[ZD25] Reported cases of lyme borreliosis and tick-borne meningoencephalitis in Slovenia

Key message

Lyme borreliosis (LB) and tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) are the most common vector-borne diseases transmitted by ticks. Between 2014 and 2023, Slovenia reported annually slightly less than 3,000 to over 7,000 cases of LB and an average of 105 TBE cases (the highest in 2020 - 187 cases, the lowest in 2015 and 2021 - 62 cases). Due to climate change, which influences the expansion of tick habitats and extends their activity season, the risk of infection may increase in the future. Increased awareness and individual prevention are key factors in reducing the burden of both diseases.
Charts
National Institute of Public Health (NIJZ), 2015–2024 (18.9.2025)
| reported cases of Lyme borreliosis[number ] | reported cases of tick-borne encephalitis[number ] | |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 3742 | 62 |
| 2016 | 4273 | 83 |
| 2017 | 4534 | 102 |
| 2018 | 7543 | 153 |
| 2019 | 3939 | 111 |
| 2020 | 7496 | 187 |
| 2021 | 2933 | 62 |
| 2022 | 4007 | 124 |
| 2023 | 2514 | 63 |
| 2024 | 3162 | 90 |
National Institute of Public Health (NIJZ), 2015–2024 (18.9.2025)
| men[Incidence rate/100.000 inh.] | women[Incidence rate/100.000 inh.] | |
|---|---|---|
| 0-4 | 264.02 | 235.42 |
| 5-9 | 312.42 | 269.96 |
| 10-14 | 152.66 | 112.11 |
| 15-19 | 97.44 | 105.32 |
| 20-24 | 121.10 | 93.60 |
| 25-29 | 122.34 | 105.83 |
| 30-34 | 123.09 | 124.40 |
| 35-39 | 145.15 | 150.15 |
| 40-44 | 171.87 | 184.69 |
| 45-49 | 198.59 | 242.87 |
| 50-54 | 213.98 | 339.88 |
| 55-59 | 237.30 | 388.65 |
| 60-64 | 253.37 | 429.66 |
| 65-69 | 257.12 | 408.05 |
| 70-74 | 220.10 | 343.09 |
| 75-79 | 183.84 | 218.20 |
| 80-84 | 126.45 | 135.12 |
| 85+ | 63.20 | 47.29 |
| Starost - SKUPAJ | 189.16 | 233.66 |
National Institute of Public Health (NIJZ), 2015–2024 (18.9.2025)
| men[Incidence rate/100.000 inh.] | women[Incidence rate/100.000 inh.] | |
|---|---|---|
| 0-4 | 1.56 | 1.67 |
| 5-9 | 5.18 | 2.26 |
| 10-14 | 4.68 | 1.70 |
| 15-19 | 4.51 | 2.78 |
| 20-24 | 4.26 | 2.24 |
| 25-29 | 6.33 | 2.58 |
| 30-34 | 5.07 | 3.92 |
| 35-39 | 3.65 | 4.13 |
| 40-44 | 3.29 | 4.17 |
| 45-49 | 4.89 | 5.51 |
| 50-54 | 5.27 | 5.95 |
| 55-59 | 8.28 | 7.76 |
| 60-64 | 8.30 | 6.86 |
| 65-69 | 9.74 | 5.98 |
| 70-74 | 7.10 | 5.50 |
| 75-79 | 6.33 | 4.66 |
| 80-84 | 8.77 | 3.23 |
| 85+ | 5.24 | 1.58 |
| Starost - SKUPAJ | 5.58 | 4.34 |
National Institute of Public Health (NIJZ), 2024 (18.9.2025)
| reported cases of Lyme disease [number ] | reported cases of tick-borne encephalitis[number ] | |
|---|---|---|
| January | 64 | 2 |
| February | 52 | 0 |
| March | 106 | 6 |
| April | 287 | 8 |
| May | 466 | 16 |
| June | 630 | 16 |
| July | 647 | 20 |
| August | 304 | 6 |
| September | 166 | 4 |
| October | 185 | 8 |
| November | 161 | 4 |
| December | 94 | 0 |
National Institute of Public Health (NIJZ), 2020–2024 (18.9.2025)
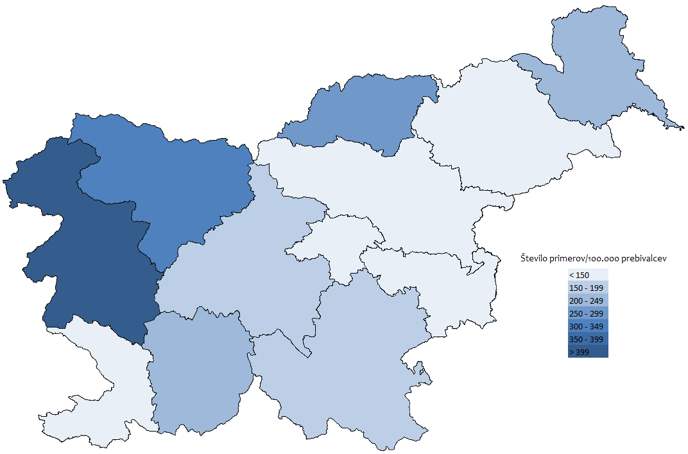
| reported cases of Lyme borreliosis[Incidence rate/100.000 inh.] | |
|---|---|
| 01-Pomurska | 235.90 |
| 02-Podravska | 119.20 |
| 03-Koroška | 280.28 |
| 04-Savinjska | 93.82 |
| 05-Zasavska | 112.40 |
| 06-Posavska | 84.60 |
| 07-Jugovzhodna Slovenija | 171.02 |
| 08-Osrednjeslovenska | 196.25 |
| 09-Gorenjska | 309.63 |
| 10-Primorsko-notranjska | 220.98 |
| 11-Goriška | 442.24 |
| 12-Obalno-kraška | 131.13 |
National Institute of Public Health (NIJZ), 2020–2024, 18.9.2025 ()
| reported cases of tick-borne encephalitis[Incidence rate/100.000 inh.] | |
|---|---|
| 01-Pomurska | 2.98 |
| 02-Podravska | 2.74 |
| 03-Koroška | 14.14 |
| 04-Savinjska | 2.55 |
| 05-Zasavska | 2.80 |
| 06-Posavska | 0.53 |
| 07-Jugovzhodna Slovenija | 4.51 |
| 08-Osrednjeslovenska | 5.04 |
| 09-Gorenjska | 11.08 |
| 10-Primorsko-notranjska | 17.60 |
| 11-Goriška | 5.24 |
| 12-Obalno-kraška | 0.51 |
Comment
Methodology
- Nacionalni inštitut za javno zdravje - NIJZ (2015–2024). Letna poročila epidemiološkega spremljanja nalezljivih bolezni v Sloveniji 2015–2024. Ljubljana, NIJZ.
- Pravilnik o prijavi nalezljivih bolezni in posebnih ukrepih za njihovo preprečevanje in obvladovanje. Uradni list RS št. 16/1999. Dostopno na: http://www.uradni-list.si/1/content?id=18409
- Rizzoli A, Hauffe H, Carpi G, Vourc HG, Neteler M, Rosa R (2011). Lyme borreliosis in Europe. Euro Surveillance. 27, vol. 16. Department of Biodiversity and Molecular Ecology, Italy.
- Sočan M (2012). Epidemiološke značilnosti prijavljenih primerov lymske borelioze v Sloveniji. V: Združenje za infektologijo pri Slovenskem zdravniškem društvu. Zbornik simpozija lymska borelioza 2012. Ljubljana: Klinika za infekcijske bolezni in vročinska stanja, UKC Ljubljana.
- Statistični urad Republike Slovenije. 2007. Projekt statistike razvoja podeželja. Kakovost življenja in raznolikost gospodarskih dejavnosti na podeželju. Ljubljana, SURS.
- Zakon o nalezljivih boleznih – ZNB (uradno prečiščeno besedilo) (ZNB-UPB1), Uradni list RS št. 33/2006. Dostopno na: http://www.uradni-list.si/1/objava.jsp?urlid=200633&
stevilka=1348 - Zavod za gozdove Slovenije (2011). Splošni podatki in dejstva o gozdovih v Sloveniji. Ljubljana, Zavod za gozdove Slovenije.