[OP01] Environmental protection taxes and other environmental pressure duties

Definition
This indicator shows financial effects and the amounts of environmental protection taxes and other duties for environmental pressures as well as use of natural resources in the Republic of Slovenia by individual year. Environmental protection taxes and other environmental pressure duties are economic instruments of environmental protection policy, the basic aim of which is to encourage reduction of environmental pressures by implementing a “polluter pays” principle. In accordance with the latter aim, expenses arising from damages caused to the environment are at least partially included in the production expenses. Regulatory decrees determine the methods of calculating the environmental pressure caused, expressed in so-called environmental load units (ELU) per individual polluter as well as the amount of tax and contribution, respectively, per individual environmental load unit (ELU). The main share of taxes and contributions is used directly for the purpose of environmental protection investments with the remaining share representing budgetary revenue.
Charts
Balance Sheet of Expenditure and Revenue of the Slovenian National Budget, Ministry of Finance, General Customs Office; databases Water Fees, Taxes and Concessions; Sources of Pollution; and Waste Management, Ministry of the Environment, and Spatial Planning – Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2005
| 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water fees | mio SIT | 1010 | 1710 | 2169 | 3267 | 3738 | 3390 |
| Water pollution tax - Slovenian budget revenue | mio SIT | 740 | 1004 | 1233 | 1363 | 1580 | 1559 |
| Water pollution tax - earmarked for financial investments |
mio SIT | 6556 | 9974 | 11697 | 14139 | 15029 | 10188 |
| CO2 emission taxes | mio SIT | 15055 | 15684 | 13998 | 7997 | 12985 | 14101 |
| Waste disposal tax - Slovenian budget revenue | mio SIT | np | np | np | np | 168 | 185 |
| Waste disposal tax - earmarked for environmental protection nvestments |
mio SIT | np | np | np | 3156 | 3064 | 2698 |
| Lubricating oil use tax | mio SIT | np | np | np | 494 | 619 | 622 |
| End-of life vehicle dismantling tax | mio SIT | np | np | np | np | 801 | 1827 |
| total | mio SIT | 23361 | 28372 | 29097 | 30416 | 37984 | 34570 |
Balance Sheet of Expenditure and Revenue of the Slovenian National Budget, Ministry of Finance, General Customs Office; databases Water Fees, Taxes and Concessions, Sources of Pollution, and Waste Management, Ministry of the Environment, Spatial Planning and Energy – Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2005; www.stat.si (December, 2005), Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia.
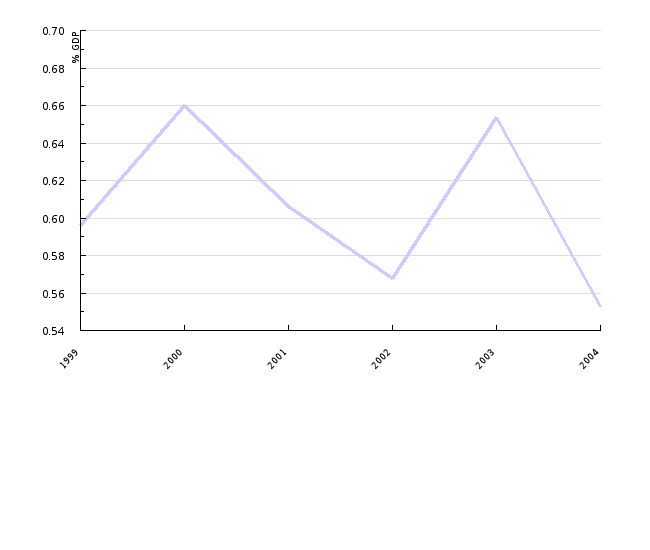
| 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP in current prices | mio SIT | 3918974 | 4300350 | 4799552 | 5355440 | 5813540 | 6251244 |
| environmental taxes and contributions | mio SIT | 23361 | 28372 | 29097 | 30416 | 37984 | 34570 |
| share of environmental taxes and contributions in GDP | % GDP | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Goals
The National Environmental Action Programme recognises the following as priority targets with regard to the economic aspects of the environment: encouragement of an increase in economic resources for investments in environmental protection projects as well as increases in budget expenditure which would indirectly entail reduction in pollution; speeding up introduction of tax relief for investments in environmental protection projects; and introduction of a deposit and refund system in relation to the system of taxation.
Comment
Slovenia is made responsible for implementation of a “polluter pays” principle by the provisions of Article 174 of the EC Treaty and also within the Slovenian legal system, the provisions of the Environmental Protection Act (OJ RS, No 41/04, 17/06, 20/06, 28/06). The introduction of this principle has given rise to a significant source of financing environmental protection policy measures. Positive experience gained in the area of waste water collection and treatment with the introduction of tax exemption for water pollution as an earmarked source of financing the construction of infrastructure facilities and equipment were also included in the legal basis for waste disposal and CO2 emissions taxes. Waste disposal tax exemptions represent an earmarked source of financing the construction of suitable networks of facilities and equipment for waste management as well as an important mechanism for achieving the set and prescribed targets. The latter are principally as follows: reduction in the quantity of waste generated at source; disposal of smallest quantities of waste possible and disposal of the most inert waste possible; reduction in the share of biodegradable waste; accelerating separated collection of individual urban waste portions; and a gradual increase in the scope of waste treatment and utilisation. The CO2 emissions tax instrument is one of the key instruments included in the programme to reduce greenhouse gas emissions for the achievement of the objectives in this area and the fulfilment of the obligations undertaken with the signing of the Kyoto Protocol, ratified by Slovenia in June 2002. With the enforcement of the Waters Act, funds arising from water fees accumulate in the Waters Fund and are intended for financing water infrastructure. A certain share of funds collected via the lubricating oil and fluid use tax is also earmarked for rehabilitation of unregulated waste landfills and old burdens, while a share of environmental pollution tax on the generation of end-of-life vehicles is earmarked for implementation of public economic service for end-of-life vehicles management.
The increase in the annual amount of environmental taxes is principally the result of an increase in the level of taxes per environmental load unit and unit of product, respectively, as well as greater coverage of polluters (introduction of stricter conditions and new contributions), rather than a rise in environmental pressures.
Methodology
Data for Slovenia
The Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, on the basis of reports from persons liable according to these decrees:
- Decree on the Water Pollution Tax (OJ RS, No 41/95, 44/95, 8/96, 124/00 and 49/01, 8/04),
- Decree on the Water Fee (OJ RS, No 41/95, 84/97, 124/00, 110/01, 103/02),
- Decree on the Carbon Dioxide Emission Tax (OJ RS, No 68/96, 2/97, 5/97 – corr., 24/98, 65/98, 51/99, 42/00 and 124/00), replaced by the Decree on the Carbon Dioxide Emissions Tax (OJ RS, No 91/02, 8/03, 67/03),
- Decree on the Waste Disposal Tax (OJ RS, No 70/01, 9/04)
maintains databases (Water Fees, Taxes and Concessions; Sources of Pollution; Waste Management), which contain information on environmental taxes and other duties for environmental protection, as well as the amounts of tax and contribution exemptions due to investments in environmental protection. As the data for 2003 concerning the amount of funds earmarked for investments from waste water and waste disposal contributions for 2003 are still incomplete, this report provides an estimate of the amount of these funds in respect of prepayments paid (technological waste waters) and the level of increase in tax per load unit (for urban waste water and municipal waste).
Ministry of Finance, Macroeconomic Analysis and Government Accounts Department issues monthly reports on the realisation of the national budget for individual budget years within the framework of the balance sheet of the national budget expenditure and revenue. In accordance with the above mentioned decrees as well as the decrees listed below, these are the sources of information on the Slovenian national budget revenues.
- Decree on the Tax on the Use of Lubricating Oils and Fluids (OJ RS, No 2/02, 20/2002),
- Decree on the tax on the Generation of
End-Of-Life Vehicles (OJ RS, No 13/03).
Data on GDP in current prices are as stated in the Statistical Yearbook 2003 (Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia); data for 2003 are as stated on www.stat.si - Indicators, GDP.
Earmarked use of funds for investments in relation to waste water and waste disposal taxes for 2003 is assessed on the basis of forecasts made by liable persons.
Data for other countries:
Europe's Environment: The Third Assessment, 2003, European Environment Agency (EEA).
The table does not include contributions exclusively covering production or public service expenses (e.g. contributions for waste collection, water supply).