[OD12] Waste batteries and accumulators 

Key message

In the upcoming years our primary objective is to implement and maintain an effective system of managing waste batteries and accumulators.
Definition
The indicator shows the annual quantity of waste batteries generated and collected in Slovenia, methods of their management and shares of various types of batteries and accumulators containing hazardous substances.
A battery or accumulator is a source of electric energy generated by direct conversion of chemical energy. It is composed of one or more primary battery cells, which cannot be recharged, or secondary battery cells, which may be recharged.
A waste battery or accumulator is any battery or accumulator which has been discarded because it can no longer be used or for other reasons and is intended for recovery or disposal. Hazardous substances in batteries and accumulators include metals (mercury, cadmium, lead) and electrolytes.
The procedures for handling batteries and accumulators containing hazardous substances, as well as other rules and obligations regarding reception, collection, recovery and disposal of waste batteries and accumulators, are determined in the Rules on the management of batteries and accumulators containing dangerous substances (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, no. 104/00). Batteries and accumulators not covered by these rules are governed by the Rules on the management of waste (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, no. 84/98 and 45/00).
Charts
Waste Management Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2006; Annual Reports, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2007
| 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| expected to be put on the market | kg | 4776882 | 4634427 | 3003742 | 1864306 |
| collected | kg | 2459134 | 1745975 | 2050370 | 1340165 |
| processing | kg | 2082928 | 1744682 | 2031187 | 1339752 |
| disposal | kg | 1283 | 1293 | 19182 | 412 |
Waste Management Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2006; Annual Reports, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2007
| 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb accumulators | kg | 4619171 | 2046527 | 1337631 |
| Ni-Cd batteries and accumulators | kg | 14694 | 988 | 1159.1 |
| batteries and accumulators containing Hg | kg | 462 | 30 | 77.49 |
| unsorted batteries | kg | - | 2824 | 1297 |
Goals
To ban the marketing of batteries with excessive content of mercury, cadmium and lead (Hg, Cd, Pb).
To implement and maintain a system of comprehensive management of waste batteries and accumulators, and to:
• enable consumers to deposit waste batteries and accumulators at specific collection points at no cost,
• enable separate collection of waste batteries and accumulators, further recovery (recycling) and disposal of recovery residues.
Comment
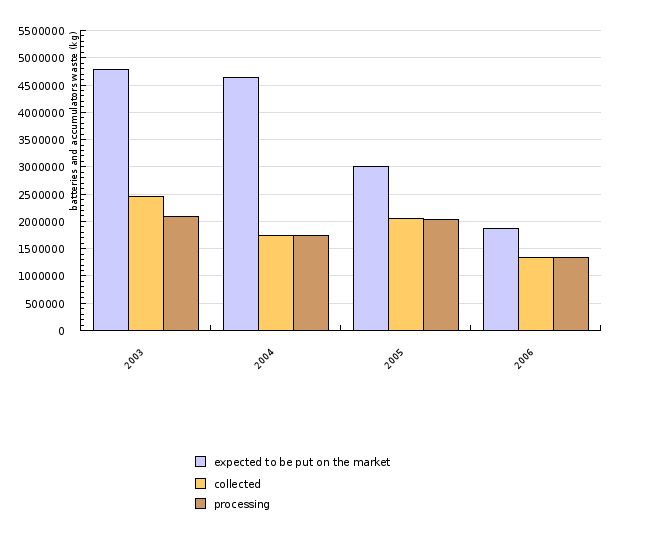
In 2006, 1.9 million kg of batteries and accumulators were anticipated to enter the market; two-thirds of these were collected as waste batteries and accumulators. The majority of waste batteries and accumulators were recovered.
The Rules on the management of batteries and accumulators containing dangerous substances outline the principles of handling batteries and accumulators containing hazardous substances (mercury, cadmium, lead) in production, traffic and consumption. The Rules also determine the management and other obligations regarding reception, collection, recovery and disposal of waste batteries and accumulators. The reception, collection and recovery of waste batteries and accumulators discarded by users must be organized by the suppliers of batteries and accumulators, who must obtain a permit from the Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia.
Records of battery and accumulator suppliers kept by the Environmental Agency indicate that in 2006 there were 50 registered suppliers. 48 of them submitted reports on collected batteries and accumulators; 2 of those failed to provide all the required data. Based on the suppliers' 4-year projection submitted at the time of entry into the record of battery and accumulator suppliers, 1,864,306.30 kg of batteries and accumulators containing hazardous substances were anticipated to enter the market in 2006. 1,340,164.59 kg or 71.9 % of these were collected. 99.97 % of batteries and accumulators were collected for the purpose of recovery, while the rest were intended for disposal. Lead accumulators were the most frequent items on the market (1,854,615 kg), followed by nickel-cadmium batteries or accumulators in much smaller amounts (9,145.85 kg), while batteries and accumulators containing mercury were the least frequent (545.45 kg). We collected 1,337,631 kg of lead residue, 1,159 kg of nickel-cadmium batteries or accumulators, 77.49 kg of batteries and accumulators containing mercury and 1,297 kg of unsorted batteries.
There are currently no facilities for the recovery of waste batteries in Slovenia. Even in other countries, the procedures are still not fully developed; in addition, the threshold at which such facilities seem rational is significantly higher than the quantities produced in Slovenia. Recycling of waste lead accumulators is carried out by a company named MPI located in Žerjav, Črna na Koroškem.
By implementing EU regulations in the area of management of waste batteries and accumulators containing hazardous substances, we have gradually reduced the burden on the environment caused by metals from waste batteries and accumulators. The ban on marketing batteries with excessive levels of mercury, cadmium and lead, special labelling of such batteries, mandatory separate collection, recycling and controlled disposal have all contributed to the virtual elimination of mercury in consumer batteries. Furthermore, nickel-cadmium accumulators are steadily being replaced by environmentally friendlier types; the manganese component in alkaline batteries is being phased out and replaced by the environmentally more acceptable iron component; lead accumulators remain the only available type for starting piston engines, though their efficiency per unit of weight has improved with their useful life virtually doubling; the stable price of lead allows for economical recycling.
In the upcoming years, Slovenia mainly wishes to implement and maintain an effective system of managing waste batteries and accumulators. This objective entails a system of depositing waste batteries and accumulators containing hazardous substances only at retailers' collection points, starting on January 1 2003. In addition, a system of collecting non-hazardous waste batteries and accumulators will be implemented within the framework of collecting separate fractions as part of the management of municipal waste in order to prevent mixing with municipal waste.
Methodology
Waste Management Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2006; Annual Reports, Environmental Agency of the republic of Slovenia, 2007
Data on the quantities of batteries and accumulators containing hazardous substances and their management are derived from Reports on collected waste batteries and/or accumulators containing hazardous substances and their management. The reporting is determined in the Rules on the management of batteries and accumulators containing dangerous substances (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, no. 104/00 and by the Rules on the management of waste (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, no. 84/98 and 45/00). Annual reports should be submitted to the Ministry of the Environment and Spatial Planning - Environmental Agency of the RS on required forms by March 31 each year.