator are available at:
- SI-STAT data portal > Environment and natural resources > Environment > Water > Irrigation > Area by method of irrigation, Irrigation by type of area
- SI-STAT data portal > Environment and natural resources > Agriculture and Fishing > Crop Production > Crops and Area > Land use and use of arable crops (ha).
Data administrator: The Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia (Polona Razboršek)
Data acquisition date for this indicator: 6 November 2009
Methodology and frequency of data collection for the indicator: Data, associated to irrigation, are collected by the Statistical Office of the RS once a year with a statistical questionnaire (questionnaire VOD-N). Irrigation systems’ administrators report the data for each hydrographical region separately.
Data processing methodology: Data on the areas and water consumption for irrigation are used directly. The share of land, prepared for irrigation, is calculated by dividing irrigable area with total utilised agricultural area (irrigable area/UAA x 100). The irrigation water allocation rates are calculated by deviding water use for irrigation with total irrigable area.
Information concerning data quality:
- Indicator advantages and disadvantages (in the light of the data): The advantage of the indicator is its regular publication within the Statistical Office of the RS. However, it is not completely clear what the data comprise. In methodological explanations, it is only stated that the data are reported by the irrigation systems’ administrators and that the lists of reporters are completed with the lists of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Food of the Republic of Slovenia and the Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia. For 2008, the data include also golf courses and sports fields, while in previous years the data applied only to agricultural land.
- Relevance, accuracy, robustness, uncertainty (in the light of the data):
Reliability of the indicator (archival data): The indicator is not completely reliable.
Uncertainty of the indicator (scenarios/projections): Scenarios and projections are not available.
- Overall assessment (1 = no major comments, 3 = data to be considered with reservation):
Relevance: 2
Accuracy: 2
Completeness over time: 2
Completeness over space: 2
Data for the EU:
Source database or source: Data on areas of agricultural land, prepared for irrigation, areas of irrigated land and utilised agricultural area for the Member States of the European Union are available at EUROSTAT databases.
Data, used for the indicator, are available at:
- EUROSTAT > Statistics > Statistics by theme > Agriculture > Database > Structure of agricultural holdings > Land use > Other farmland > Irrigation: Number of farms, areas and equipment by size of farm (UAA) and region
- EUROSTAT > Statistics > Statistics by theme > Agriculture > Database > Structure of agricultural holdings > Land Use > Land use overview > Farmland: Number of farms and areas by size of farm (UAA) and region.
Data administrator: European Commission, EUROSTAT.
Data acquisition date for this indicator: 6 November 2009
Methodology and frequency of data collection for the indicator: Data are collected within the survay on the structure of agricultural holdings, which is carried out four times in the period of ten years (the last time in 2007).
Data processing methodology: Relative indicator is calculated so that the areas, prepared for irrigation, are divided by total utilised agricultural area in each country (irrigable area /UAA x 100).
Information concerning data quality:
- Indicator advantages and disadvantages (in the light of the data): Taking into account that the data on areas, prepared for irrigation, in the period between two complete agricultural censuses (the last in 2000, the next in 2010) aare obtained with a sample survey, the reliability of the data depends primarily on the representativity of the sample. In Slovenia, due to small number of holdings with irrigation this kind of data are not representative, and therefore the Statistical Office of the RS do not publish them. Similar problems with the representativity of the sample may occur also in other countries with a small scope of irrigated land. In the comparison of the data between countries, certain precaution is therefore needed.
- Relevance, accuracy, robustness, uncertainty (in the light of the data):
Reliability of the indicator (archival data): The indicator is not completely reliable.
Uncertainty of the indicator (scenarios/projections): Scenarios and projections are not available.
- Overall assessment (1 = no major comments, 3 = data to be considered with reservation):
Relevance: 2
Accuracy: 2
Completeness over time: 2
Completeness over space: 2