[OD09] Health-care waste

Definition
The indicator shows the annual quantities of waste generated and collected in the health-care sector as well as the methods of its disposal.
Health-care waste is defined as waste generated by health services and related research. The list of waste produced in the health-care sector and the methods of its disposal are formulated in the Rules on the management of waste generated by health services and related research activities (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, no. 47/04). Examples of health-care waste include sharp objects, infectious waste, chemicals, and medication.
Charts
Analysis of annual reports on waste management in 2005; Waste Management Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2009
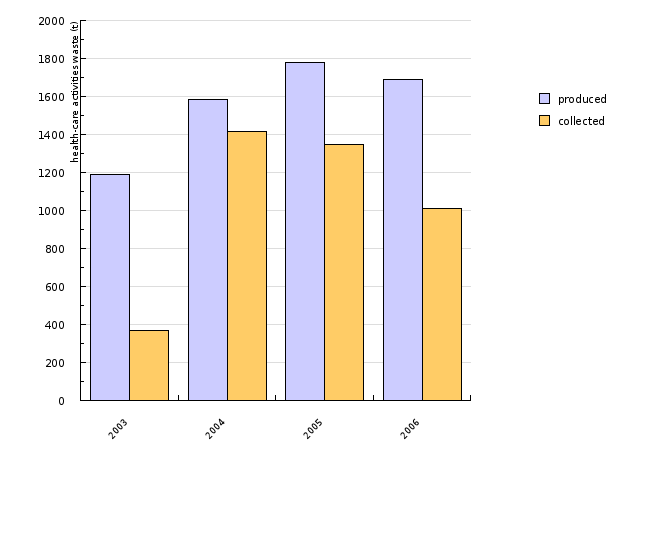
| 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| produced | t | 1187 | 1584 | 1780 | 1691 |
| collected | t | 367 | 1415 | 1350 | 1013 |
Waste Management Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2009
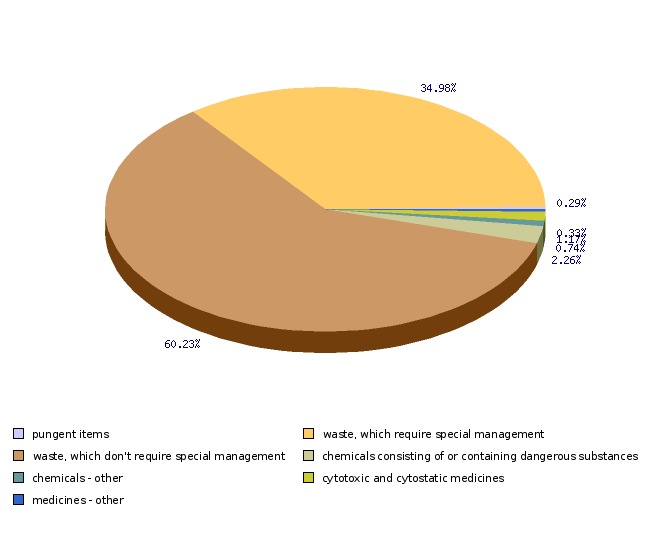
| 2006 | ||
|---|---|---|
| pungent items | kg | 4964 |
| waste, which require special management | kg | 591534 |
| waste, which don't require special management | kg | 1018381 |
| chemicals consisting of or containing dangerous substances | kg | 38181 |
| chemicals - other | kg | 12498 |
| cytotoxic and cytostatic medicines | kg | 19737 |
| medicines - other | kg | 5586 |
| pungent items | % | 0.3 |
| waste, which require special management | % | 35 |
| waste, which don't require special management | % | 60.2 |
| chemicals consisting of or containing dangerous substances | % | 2.3 |
| chemicals - other | % | 0.7 |
| cytotoxic and cytostatic medicines | % | 1.2 |
| medicines - other | % | 0.3 |
Waste Management Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2009
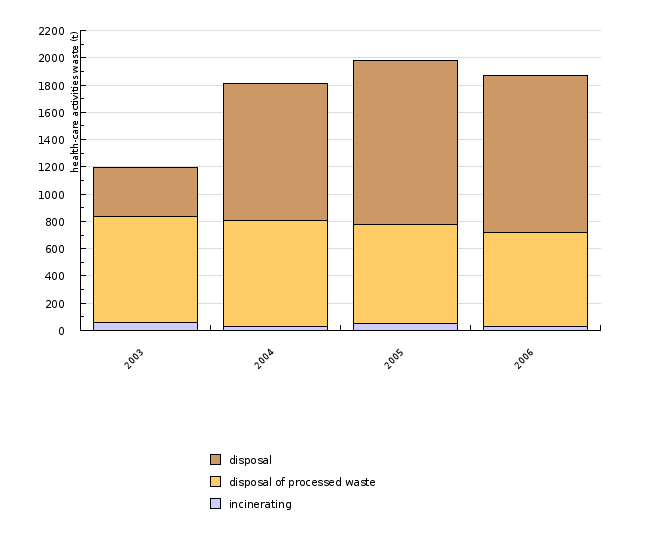
| 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| incinerating | t | 60 | 28 | 48 | 26 |
| disposal of processed waste | t | 774 | 777 | 731 | 692 |
| disposal | t | 365 | 1004 | 1202 | 1154 |
Goals
To ensure 100 % collection of all waste produced in the health-care sector and ensure thermal treatment of infectious waste, sharp objects, pharmaceutical waste and hazardous chemical waste.
To substitute the disinfection of infectious waste with more effective thermal processes and to render the waste inert.
Comment
In addition to the Rules on the management of waste, health-care waste is governed by the Rules on the management of waste generated by health services and related research activities, adopted in 2004. In accordance with these Rules, the generator of the waste must ensure that health-care waste is not mixed with other waste and that individual types of health-care waste do not come in contact with one another, either. The generator must enable health-care waste to be handled by an appropriate collector. Collection services may only be performed by holders of a collection permit issued by the Ministry. The collector must dispose of health-care waste in the manner outlined in Annex 1 of the Rules.
Due to modifications of the waste classification list implemented in 2001, comparisons of data on the generation and management of waste can reasonably be drawn from 2003 onwards.
According to the data obtained by the Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, the generation of health-care waste has been on the rise in the past three years, resulting in an increased quantity of health-care waste which has been disposed of. 2004 saw a notable increase in the quantity of health-care waste collected that year, which may be attributed to the newly adopted Rules. The discrepancy between the quantities of generated waste and collected waste is a result of liable entities failing to report their waste. Also contributing to the difference in quantities is a provision in the Rules on the management of waste which stipulates that reporting is required for those individuals who generate a minimum of 10 tonnes of non-hazardous waste or 5 tonnes of hazardous waste per year. The quantity of collected health-care waste is observed to be lower than the quantity of waste generated and disposed of, since certain types of waste, particularly medication, are remitted directly for disposal.
The Rules on the management of waste generated by health services and related research activities govern the handling of certain waste generated by the health-care sector. Health-care waste is also produced by generators of municipal waste. Municipal waste generators, however, are bound by the provisions in the Order on the management of separately collected fractions in the public service of urban waste management (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, nos. 21/01 and 41/04), which does not cover this type of waste (e.g. sharp objects, infectious waste). For this reason, amendments to the relevant legislation are anticipated.
Methodology
The data used for the indicator have been obtained from annual reports submitted to the Ministry of the Environment and Spatial Planning - Environmental Agency of the RS on required forms by March 31 each year. The reporting is determined in the Rules on the management of waste (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, nos. 84/98, 45/00, 20/01, 13/03 and 41/04) for the following groups:
- for generators of waste required to submit reports on the generated waste and its management,
- for waste collectors, who submit their reports on the collected waste and its management,
- for waste disposers, who submit reports on the received waste and its disposal.
The submitted reports are entered into a database. An annual report is compiled based on the reports on the collection of health-care waste. The Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia examines the content of the submitted reports on the collection of health-care waste. Furthermore, the Agency checks whether all liable entities have submitted their reports. In the event of irregularities or failure to report, the data are verified with each liable entity.