[NV03] Natura 2000

Key message

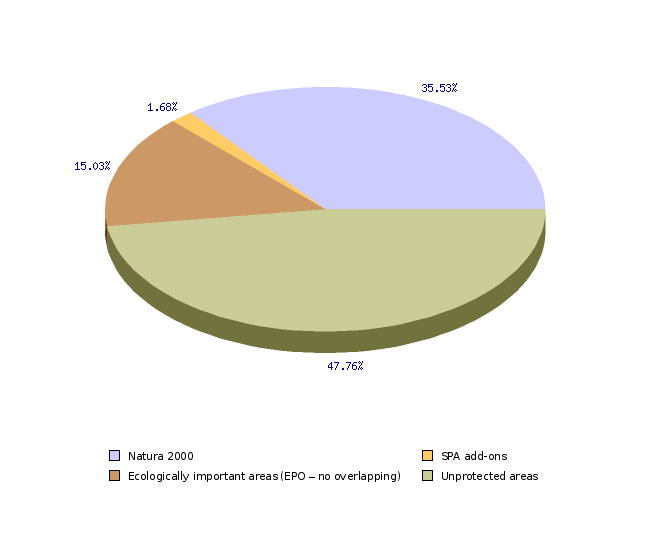
Natura 2000 sites were established in 2004 and occupy almost 7203 km2 or 35.5% of the Slovenian territory. Additional areas that according to the European Commission fulfil the conditions for Special Protection Areas, the so-called SPA add-ons, which occupy an additional 1.7% of the surface area, were designated in May 2008.
The Natura 2000 sites form a constituent part of ecologically important areas (EIA), that is areas of significant habitat types, parts thereof or larger ecosystem units, which significantly contribute to the preservation of biodiversity. Ecologically important areas occupy 52.2% of the Republic of Slovenia.
Definition
The indicator shows the Natura 2000 network and represents those areas which are most suitable for the preservation or achievement of a favourable state of species and habitats in the EU's and Slovenia's interests. Protection measures and measures for modified use of natural assets are foreseen in these areas.
The Natura 2000 areas (the EU's ecological network) have been designated by means of the Decree on special protection areas (Natura 2000 areas), OG of the RS, Nos. 49/04, 110/04, 59/07. Sites of Community Interest (SCI) have been defined on the basis of the Habitats Directive (Council Directive 92/43/EEC) and Special Protection Areas (SPA) have been designated on the basis of the Birds Directive (Council Directive 79/409/EEC). SPA and SCI areas partially overlap.
Charts
Register of Natura 2000 areas, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2008, Natura 2000 Barometer, European Topic Centre for Biodiversity, 2008.
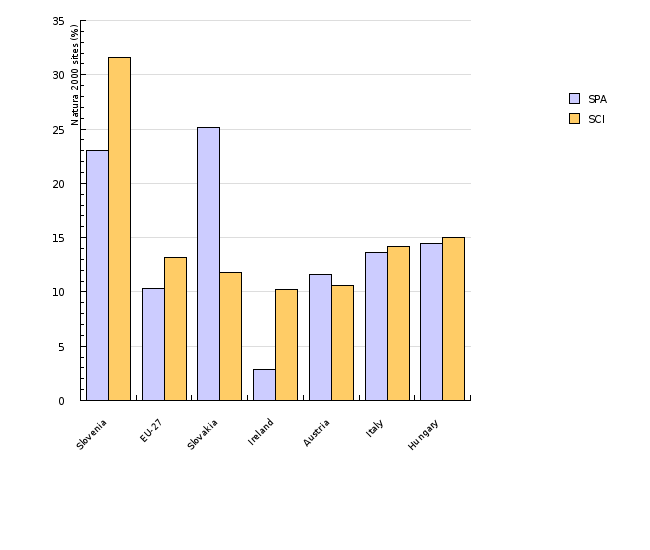
| Slovenia | EU-27 | Slovakia | Ireland | Austria | Italy | Hungary | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPA | % | 23 | 10 | 25 | 3 | 12 | 14 | 15 |
| SCI | % | 32 | 13 | 12 | 10 | 11 | 14 | 15 |
| SPA | km2 | 4618 | 442196 | 12236 | 2004 | 9744 | 41080 | 13519 |
| SCI | km2 | 6397 | 567623 | 5739 | 7175 | 8889 | 42830 | 13929 |
Register of Natura 2000 areas, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2008, Register of ecologically important areas, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2005.
| 2008 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Natura 2000 | % | 35.53 |
| SPA add-ons | % | 1.68 |
| Ecologically important areas (EPO – no overlapping) | % | 15.03 |
| Unprotected areas | % | 47.76 |
| - | ||
| Natura 2000 | ha | 720287.82 |
| SPA add-ons | ha | 33989.48 |
| Ecologically important areas (EPO – no overlapping) | ha | 304799.97 |
| Unprotected areas | ha | 968223.69 |
Goals
To prepare and adopt an operational program – action plan for preserving biodiversity by means of the Natura 2000 Site Management Programme (Resolution on National Environmental Action Plan, 2005) in order to establish a system for Natura 2000 site management.
In October 2007, the Government of the RS adopted an operational programme, the Natura 2000 Site Management Programme 2007 – 2013, containing certain protection measures which are essential for the preservation of a favourable state of animal and plant species as well as habitat types and are aimed at achieving protection goals.
Comment
Joining the EU has obliged Slovenia to designate and maintain Natura 2000 sites, which occupy slightly more than 7202 km2 or 35.5% of the Slovenian territory.
Suggested areas (Sites of Community Interest – SCI), which Slovenia has defined by means of a governmental decree on the basis of the Habitats Directive, will be adopted by the European Commission in accordance with a special procedure, which normally takes a few years. Negotiations with the European Commission commenced with two biogeographical seminars, namely a biogeographical seminar for the Alpine region, held in May 2005, and a biogeographical seminar for the continental region, held in April 2006. On the basis of the conclusions of both seminars Slovenia will be bound to designate further areas according to the Habitats Directive for those habitat types or species which the European Commission has determined as insufficiently designated. Potential Sites of Community Interest (pSCI) were renamed to Sites of Community Interest (SCI) after European Commission confirmed and officially published lists of sites for Continental (15.1.2008) and Alpine (19.3.2008) biogeographical region.
Based on the Birds Directive, the decree also designates Special Protection Areas (SPA) which are significant for preserving or achieving a favourable state of bird species. After reviewing the harmonization the European Commission found that Slovenia had not designated a sufficient number of areas, both in terms of number and extent. Therefore additional areas which according to the European Commission fulfil the conditions for Special Protection Areas, the so-called SPA add-ons, were designated by means of an amendment to the decree in May 2008. The aim of the decree is to prevent the deterioration of the state of bird species and their habitats until all Natura sites have been ultimately regulated and confirmed.
About 70% of the Slovenian Natura 2000 network is covered by forests, which suggests their generally good state of preservation. Lowland swamp forests were heavily deforested in the past, are not in a favourable state of preservation and are additionally protected through the network. Out of all non-forest areas, the Natura 2000 network comprises ca. 20% of agricultural land, the most important thereof being extensive meadows. In several areas, the meadows are still in a favourable state of preservation, though pressures decreasing the favourable state are great and include both natural overgrowth due to the discontinuation of farming as well as intensified use of meadows.
The Natura 2000 network also specifically protects caves (in 70 areas of altogether 260). Surface continental waters represent only slightly over one percent of the network, yet they are of great importance for the preservation of the network. Several waters are nevertheless not in the most favourable state of preservation. Human dwellings are of significance for reproduction, resting or wintering of certain species, making certain built-up areas vital in the Natura 2000 network. The species in question are mainly animals from bird groups (for example the white stork, the European scops owl) and mammals (such as bats).
Ecologically important areas were designated by the Decree on ecologically important areas in 2004. These are areas of significant habitat types, parts thereof or larger ecosystem units which greatly contribute to the preservation of biodiversity. Certain protection guidelines and rules must be taken into consideration in spatial planning and use of natural assets. However, building objects in ecologically important areas which are not simultaneously a Natura 2000 site, a protected area or an area of high nature value does not require natural protection consents or conditions to be given or imposed.
Among ecologically important areas are the main habitat of big game,the sea and the sea coast. Natura 2000 areas are an element of ecologically important areas.
Methodology
Data for Slovenia:
Register of Natura 2000 areas, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2008 (as of June 30th, 2008)
Register of ecologically important areas, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2005
Data on Natura 2000 areas are managed in the database Register of Natura 2000 areas in the framework of registers of areas which are significant for maintaining biodiversity. The data are maintained by the Nature Conservation Sector of the Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia on the basis of Article 34 of the Nature Conservation Act (NCA-OCT1, OG of the RS, No. 96/04) and Article 5 of the Decree on special protection areas (Natura 2000 areas) (OG of the RS, Nos. 49/04, 110/04, 59/07 and 43/08). As part of these records the Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia also maintains the register of ecologically important areas on the basis of Article 4 of the Decree on ecologically important areas (OG of the RS, No. 48/04).
Data for other countries:
Natura 2000 Barometer, European Topic Centre for Biodiversity