[KM19] Plant protection poducts and their degradation products in groundwater (replaced by indicator VD06)

Key message

In most aquifers in Slovenia, levels of plant protection products and their degradation products (metabolites) indicate a decreasing trend, which is mainly due to the decreased concentrations of atrazine and its metabolite desethylatrazine. The number of individual active substances and their degradation products exceeding the 0.1 µg/l threshold value for individual active substances is also decreasing. Despite the removal of atrazine from the market in 2002, the highest share of threshold value exceedances at sampling points are established for atrazine and especially its metabolite desethylatrazine. Along with these, the only substance that appears in groundwater more frequently than others is metolachlor, which is one of the most frequently used active substances in Slovenia in the production of maize.
Definition
Pollution of groundwater with plant protection products is presented by the share of sampling points at aquifers with intergranular and karst-fractured porosity where threshold concentration values of individual products and their degradation products or their totals in the samples taken were exceeded at all times, periodically or never. In Slovenia, threshold values concerning concentrations of the residues of plant protection products in groundwater are defined by the Degree on Groundwater Quality Standards (Official Gazette RS No. 100/2005) as 0.1 µg/l for individual active substances, and 0.5 µg/l for the total residues of plant protection products. Along with the entire legislation governing this field, these measures are in accordance with the Drinking Water Directive (98/83/EC), which applies to the entire European Union.
Charts
| Total P output [t P] | Temporary and permanent pasture nett production [t P] | Cereals [t P] | Plants harvested green/Fodder from arable land [t P] | Root crops [t P] | Fruits [t P] | Industrial crops [t P] | Vegetables [t P] | Dried Pulses [t P] | Temporary and permanent pasture nett production [%] | Cereals [%] | Plants harvested green/Fodder from arable land [%] | Root crops [%] | Fruits [%] | Industrial crops [%] | Vegetables [%] | Dried Pulses [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | 4680.49 | 2748.49 | 1131.92 | 444.54 | 233.73 | 40.19 | 56.74 | 22.35 | 2.52 | 58.72 | 24.18 | 9.50 | 4.99 | 0.86 | 1.21 | 0.48 | 0.05 |
| 1993 | 4845.59 | 2575.64 | 1299.28 | 577.63 | 271.90 | 43.03 | 50.89 | 24.33 | 2.86 | 53.15 | 26.81 | 11.92 | 5.61 | 0.89 | 1.05 | 0.50 | 0.06 |
| 1994 | 8170.58 | 5018.04 | 1631.95 | 956.35 | 416.64 | 48.04 | 69.62 | 22.71 | 7.22 | 61.42 | 19.97 | 11.70 | 5.10 | 0.59 | 0.85 | 0.28 | 0.09 |
| 1995 | 7701.48 | 4594.70 | 1578.83 | 990.43 | 429.11 | 43.19 | 31.88 | 25.26 | 8.08 | 59.66 | 20.50 | 12.86 | 5.57 | 0.56 | 0.41 | 0.33 | 0.10 |
| 1996 | 7449.33 | 4372.03 | 1510.81 | 1018.40 | 431.47 | 50.11 | 34.16 | 26.34 | 6.01 | 58.69 | 20.28 | 13.67 | 5.79 | 0.67 | 0.46 | 0.35 | 0.08 |
| 1997 | 8111.81 | 4847.77 | 1685.29 | 1093.31 | 383.34 | 42.67 | 28.13 | 25.95 | 5.35 | 59.76 | 20.78 | 13.48 | 4.73 | 0.53 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.07 |
| 1998 | 8128.08 | 4752.71 | 1727.25 | 1099.68 | 441.27 | 49.19 | 29.12 | 24.04 | 4.83 | 58.47 | 21.25 | 13.53 | 5.43 | 0.61 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.06 |
| 1999 | 7802.14 | 4776.79 | 1483.98 | 983.92 | 458.95 | 41.89 | 26.09 | 27.16 | 3.36 | 61.22 | 19.02 | 12.61 | 5.88 | 0.54 | 0.33 | 0.35 | 0.04 |
| 2000 | 6698.44 | 3929.17 | 1531.20 | 768.29 | 366.06 | 57.66 | 19.17 | 23.91 | 2.97 | 58.66 | 22.86 | 11.47 | 5.46 | 0.86 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.04 |
| 2001 | 6545.10 | 4024.06 | 1538.03 | 650.67 | 239.51 | 42.74 | 28.06 | 18.90 | 3.14 | 61.48 | 23.50 | 9.94 | 3.66 | 0.65 | 0.43 | 0.29 | 0.05 |
| 2002 | 8241.33 | 5087.98 | 1894.00 | 830.78 | 282.00 | 54.61 | 65.72 | 20.59 | 5.64 | 61.74 | 22.98 | 10.08 | 3.42 | 0.66 | 0.80 | 0.25 | 0.07 |
| 2003 | 5475.63 | 3190.76 | 1236.66 | 697.97 | 218.68 | 49.02 | 59.36 | 19.60 | 3.57 | 58.27 | 22.58 | 12.75 | 3.99 | 0.90 | 1.08 | 0.36 | 0.07 |
| 2004 | 8312.73 | 5129.58 | 1808.36 | 949.06 | 263.35 | 64.27 | 64.78 | 24.61 | 8.72 | 61.71 | 21.75 | 11.42 | 3.17 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| 2005 | 8944.42 | 5542.97 | 1787.70 | 1164.11 | 279.60 | 52.06 | 68.35 | 25.82 | 23.81 | 61.97 | 19.99 | 13.01 | 3.13 | 0.58 | 0.76 | 0.29 | 0.27 |
| 2006 | 7235.09 | 4451.81 | 1530.85 | 828.35 | 238.53 | 51.00 | 68.17 | 23.26 | 43.12 | 61.53 | 21.16 | 11.45 | 3.30 | 0.70 | 0.94 | 0.32 | 0.60 |
| 2007 | 7938.95 | 5071.75 | 1649.78 | 895.17 | 87.37 | 54.14 | 136.38 | 19.40 | 24.97 | 63.88 | 20.78 | 11.28 | 1.10 | 0.68 | 1.72 | 0.24 | 0.31 |
| 2008 | 8256.25 | 5270.70 | 1797.80 | 928.48 | 68.09 | 47.92 | 102.59 | 23.00 | 17.67 | 63.84 | 21.77 | 11.25 | 0.82 | 0.58 | 1.24 | 0.28 | 0.21 |
| 2009 | 8093.00 | 5210.32 | 1652.79 | 973.26 | 72.59 | 50.20 | 99.90 | 24.91 | 9.04 | 64.38 | 20.42 | 12.03 | 0.90 | 0.62 | 1.23 | 0.31 | 0.11 |
| 2010 | 8503.20 | 5495.26 | 1764.31 | 954.48 | 63.61 | 51.44 | 147.93 | 17.82 | 8.35 | 64.63 | 20.75 | 11.22 | 0.75 | 0.60 | 1.74 | 0.21 | 0.10 |
| 2011 | 8050.13 | 4887.94 | 1885.13 | 987.11 | 59.54 | 52.63 | 140.29 | 23.20 | 14.28 | 60.72 | 23.42 | 12.26 | 0.74 | 0.65 | 1.74 | 0.29 | 0.18 |
| 2012 | 7183.67 | 4259.94 | 1787.89 | 872.36 | 50.66 | 36.34 | 148.58 | 21.23 | 6.67 | 59.30 | 24.89 | 12.14 | 0.71 | 0.51 | 2.07 | 0.30 | 0.09 |
| 2013 | 6327.95 | 3912.08 | 1418.71 | 746.67 | 41.82 | 52.24 | 130.67 | 21.66 | 4.10 | 61.82 | 22.42 | 11.80 | 0.66 | 0.83 | 2.06 | 0.34 | 0.06 |
| 2014 | 8760.70 | 5288.02 | 2013.19 | 1142.18 | 57.59 | 49.17 | 177.31 | 26.34 | 6.90 | 60.36 | 22.98 | 13.04 | 0.66 | 0.56 | 2.02 | 0.30 | 0.08 |
| 2015 | 8714.36 | 5331.43 | 1936.34 | 1207.42 | 54.18 | 61.84 | 85.41 | 29.43 | 8.32 | 61.18 | 22.22 | 13.86 | 0.62 | 0.71 | 0.98 | 0.34 | 0.10 |
| 2016 | 8915.47 | 5395.54 | 1979.61 | 1261.15 | 51.09 | 40.52 | 141.91 | 32.92 | 12.73 | 60.52 | 22.20 | 14.15 | 0.57 | 0.45 | 1.59 | 0.37 | 0.14 |
| 2017 | 7079.32 | 4090.15 | 1697.26 | 1036.13 | 47.89 | 29.77 | 136.29 | 30.12 | 11.70 | 57.78 | 23.97 | 14.64 | 0.68 | 0.42 | 1.93 | 0.43 | 0.17 |
| 2018 | 8685.06 | 5297.83 | 1851.54 | 1256.82 | 49.10 | 67.02 | 120.06 | 31.32 | 11.36 | 61.00 | 21.32 | 14.47 | 0.57 | 0.77 | 1.38 | 0.36 | 0.13 |
| 2019 | 8785.42 | 5327.37 | 1990.87 | 1207.71 | 47.98 | 39.07 | 121.62 | 39.33 | 11.47 | 60.64 | 22.66 | 13.75 | 0.55 | 0.44 | 1.38 | 0.45 | 0.13 |
Standardised Database for Water Quality Monitoring, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2007.
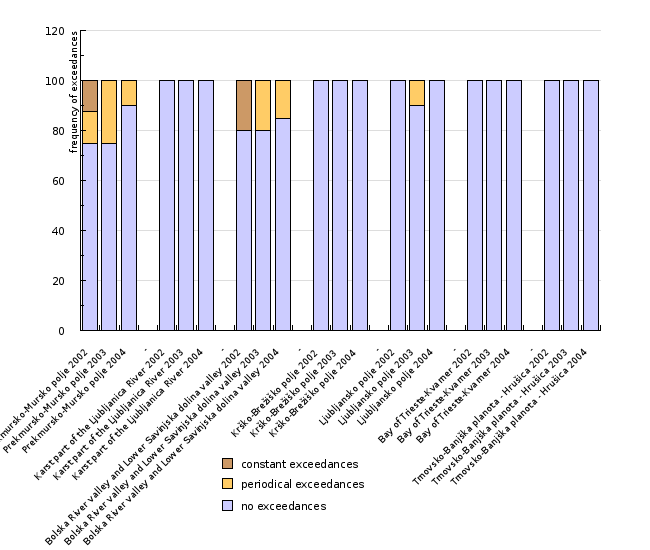
| Prekmursko-Mursko polje 2002 | Prekmursko-Mursko polje 2003 | Prekmursko-Mursko polje 2004 | - | Karst part of the Ljubljanica River 2002 | Karst part of the Ljubljanica River 2003 | Karst part of the Ljubljanica River 2004 | - | Bolska River valley and Lower Savinjska dolina valley 2002 | Bolska River valley and Lower Savinjska dolina valley 2003 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| no exceedances | number | 6 | 6 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 8 | ||
| periodical exceedances | number | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||
| constant exceedances | number | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||
| total | number | 8 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 10 | ||
| no exceedances | % | 75 | 75 | 90 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 80 | 80 | ||
| periodical exceedances | % | 12.5 | 25 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | ||
| constant exceedances | % | 12.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 0 | ||
| Bolska River valley and Lower Savinjska dolina valley 2004 | - | Krško-Brežiško polje 2002 | Krško-Brežiško polje 2003 | Krško-Brežiško polje 2004 | - | Ljubljansko polje 2002 | Ljubljansko polje 2003 | Ljubljansko polje 2004 | - | ||
| no exceedances | number | 11 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 10 | |||
| periodical exceedances | number | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |||
| constant exceedances | number | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| total | number | 13 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 9 | 10 | 10 | |||
| no exceedances | % | 84.6 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 90 | 100 | |||
| periodical exceedances | % | 15.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | |||
| constant exceedances | % | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Bay of Trieste-Kvarner 2002 | Bay of Trieste-Kvarner 2003 | Bay of Trieste-Kvarner 2004 | - | Trnovsko-Banjška planota - Hrušica 2002 | Trnovsko-Banjška planota - Hrušica 2003 | Trnovsko-Banjška planota - Hrušica 2004 | |||||
| no exceedances | number | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | ||||
| periodical exceedances | number | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| constant exceedances | number | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| total | number | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | ||||
| no exceedances | % | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||
| periodical exceedances | % | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| constant exceedances | % | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Standardised Database for Water Quality Monitoring, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2005
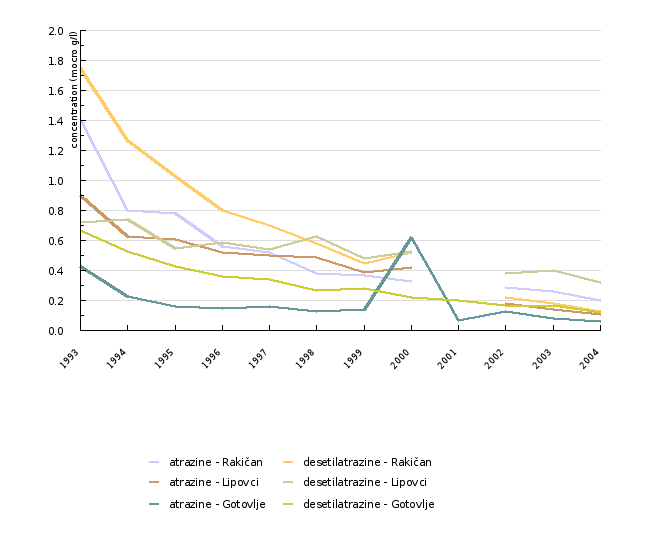
| 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| atrazine - Rakičan | micro g/l | 1.41 | 0.8 | 0.78 | 0.56 | 0.52 | 0.38 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.29 | |
| desetilatrazine - Rakičan | micro g/l | 1.75 | 1.27 | 1.03 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.58 | 0.45 | 0.52 | 0.22 | |
| atrazine - Lipovci | micro g/l | 0.9 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.52 | 0.5 | 0.49 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.18 | |
| desetilatrazine - Lipovci | micro g/l | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 0.54 | 0.63 | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.38 | |
| atrazine - Gotovlje | micro g/l | 0.43 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 0.13 |
| desetilatrazine - Gotovlje | micro g/l | 0.67 | 0.53 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.2 | 0.17 |
| 2003 | 2004 | ||||||||||
| atrazine - Rakičan | micro g/l | 0.26 | 0.2 | ||||||||
| desetilatrazine - Rakičan | micro g/l | 0.18 | 0.13 | ||||||||
| atrazine - Lipovci | micro g/l | 0.14 | 0.11 | ||||||||
| desetilatrazine - Lipovci | micro g/l | 0.4 | 0.32 | ||||||||
| atrazine - Gotovlje | micro g/l | 0.08 | 0.06 | ||||||||
| desetilatrazine - Gotovlje | micro g/l | 0.17 | 0.12 |
Standardised Database for Water Quality Monitoring, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2005.
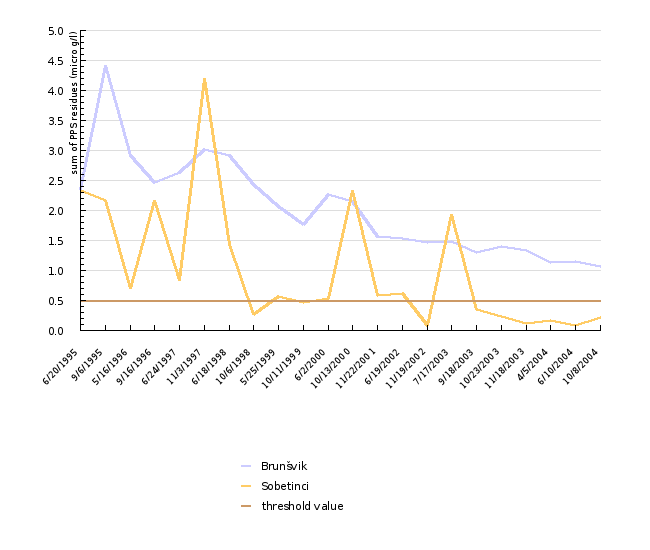
| 6/20/1995 | 9/6/1995 | 5/16/1996 | 9/16/1996 | 6/24/1997 | 11/3/1997 | 6/18/1998 | 10/6/1998 | 5/25/1999 | 10/11/1999 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brunšvik | micro g/l | 2.35 | 4.41 | 2.91 | 2.47 | 2.64 | 3.02 | 2.92 | 2.44 | 2.07 | 1.76 |
| Sobetinci | micro g/l | 2.34 | 2.17 | 0.7 | 2.17 | 0.84 | 4.2 | 1.44 | 0.27 | 0.57 | 0.46 |
| threshold value | micro g/l | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 6/2/2000 | 10/13/2000 | 11/22/2001 | 6/19/2002 | 11/19/2002 | 7/17/2003 | 9/18/2003 | 10/23/2003 | 11/18/2003 | 4/5/2004 | ||
| Brunšvik | micro g/l | 2.27 | 2.15 | 1.56 | 1.53 | 1.47 | 1.49 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.33 | 1.14 |
| Sobetinci | micro g/l | 0.54 | 2.33 | 0.59 | 0.62 | 0.09 | 1.93 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.11 | 0.16 |
| threshold value | micro g/l | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 6/10/2004 | 10/8/2004 | ||||||||||
| Brunšvik | micro g/l | 1.15 | 1.06 | ||||||||
| Sobetinci | micro g/l | 0.09 | 0.21 | ||||||||
| threshold value | micro g/l | 0.5 | 0.5 |
Standardised Database for Water Quality Monitoring, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2005
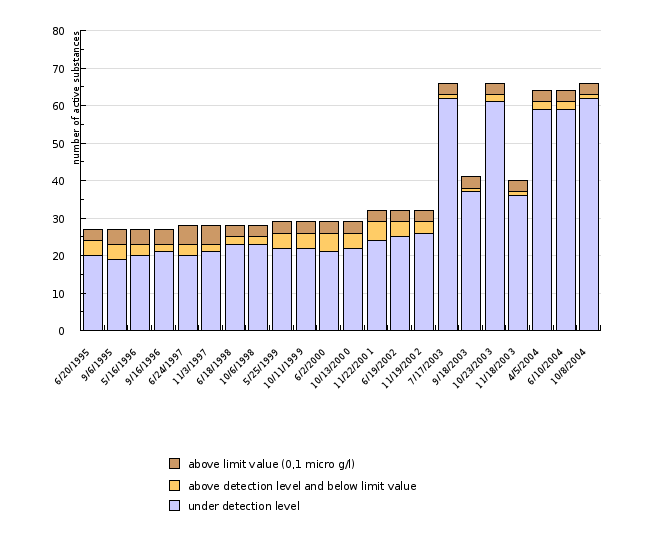
| 6/20/1995 | 9/6/1995 | 5/16/1996 | 9/16/1996 | 6/24/1997 | 11/3/1997 | 6/18/1998 | 10/6/1998 | 5/25/1999 | 10/11/1999 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| under detection level | number | 20 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 20 | 21 | 23 | 23 | 22 | 22 |
| above detection level and below limit value | number | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| above limit value (0,1 micro g/l) | number | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| all active substances | number | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 29 | 29 |
| 6/2/2000 | 10/13/2000 | 11/22/2001 | 6/19/2002 | 11/19/2002 | 7/17/2003 | 9/18/2003 | 10/23/2003 | 11/18/2003 | 4/5/2004 | ||
| under detection level | number | 21 | 22 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 62 | 37 | 61 | 36 | 59 |
| above detection level and below limit value | number | 5 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| above limit value (0,1 micro g/l) | number | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| all active substances | number | 29 | 29 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 66 | 41 | 66 | 40 | 64 |
| 6/10/2004 | 10/8/2004 | ||||||||||
| under detection level | number | 59 | 62 | ||||||||
| above detection level and below limit value | number | 2 | 1 | ||||||||
| above limit value (0,1 micro g/l) | number | 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| all active substances | number | 64 | 66 |
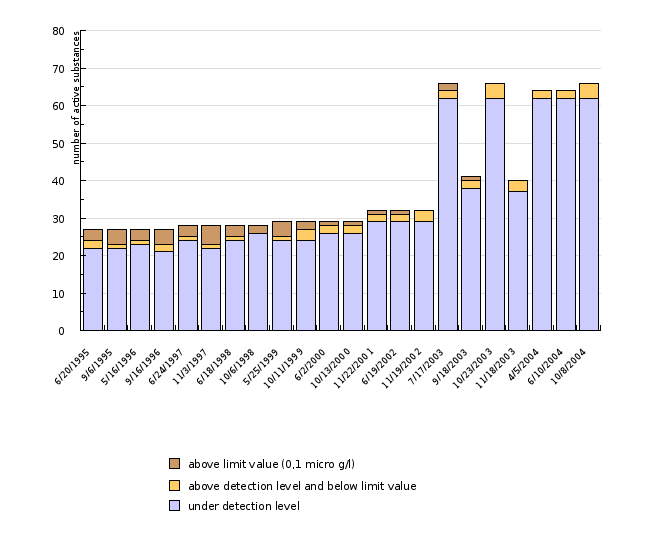
Standardised Database for Water Quality Monitoring, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2005.
| 6/20/1995 | 9/6/1995 | 5/16/1996 | 9/16/1996 | 6/24/1997 | 11/3/1997 | 6/18/1998 | 10/6/1998 | 5/25/1999 | 10/11/1999 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| under detection level | number | 22 | 22 | 23 | 21 | 24 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 24 | 24 |
| above detection level and below limit value | number | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| above limit value (0,1 micro g/l) | number | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| all active substances | number | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 29 | 29 |
| 6/2/2000 | 10/13/2000 | 11/22/2001 | 6/19/2002 | 11/19/2002 | 7/17/2003 | 9/18/2003 | 10/23/2003 | 11/18/2003 | 4/5/2004 | ||
| under detection level | number | 26 | 26 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 62 | 38 | 62 | 37 | 62 |
| above detection level and below limit value | number | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| above limit value (0,1 micro g/l) | number | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| all active substances | number | 29 | 29 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 66 | 41 | 66 | 40 | 64 |
| 6/10/2004 | 10/8/2004 | ||||||||||
| under detection level | number | 62 | 62 | ||||||||
| above detection level and below limit value | number | 2 | 4 | ||||||||
| above limit value (0,1 micro g/l) | number | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| all active substances | number | 64 | 66 |
Goals
The National Environment Action Plan anticipates the prevention of groundwater pollution with the residues of plant protection products. The legal framework to achieve this goal is provided by the Decree on the Quality of Underground Water (Official Gazette RS, No. 11/02), Decree on the Designation of the Status of Endangerment due to Phytophramaceuticals to Areas of Aquifers and their Drainage Basins and on the Integrated Rehabilitation Measures (Official Gazette RS, No. 97/02), Ordinance on the Areas of Aquifers and their Drainage Basins Endangered due to Phytopharmaceuticals (Official Gazette RS, No. 97/02), Rules on Drinking Water Quality (Official Gazette RS, No. 46/97, 54/98 in 7/00) and Drinking Water Directive (98/83/EC).
The implementation of the measures outlined in the Rural Development Plan for the Republic of Slovenia 2004-2006 plays an important role in decreasing the pollution of groundwater with the residues of plant protection products. The plan is implemented under the patronage of the Ministry for Agriculture, Forestry and Food in cooperation with the Agency of the Republic of Slovenia for Agricultural Markets and Rural Development. Its most important aspect are agri-environmental measures, implemented on more than 270,000 ha of agricultural land are of utmost importance.
Comment
In 2004, arithmetic mean values for the total residues of the plant protection products did not exceed the 0.5 µg/l threshold value in groundwater in any of the observed aquifers. Between 1993 and 2004, a decrease in the total residues of the above-mentioned products and their degradation products was noted in the aquifers along the Mura River (Prekmursko-Mursko polje) and along the Savinja River (Lower Savinjska dolina valley – the Bolska River valley). In the 1993-2004 period, total residue contents of plant protection products at Ljubljansko polje and Krško-Brežiško polje were within the permissible values. In karst-fractured aquifers, these contents were below the identifiable levels for analytical methods.
At sampling points, threshold values were most frequently exceeded for atrazine and its metabolite desethylatrazine. In Slovenia, the share of sampling points where the concentrations of threshold values exceeded the threshold values determined in the legislation is above the European average. In spite of that, the monitoring results indicate a clear decrease in the concentration of atrazine and desethylatrazine residues at the sampling points most polluted in the past, such as Rakičan, Lipovci and Gotovlje. It should be noted that in most parts of Slovenia, atrazine values are already below the threshold value of 0.1 µg/l, while desethylatrazine values still exceed it in some places. Atrazine has been out of use for the last four years, but it will take a few more years for its concentration in the lower levels of groundwater to fall below the 0.1 µg/l threshold value. The reason for the slow decrease of desethylatrazine is its slow degradation.
In spite of the increasing number of active substances included in regular monitoring (27 in 1995 and 66 in 2004), it is encouraging to know that the number of active substances exceeding the 0.1 µg/l threshold value is actually decreasing. Between 1995 and 2004, we observed a decrease in the total residues of the plant protection products and their degradation products at the considerably polluted Brunšvik sampling point, but in spite of that, in 2004 the total value was still above the 0.5 µg/l threshold value. Between 1995 and 2004, the total value of residues of these products and their degradation products was also on the decrease at the Sobetinci sampling point. In the last two years, it was considerably below the 0.5 µg/l threshold value, in spite of its high values in the past.
Methodology
Data for Slovenia
The quality of groundwater in Slovenia is monitored within the framework of the national monitoring of groundwater, springs and surface waters (Ministry of the Environment, Spatial Planning and Energy, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia). Pollution of shallow-water alluvial aquifers (populated and agricultural areas) and karst-fracture aquifers, where pollution is lower due to land-use, is monitored.
Groundwater bodies are selected according to the intermediate phase, i.e. phase II intended for the determination of such bodies. Representation of individual types of aquifers in the area of water supply was also taken into consideration, and constitutes 60% of population as regards alluvial aquifers and 40% of population as regards karst-fracture aquifers. For the purpose of representation of the indicator, the proposed groundwater bodies indicated here below were taken into consideration: Prekmursko-Mursko polje (10 sampling points, alluvial) and Bolska Valley and Lower Savinjska Valley (13 sampling points, alluvial), Ljubljansko polje (10 sampling points, alluvial), Krško-Brežiško polje (12 sampling points, alluvial), Trieste-Kvarner Gulf watershed (1 sampling point, karst), Karst Ljubljanica River (2 sampling points, karst) and Trnovsko-Banjška Plateau-Hrušica (4 sampling points, karst).
The following are sampling points for nitrates: drinking water pumping stations (33.3%), industrial wells (8.9%), common facilities for water quantity and quality monitoring (42.2%) and facilities for water quality monitoring (15.6%). 52 sampling points (wells, drilling wells, springs) were taken into consideration for the purposes of representation of this indicator. Samplings were conducted 2-6 times a year.
Data: Standardised Database for Water Quality Monitoring, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2005
Data for other countries
Standardised Database for Water Quality Monitoring, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2003
Pesticides in Groundwater, Indicator Fact Sheet, European Environment Agency, 2005