[EN18] Renewable energy sources

Key message

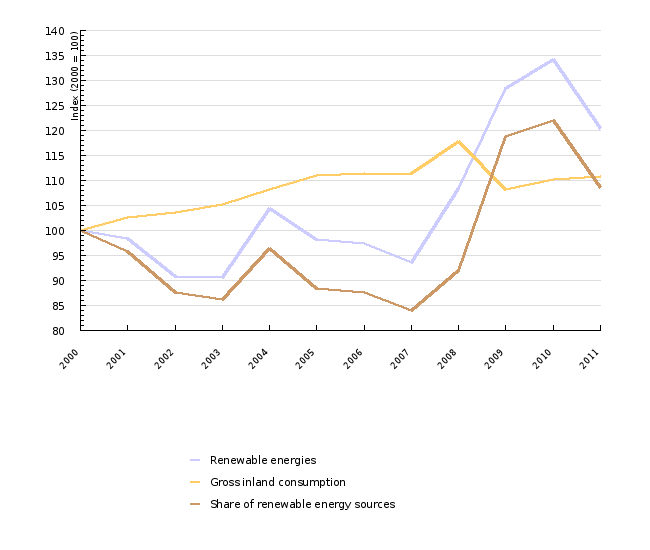
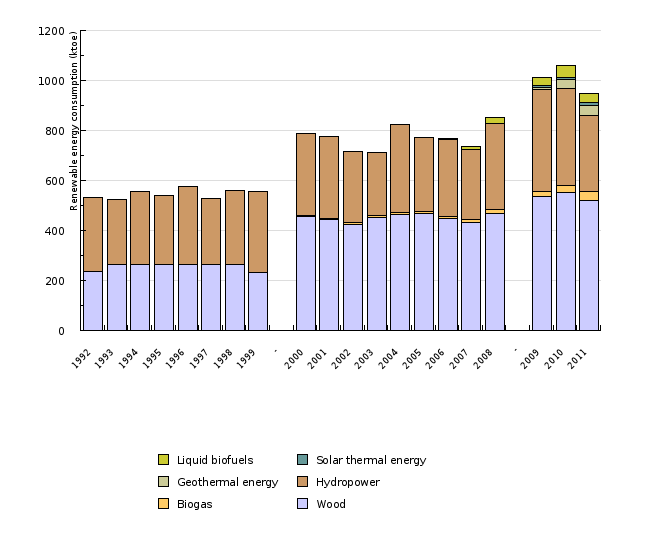
Renewables in 2011 represented 13.2 % of inland gross consumption, which is less than in the previous year. Although this was higher than the target for 2010. Among the reasons for higher share are increased use of renewable energy sources, reduced gross inland consumption due to economic crisis and improvement of the statistics for renewable energy sources. The most important renewable energy source is wood biomass, followed by hydropower.
Definition
The indicator shows the consumption from renewable energy sources in Slovenia, incorporating the use of solar energy, biomass (wood, biogas, biofuels) and waste, geothermal energy, hydropower and wind energy.
The indicator can be shown in relative (share of renewable energy sources) or absolute units (use of renewable energy sources). For the indication in absolute units, a thousand tonnes of oil equivalent (ktoe) are used.
Charts
Statistical Office of the RS, 2012; Jožef Stefan Institute, 2012.
| 2011 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Wood | [%] | 52.0959918664 |
| Biogas | [%] | 2.87165685431 |
| Hydropower | [%] | 36.6552288702 |
| Geothermal energy | [%] | 3.16824692889 |
| Solar thermal energy | [%] | 0.887704103322 |
| Liquid biofuels | [%] | 4.3211713769 |
Statistical Office of the RS, 2012; Jožef Stefan Institute, 2012.
| 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable energies | ktoe | 788 | 775 | 715 | 714 | 822 | 774 | 768 | 737 | 854 | 1012 |
| Gross inland consumption | ktoe | 6491 | 6665 | 6730 | 6823 | 7030 | 7207 | 7225 | 7234 | 7651 | 7020 |
| Share of renewable energy sources | ktoe | 12 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 11 | 14 |
| Renewable energies | Index (2000 = 100) | 100 | 98 | 91 | 91 | 104 | 98 | 97 | 94 | 108 | 128 |
| Gross inland consumption | Index (2000 = 100) | 100 | 103 | 104 | 105 | 108 | 111 | 111 | 111 | 118 | 108 |
| Share of renewable energy sources | Index (2000 = 100) | 100 | 96 | 88 | 86 | 96 | 88 | 88 | 84 | 92 | 119 |
| 2010 | 2011 | ||||||||||
| Renewable energies | ktoe | 1058 | 949 | ||||||||
| Gross inland consumption | ktoe | 7150 | 7198 | ||||||||
| Share of renewable energy sources | ktoe | 15 | 13 | ||||||||
| Renewable energies | Index (2000 = 100) | 134 | 120 | ||||||||
| Gross inland consumption | Index (2000 = 100) | 110 | 111 | ||||||||
| Share of renewable energy sources | Index (2000 = 100) | 122 | 109 |
Jožef Stefan Institute, 2012; Statistical Office of the RS, 2012.
| 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | - | 2000 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | ktoe | 236.7 | 264.3 | 263.2 | 262.9 | 262.7 | 262.6 | 262.8 | 230.2 | 454.7 | |
| Biogas | ktoe | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.7 | 3.6 | |
| Hydropower | ktoe | 293.4 | 259.8 | 292.3 | 278.6 | 315.3 | 265.9 | 296.6 | 321.5 | 329.7 | |
| Geothermal energy | ktoe | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | |
| Solar thermal energy | ktoe | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | |
| Liquid biofuels | ktoe | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | |
| Total | ktoe | 530.2 | 524 | 555.5 | 541.5 | 578 | 528.5 | 559.4 | 555.4 | 788 | |
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | - | 2009 | ||
| Wood | ktoe | 444.5 | 425.5 | 453.8 | 463.4 | 469.5 | 448.7 | 430.2 | 468.7 | 534.5 | |
| Biogas | ktoe | 4.3 | 5.1 | 5.8 | 6.6 | 6.8 | 8.4 | 11.9 | 14.1 | 22.4 | |
| Hydropower | ktoe | 326.4 | 284.9 | 254.3 | 352 | 297.6 | 308.8 | 280.8 | 345.5 | 405.2 | |
| Geothermal energy | ktoe | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | 11.1 | |
| Solar thermal energy | ktoe | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | np | 8.1 | |
| Liquid biofuels | ktoe | np | np | np | np | np | 2 | 14.1 | 25.5 | 30.4 | |
| Total | ktoe | 775.3 | 715.5 | 713.9 | 822.1 | 773.9 | 767.9 | 737.1 | 853.7 | 1011.7 | |
| 2010 | 2011 | ||||||||||
| Wood | ktoe | 551.3 | 518.2 | ||||||||
| Biogas | ktoe | 30.4 | 36 | ||||||||
| Hydropower | ktoe | 387.9 | 306 | ||||||||
| Geothermal energy | ktoe | 33.5 | 37.9 | ||||||||
| Solar thermal energy | ktoe | 9.4 | 14.4 | ||||||||
| Liquid biofuels | ktoe | 45.7 | 36.4 | ||||||||
| Total | ktoe | 1058.2 | 948.9 |
EUROSTAT, 2012
| 2010 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Wood | [%] | 48.6 |
| Biogas | [%] | 6.4 |
| Hydropower | [%] | 18.3 |
| Geothermal energy | [%] | 3.4 |
| Solar thermal energy | [%] | 2.1 |
| Tide, Wave and Ocean | [%] | 0 |
| Liquid biofuels | [%] | 9 |
| Wind energy | [%] | 7.4 |
| Rnewable waste | [%] | 4.7 |
Eurostat, 2012.
| EU27 | EU25 | EU15 | EU10 | - | Latvia | Sweden | Austria | Finland | Portugal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | % | 5.622 | 5.521 | 5.613 | 4.84 | 31.828 | 30.93 | 22.53 | 23.538 | 14.972 | |
| 2010 | % | 9.786 | 9.668 | 9.874 | 8.267 | 34.619 | 33.899 | 26.203 | 24.509 | 22.483 | |
| Denmark | Romania | Lithuania | Slovenia | Estonia | Spain | Italy | Germany | Bulgaria | Slovakia | ||
| 2000 | % | 9.219 | 10.971 | 9.427 | 12.263 | 10.332 | 5.589 | 5.753 | 2.647 | 4.148 | 2.715 |
| 2010 | % | 20.232 | 16.33 | 15.516 | 14.73 | 13.883 | 11.572 | 10.274 | 9.686 | 8.009 | 7.844 |
| France | Hungary | Greece | Poland | Czech Republic | Ireland | Belgium | Cyprus | Netherlands | United Kingdom | ||
| 2000 | % | 6.16 | 3.281 | 4.964 | 4.233 | 3.252 | 1.649 | 1.077 | 1.922 | 1.63 | 0.977 |
| 2010 | % | 7.803 | 7.656 | 7.482 | 7.157 | 6.207 | 4.351 | 4.149 | 3.717 | 3.412 | 3.192 |
| Luxembourg | Malta | ||||||||||
| 2000 | % | 1.075 | 0 | ||||||||
| 2010 | % | 2.855 | 0 |
Goals
- 12 % share of renewable energy sources in total energy consumption in 2010;
- 20 % share of renewable energy sources in total energy consumption in the EU in 2020;
- 25 % share of renewable energy sources in final energy use in Slovenia in 2020;
- attainment of the target shares for the content of biofuels in motor vehicle fuels: 2% in 2007, 3% in 2008, 4% in 2009, 5% in 2010, 6,5% in 2013, 7% in 2014 and 7,5% in 2015 (MOP, 2007); (EU, 2009);
- Targets for 2020 are alaborated in EN24 Share of renewables in final energy consumption.
Methodology
Data for Slovenia and other countries
Objectives summarised by: Resolucija o Nacionalnem energetskem programu (ReNEP) (Resolution on the National Energy Programme, Official Gazette of the RS, No. 57/04), proposal of the climate-energy package, Directive 2009/28/EC on the promotion of the use of energy from renewable sources and Pravilnik o vsebnosti biogoriv v gorivih za pogon motornih vozil (Rules on the content of biofuels in motor vehicle fuels, Official Gazette of the RS, No. 83/05, 108/05, 103/07).
Source database or source:
- Joint questionnaire - EUROSTAT (1992-2002) and EUROSTAT > Environment and energy.
- SI-STAT Data Portal > Environment and natural resources > Renewables and wastes > Renewable energy and waste use, Slovenia, annual (after 2002).
- EurObserv'ER.
Data administrator: Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia (Jože Zalar), IJS (geothermal and solar energy – Fouad Al Mansour), MESP (biofuels - Mirko Bizjak) and EUROSTAT.
Date of acquisition for this indicator: 8 December 2009
Methodology and frequency of data collection for the indicator: The data were prepared on an annual basis. The data for the period 1992-2002 were obtained from completed questionnaires that were communicated by SORS to EUROSTAT (Joint Annual Questionnaire).
The data after 2002 were obtained on the SORS website on the SI-STAT Data Portal (Environment and natural resources > Renewables and wastes > Renewable energy and waste use, Slovenia, annual). The Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia is monitoring the use of hydropower, biomass (wood, wood waste, other renewable waste), biogas and industrial and municipal waste. For the calculation of the share of RES in total energy consumption, the total energy consumption from the EN16 indicator was used. For the use of solar and geothermal energy, the IJS data were used, and for the use of biofuels, the data of the Ministry of Environment and Spatial Planning.
The data for the EU-25 were obtained on the EUROSTAT website under the column »Environment and energy«. The data for the use of individual renewable sources were used: solar energy 5530 gross inland consumption 100900 + biomass and waste 5540 gross inland consumption 100900 + geothermal energy 5550 gross inland consumption 100900 + hydropower 5510 gross inland consumption 100900 + wind energy 5520 gross inland consumption 100900. For the calculation of the share of RES, sector 100900 »Gross inland consumption« was used as the denominator.
Data processing methodology:
Average annual rate of growth calculated using: [(last year/base year) ^ (1/number of years) –1]*100
The share of renewable energy sources in total energy consumption is calculated as the quotient between the total consumption from renewable energy sources and the total energy consumption in an individual year.
For the calculation of the share of RES in total energy consumption, total energy consumption is the denominator and the total energy consumption from RES is the numerator.
A percentage point is a unit used for the comparison of different rates of growth. A percentage point includes an absolute comparison calculated by the formula (nthis year)-(nlast year)=16 %–15 %=1 pp (for instance: if last year the growth was 15 % and this year 16 %, then this year the growth was higher by 1 percentage point). The difference in growth can also be expressed in a relative comparison using the formula [(nthis year/nlast year)*100]–100=[(16 %/15 %)*100]–100=6.7 %, where the growth is indicated in percentages.
Geographical coverage: The EU-15 is composed of the old EU Member States: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, the United Kingdom. The EU-10 (NMS-10) includes the Member States that joined the EU in 2004 (Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Lithuania, Latvia, Malta, Poland, Slovenia, Slovakia). The EU-25 includes the EU-15 and EU-10.
Information concerning data quality:
- Advantages and disadvantages of the indicator: /
- Relevance, accuracy, robustness, uncertainty:
Reliability of the indicator (archival data): Data reliability is limited, since the use of wood biomass, which represents the most important renewable energy source, is assessed every five years and does not enable the monitoring of the trends of the use of wood biomass. Moreover, the Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia also does not monitor the use of solar energy and geothermal energy. The data for 1992–1999 and after 2000 are not comparable due to different assessments on the use of wood biomass.
Uncertainty of the indicator (scenarios/projections): Scenarios and projections are not available.
- Overall assessment (1 = no major comments, 3 = data to be considered with reservation):
Relevance: 1
Accuracy: 2
Completeness over time: 3
Completeness over space: 1
References:
- EEA, 2007. EN29 Renewable Energy.
- EurObserv'ER, 2007. Barometri za toploto iz sonca, fotovoltaiko in geotermalno energijo (Barometers for heat from sun, photovoltaics and geothermal energy).
- IBE, 2005. Indikativni razvojni načrt energetskega sektorja (Indicative development plan of the energy sector).
- MESP, 2009a. Operativni program zmanjševanja emisij toplogrednih plinov do leta 2012 (Operational programme for limiting greenhouse gas emissions until 2012).
- MESP, 2009b. Raba biogoriv v transportnem sektorju v Republiki Sloveniji v letu 2008 (The use of biofuels in transport sector in the Republic of Slovenia in 2008).
- Nowak, 2009. The EU RES Directive and heat pumps.
- Renewable Energy Road Map: Renewable energies in the 21st century: building a more sustainable future (COM(2006) 848 – final).
- Ljubljana thermal power and heating plant, 2009. Megavat (21 March 2009).
- Šoštanj thermal power plant, 2009. Annual report 2008 – Energy for the future.
- Trbovlje thermal power plant, 2009. Annual report for 2008.
- Slovenian Forest Service, 2009. Poročilo ZGS o gozdovih Slovenije za leto 2008 (Slovenian Forest Service report on Slovenia's forests for 2008).