[OP03] Eco-schools

Key message

In Slovenia, the number of educational institutions included in the Eco-Schools Programme grows constantly. In the school year 2015/2016, 712 institutions were registered as eco-schools, which represents 35% of all schools and kindergartens in Slovenia. Thus, more than 132,000 children and 15,950 teachers were engaged in environmental projects and thus included in the environmental education system. Internationally, the Eco-Schools Programme in the school year 2014/2015 included more than 45,000 institutions, of which 16,000 were awarded with the Green Flag. According to the most recent data, more than 20 million children and more than 900,000 teachers participated in the programme at the global level. This means that more than 6,000 local communities were included in the environmental education system.
Definition
This indicator follows the number of institutions participating in the Eco-Schools Programme in Slovenia in the period of the school years 1995/96 through 2015/16 and the percentage of institutions participating in the Eco-Schools Programme, as well as the number of institutions participating in the Eco-Schools Programme in selected EU countries in the period of the school years 1997/98 through 2015/16.
The international Eco-Schools Programme is a programme run by the International Foundation for Environmental Education that has been carried out in Slovenia by the DOVES – FEE Slovenia society since 1996. DOVES is an acronym for the Society for Environmental Education in Europe – Slovenia.
The Eco-Schools Programme is the largest network of children, kindergarten teachers and school teachers who transfer and integrate sustainable development principles to everyday learning and life. The Programme fosters systematic environmental education and awareness among youth, particularly regarding the importance of environmental protection and human health. Work in the Programme is carried out in accordance with the internationally comparable Seven Steps methodology. The steps are as follows: form an eco-committee, carry out an environmental review, develop an action plan, monitor and evaluate, implement curriculum work, inform and involve others and produce an eco-code. (Guidelines of education for sustainable development from pre-school to university level, 2010)
When an institution carries out activities in accordance with the seven steps, it is awarded an internationally recognized environmental Green Flag Award as a certificate of meeting the criteria of the international Eco-Schools Programme. The Programme is also being developed with the support of the European Commission and the United Nations Organisation. In Slovenia, it is based on the environmental education goals defined in the national environmental education curriculum and in the “Guidelines of education for sustainable development from pre-school to university level”. The indicator follows the number of institutions participating in the Eco-Schools Programme in Slovenia and the number of institutions that have received the Green Flag Award. Participating institutions carry out environmental activities in accordance with the seven steps methodology, while the awarded institutions are those who have successfully completed the activities.
Charts
| registered Eco-Schools | awarded Eco-Schools | schools total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1995/96 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 1996/97 | 37 | 0 | 37 |
| 1997/98 | 47 | 17 | 47 |
| 1998/99 | 54 | 33 | 54 |
| 1999/00 | 59 | 43 | 59 |
| 2000/01 | 78 | 56 | 78 |
| 2001/02 | 105 | 79 | 105 |
| 2002/03 | 170 | 127 | 170 |
| 2003/04 | 206 | 159 | 206 |
| 2004/05 | 209 | 175 | 209 |
| 2005/06 | 263 | 199 | 263 |
| 2006/07 | 307 | 238 | 307 |
| 2007/08 | 383 | 284 | 383 |
| 2008/09 | 535 | 380 | 535 |
| 2009/10 | 628 | 423 | 628 |
| 2010/11 | 690 | 560 | 690 |
| 2011/12 | 705 | 560 | 705 |
| 2012/13 | 712 | 644 | 712 |
| 2013/14 | 717 | 646 | 717 |
| 2014/15 | 710 | 645 | 710 |
| 2015/16 | 712 | 0 | 0 |
| Eco-Schools | other schools | Eco-Schools | other schools | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008/09 | 535 | 1821 | 29.38 | 70.62 |
| 2009/10 | 628 | 1836 | 34.20 | 65.80 |
| 2010/11 | 690 | 1861 | 37.08 | 62.92 |
| 2011/12 | 705 | 1891 | 37.28 | 62.72 |
| 2012/13 | 712 | 1907 | 37.34 | 62.66 |
| 2013/14 | 717 | 1926 | 37.23 | 62.77 |
| 2014/15 | 710 | 1817 | 39.08 | 60.92 |
| 2015/16 | 712 | 2030 | 35.07 | 64.93 |
Opomba k Preglednici OP3-3 (*): Podatki za države EU je zagotovil FEE (FoundationofEnvironmentalEducation). Po informaciji FEE, ki je skrbnik baze podatkov, so v tabeli navedeni podatki, ki so zaradi težav pri vzdrževanju baze nepreverjeni in zato manj zanesljivi.
np = ni podatka
Goals
- to provide high-quality education and to create opportunities for lifelong education for everyone,
- to improve general knowledge of the environment and of sustainable development principles,
- to establish the concept of sustainable development as an integral component of development in Slovenia,
- to provide systemic and infrastructural support for existing environmental programmes and to enable their interconnection,
- to develop new environmental projects,
- to integrate environmental programmes and activities into existing networks and to develop new ones.
Comment
Since 1995, when the Eco-Schools Programme began running in Slovenia, the number of participating schools has been constantly growing. In the school year 2015/16, 712 eco-schools were included in the Programme. Over the 20-year period, the Eco-Schools Programme made exceptional progress as the eco-schools network expanded throughout the territory of Slovenia and covered several educational age levels and institution types. Eco-schools represent 35% of all schools in Slovenia, which means that environmental education is becoming part of Slovenian children’s everyday life.
The holistic and systematic approach significantly contributes to the success and distribution of the Programme, which enables pre-school and school teachers to integrate the contents and activities into the everyday educational programme and adapt the activities to planned work. Globally, the success of the programme can also be attributed to partnership with FEE International and UNEP as a global environmental protection knowledge base, particularly in developing countries. It offers various practical solutions and incentives for environmental awareness both inside and outside of schools. The Eco-Schools Programme promotes the principles of democracy, openness and involvement of various stakeholders. Therefore, it also promotes a democratic citizenship culture, in addition to environmental education.
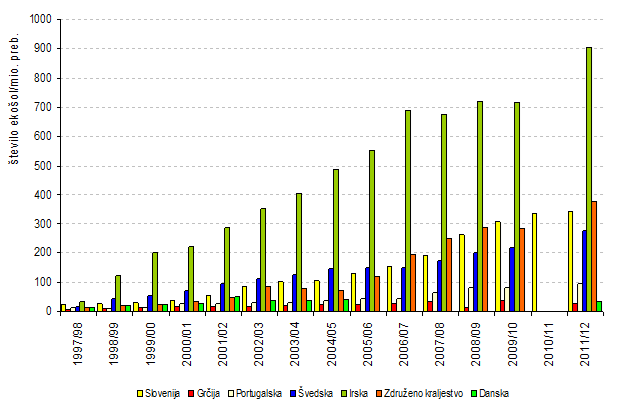
The international Eco-Schools Programme has become one of the most recognised and widespread environmental education programmes in almost all EU Member States and the network is expanding in other continents. Currently, 58 countries from all continents participate; in 2003, South Africa was the first country outside Europe to become a FEE member.
Financing of the Eco-Schools Programme
In most European countries, the Eco-Schools Programme is financed mostly or exclusively through budgetary funds provided by relevant ministries. In Slovenia, the Programme is financed through fees paid by participating institutions, sponsorship funds and, to a lesser extent, through funds provided by ministries responsible for education and the environment.
Slovenia has a special status within the international Eco-Schools Programme, as it is considered to be one of the most successful countries and is used as an example to others. In recent years, the topics proposed in the UNECE Strategy for Education for Sustainable Development (UNECE, 2005) have been included in eco-school activities in Slovenia in addition to regular environmental education.
Methodology
Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for sustainable development (UN, 2015), Resolucija o Nacionalnem programu varstva okolja 2005-2012 (ReNPVO), Uradni list RS, št. 2/2006.
Podatki so prikazani za obdobje od šolskega leta 1995/96 do 2015/16 za ekošole oziroma za šole do konca šolskega leta 2014/2015. Podatki se zbirajo letno in so na voljo konec leta za prejšnje šolsko leto. Podatki o številu prebivalstva se nanašajo na popis prebivalstva, ki se praviloma osvežuje vsakih 10 let (2000, 2010).
Podatki o gibanju števila ekošol niso preračunani. Delež registriranih ekošol je izračunan kot razmerje med številom registriranih ekošol in vseh šol v prejšnjem šolskem letu oziroma v šolskem letu, za katerega so dostopni najnovejši podatki.
Fundacija za izobraževanje o okolju, FEE (Fundation on EnvironmentalEducation – FEE)
EUROSTAT
Društvo DOVES- FEE Slovenija
Statistični urad RS
Podatki o skupnem številu šol v Sloveniji (graf OP03-2) so povzeti iz statistične podatkovne baze, ki jo vodi Statistični urad RS in zajemajo naslednje:
- podatke o številu vrtcev in številu OŠ: SI-STAT podatkovni portal → Demografsko in socialno področje → Izobraževanje → Otroci vključeni v vrtce (Vrtci po vrstah programov, ki jih izvajajo, številu oddelkov in otrok, občine, Slovenija, letno)/Osnovnošolsko izobraževanje (Mladina in odrasli v osnovnošolskem izobraževanju, Slovenija, konec šolskega leta, letno). Za OŠ sp povzeti podatki: »Osnovne šole« in »Osnovne šole in zavodi s prilagojenim programom«. S tem so zajete tudi podružnične šole, šole za odrasle niso zajete.
-podatke o številu srednjih šol: za obdobje 1995-2000 so povzeti iz Statističnega letopisa RS( → Izobraževanje → Šole, oddelki, učenci, dijaki, slušatelji in strokovni delavci. Povzeti so podatki »Srednje šole – za izobraževanje mladine«. Podatki o srednjih šolah za izobraževanje odraslih niso zajeti. V kategorijo »vse šole« ni zajeto število dijaških domov in centrov šolskih in obšolskih dejavnosti, kljub temu, da nekateri izmed njih sodelujejo v programu Ekošola.), za obdobje med letoma 2000 in 2012: SI- STAT podatkovni portal → Demografsko in socialno področje → Izobraževanje →izbrani podatki o udeležencih in strokovnih delavcih v srednješolskem izobraževanju,za obdobje po 2012 pa po povpraševanju na SURS.
Prednosti in slabosti kazalca:
- Prednosti: Kazalec je zaradi enotne metodologije za vključitev ustanov v program Ekošola in kriterijev za pridobitev zelene zastave mednarodno primerljiv. Metodologija je opredeljena s strani Fundacije za izobraževanje o okolju (FEE).
- Slabosti: Podatki o številu vključenih ustanov v program Ekošola, pridobljeni preko FEE International in drugih virov, se med seboj razlikujejo zaradi težav pri vzdrževanju enotne baze podatkov.
Relevantnost, točnost, robustnost, negotovost:
- Zanesljivost kazalca (arhivski podatki): srednje zanesljiv (neusklajeni podatki med različnimi viri)
- Negotovost kazalca (scenariji/projekcije): Projekcije/scenariji niso na voljo.
- Skupna ocena (1 = brez večjih pripomb, 3 = podatki z zadržkom):
- Relevantnost: 1
- Točnost: 2 (neusklajeni podatki med različnimi viri)
- Časovna primerljivost: 2 (neusklajeni podatkovni nizi med FEE International in Slovenijo)
- Prostorska primerljivost: 1
Podatki o številu ekošol se zbirajo letno in so na voljo konec leta za prejšnje šolsko leto. Podatki o številu prebivalstva se nanašajo na popis prebivalstva, ki se praviloma osvežuje vsakih 10 let (2000, 2010).
Podatki o številu ekošol so zaradi boljše primerljivosti med posameznimi državami preračunani na milijon prebivalcev. Število prebivalcev v posamezni državi je povzeto iz spletne strani Evropskega statističnega urada, EUROSTAT. Dostop do podatkov: Eurostat>Population>Demography - Nationaldata>Population>Population on 1. Januaryby age andsex (demo_pjan), 2010. Podatek o številu ekošol na milijon prebivalcev je izračunan npr. za obdobje 1997/98 na način: število ekošol v obdobju 1997/98 deljeno s številom prebivalstva na dan 1 januar 1998 krat milijon.
- Prednosti in slabosti kazalca: Prednosti: Kazalec je zaradi enotne metodologije za vključitev ustanov v program Ekošola in kriterijev za pridobitev zelene zastave mednarodno primerljiv. Metodologija je opredeljena s strani FEE International. Slabosti: Podatki o številu vključenih ustanov, pridobljeni preko FEE International, se mnogokrat razlikujejo od podatkov, ki jih dajejo na voljo posamezne države zaradi težav pri vzdrževanju enotne baze podatkov. Večina držav, v katerih preko organizacije FEE International izvajajo program Ekošola, ne objavi javno podatkov o številu vključenih ekošol. - Relevantnost, točnost, robustnost, negotovost: Zanesljivost kazalca (arhivski podatki): srednje zanesljiv (neusklajeni podatki med FEE ter posameznimi državami) Negotovost kazalca (scenariji/projekcije): Projekcije/scenariji niso na voljo. - Skupna ocena (1 = brez večjih pripomb, 3 = podatki z zadržkom): Relevantnost: 1 Točnost: 3 (neusklajeni podatki med FEE International ter posameznimi državami) Časovna primerljivost: 2 (neusklajeni podatki med različnimi viri) Prostorska primerljivost: 1
- ReNPVO, 2006. Resolucija o Nacionalnem programu varstva okolja 2005–2012 (Uradni list RS, št. 2/06).
- Smernice vzgoje in izobraževanja za trajnostni razvoj od predšolske vzgoje do univerzitetnega izobraževanja. Ministrstvo za šolstvo in šport, 2010.
- Statistični letopis 2010. Statistični urad RS, 2010.
- Statistični letopis 2011. Statistični urad RS, 2011.
- Statistični letopis 2012. Statistični urad RS, 2012.
- Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for sustainable development (UN, 2015)
- UNECE, 2005. UNECE strategija. Strategija vzgoje in izobraževanje za trajnostni razvoj UNECE, sprejeto na srečanju na visoki ravni ministrov za izobraževanje in okolje. Vilna: marec, 2005.