[OD08] Sewage sludge from urban waste water treatment plants

Definition
The indicator shows the annual quantity of sludge from wastewater treatment plants in Slovenia and ways of sludge treatment.
Sludge from wastewater treatment plants is defined as waste material that is a by-product of wastewater purification in wastewater treatment plants or remains after emptying domestic wastewater cesspools.
The treatment of this kind of waste is governed by the Decree on waste management (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, nos. 34/08), and the input of this waste in soil and agricultural surfaces is governed by the Decree on the limit input concentration values of dangerous substances and fertilisers in soil. Special requirements regarding the emission of substances in wastewater discharged from urban wastewater treatment plants are defined in the Decree on the emission of substances in wastewater discharged from urban wastewater treatment plants.
Charts
Waste Water Treatment Plants Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2007
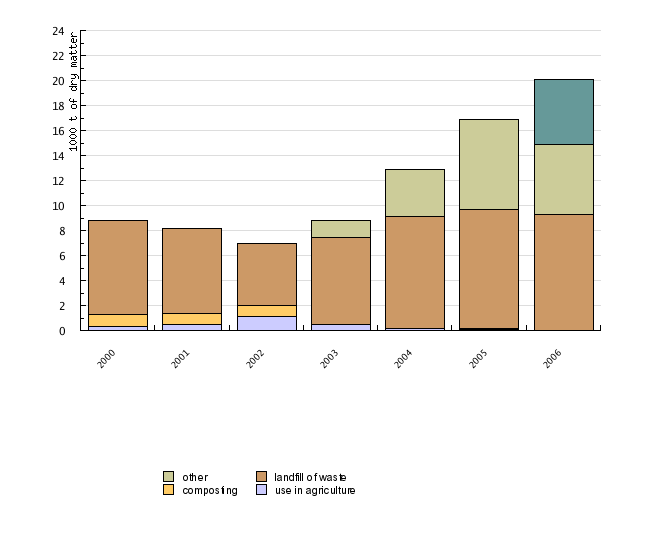
| 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| production of sewage sludge | 1000 t of dry matter | 8.8 | 8.2 | 7 | 8.8 | 12.9 | 16.9 | 20.1 |
| use in agriculture | 1000 t of dry matter | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 |
| composting | 1000 t of dry matter | 1 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0 |
| landfill of waste | 1000 t of dry matter | 7.5 | 6.8 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 9.5 | 9.2 |
| other | 1000 t of dry matter | np | np | np | 1.4 | 3.7 | 7.2 | 5.6 |
| 1000 t of dry matter | np | np | np | np | np | np | 5.2 |
Goals
Biologically recover of sludge at appropriate plants, especially at Regional waste management centres, and particularly those types of sludge that are less contaminated with heavy metals or not at all.
To ensure sufficient facilities for thermal treatment of waste, where up to 70,000 t of sludge from wastewater plants drained to 30% of dry matter can be recovered.
Comment
Sludge is generated in wastewater treatment plants. In the past years, more than half of it was disposed of at non-hazardous waste landfills; however, according to the Decree on the landfill of waste, the volume should slowly reduce. The sludge contains 40-50% of organic substances and its decomposition contributes to the release of greenhouse gasses.
After 2002, the recovery of sludge into compost and depositing sludge onto agricultural surfaces were reduced to slightly more than one per cent of the annual quantity of produced sludge. Sludge from wastewater treatment plants is rich in nutrients, but it can contain hazardous substances if produced in combined wastewater treatment plants in urban and industrial areas. Owing to their volume and characteristics, these substances can have a negative effect on agricultural areas or the quality of groundwater. That is why the Decree on the limit input concentration values of dangerous substances and fertilisers in soil must be taken into account when using sludge on agricultural areas. The Decree also stipulates that sludge must undergo biological, thermal or chemical treatment or long-term storage, or any other appropriate treatment before it is used on agricultural areas in order to reduce its fermentability and the health hazards resulting from its use.
The remaining sludge was exported for the preparation of artificial soil and other recovery methods.
In European countries, the volume of sludge deposited in landfills and sludge used in agricultural areas is reducing, whereas the use of the methods of co-incineration and incineration is increasing.
Methodology
The data on quantities of excess sludge from urban and combined wastewater treatment plants were gathered from the reports on operational monitoring of urban and combined wastewater treatment plants. The obligation to carry out the monitoring and submit reports is defined in Article 27 of the Decree on the emission of substances and heat in the discharge of wastewater into waters and public sewage system (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, no. 47/05). The form of monitoring is defined in the Rules on initial measurements and operational monitoring of waste water and on conditions for their implementation (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, nos. 35/96, 29/00, 106/01). The data are collected in written and electronic form and than processed in the Urban and combined wastewater treatment plant database at the Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia.