[EN21] Energy taxes

Key message

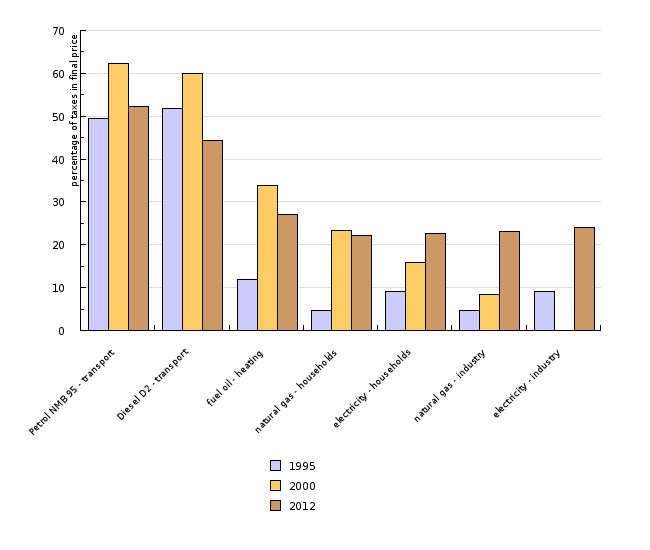
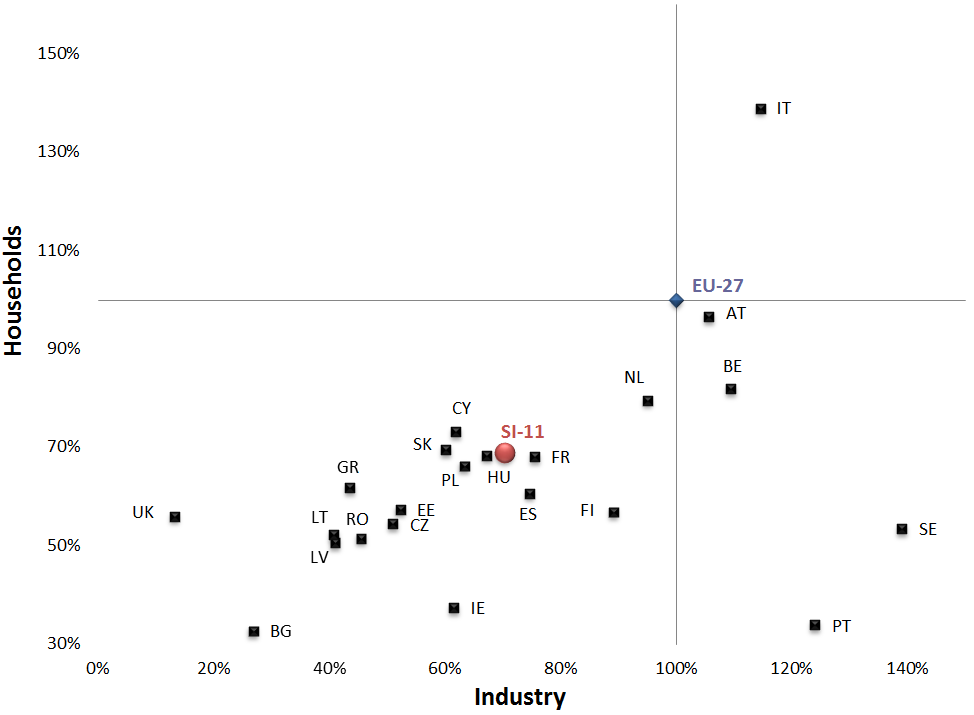
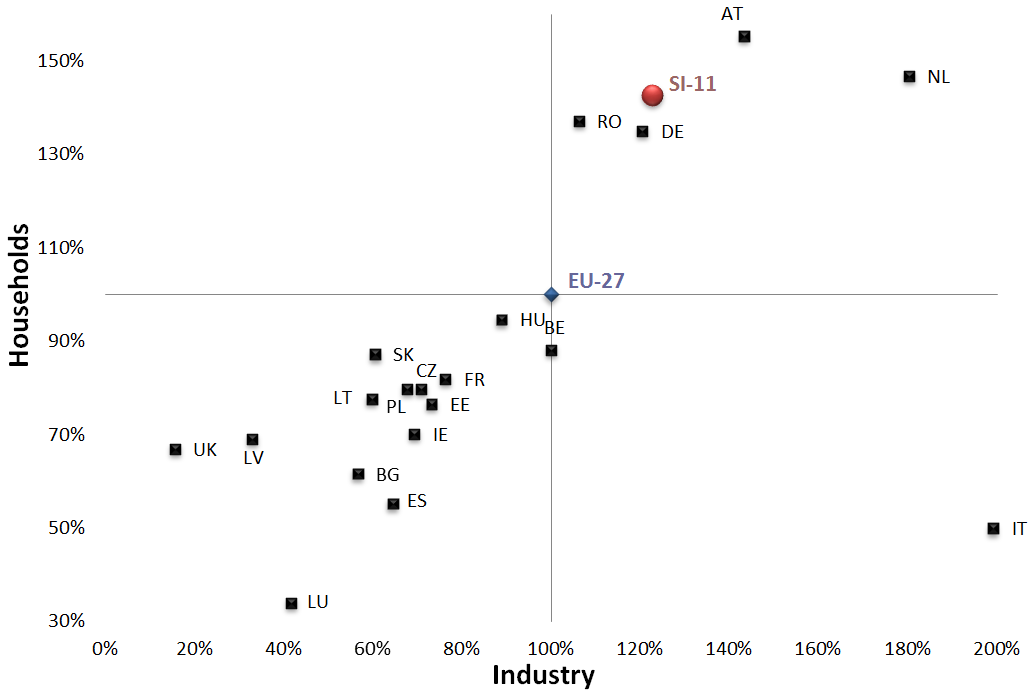
In recent years, energy taxes have increased mainly due to higher excise duties and taxes. The share of tax in the price of energy in industry has reached the same level as in the price paid by households. In Slovenia, taxes on transport fuels and electricity were below the EU-27 average, while taxes on natural gas in industry and households were above that average, exceeded only by Austria, Italy, Denmark and Sweden.
Definition
The indicator Energy tax shows the level of taxation of individual energy products. Electricity tax is indicated in EUR per kilowatt hour (EUR/kWh), natural gas tax in EUR per gigajoul (EUR/GJ), and liquid fuel tax in EUR per litre of fuel (EUR/l).
Electricity and natural gas taxes show the level of taxation for typical consumer groups for industrial and household consumers; however, the tax for industrial consumers does not consider the value-added tax (VAT).
Charts
Statistical Office of the RS, 2012.
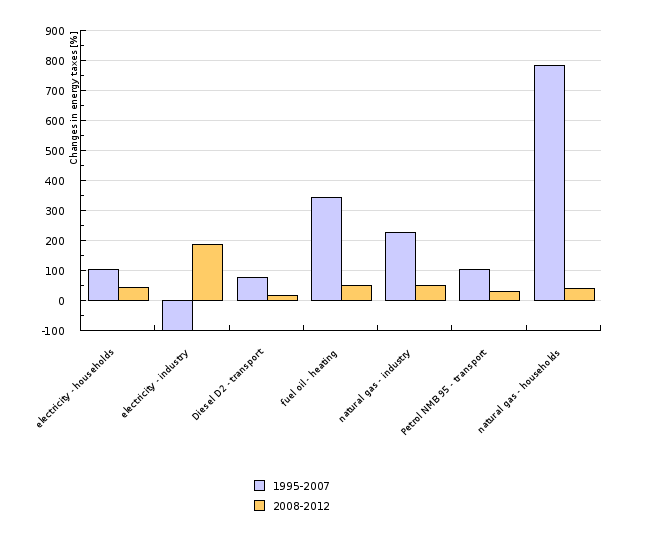
| electricity - households | electricity - industry | Diesel D2 - transport | fuel oil - heating | natural gas - industry | Petrol NMB 95 - transport | natural gas - households | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995-2007 | % | 104.1 | -100 | 76.9 | 343.3 | 225.7 | 103 | 784 |
| 2008-2012 | % | 42.8 | 185.9 | 17.2 | 49 | 51.7 | 30 | 41.2 |
Statistical Office of the RS, 2012.
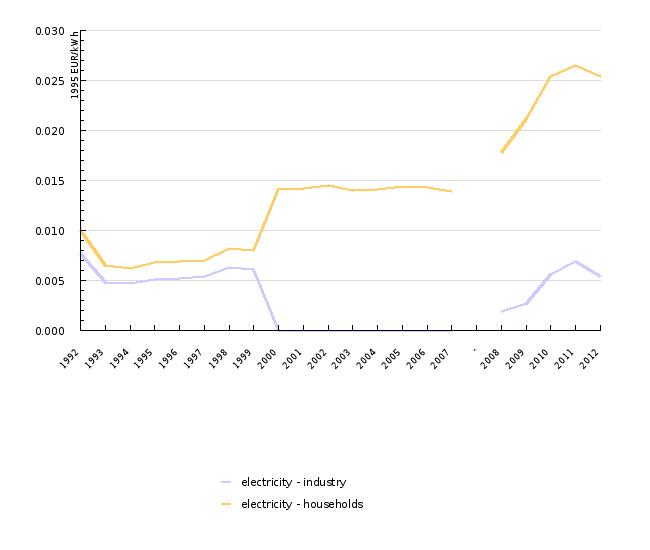
| 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| electricity - industry | EUR/kWh | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0 | 0 |
| electricity - households | EUR/kWh | 0.01 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.014 | 0.014 |
| 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | - | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | ||
| electricity - industry | EUR/kWh | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.006 | |
| electricity - households | EUR/kWh | 0.015 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.018 | 0.021 | 0.025 | |
| 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| electricity - industry | EUR/kWh | 0.007 | 0.005 | ||||||||
| electricity - households | EUR/kWh | 0.026 | 0.025 |
Statistical Office of the RS, 2012.
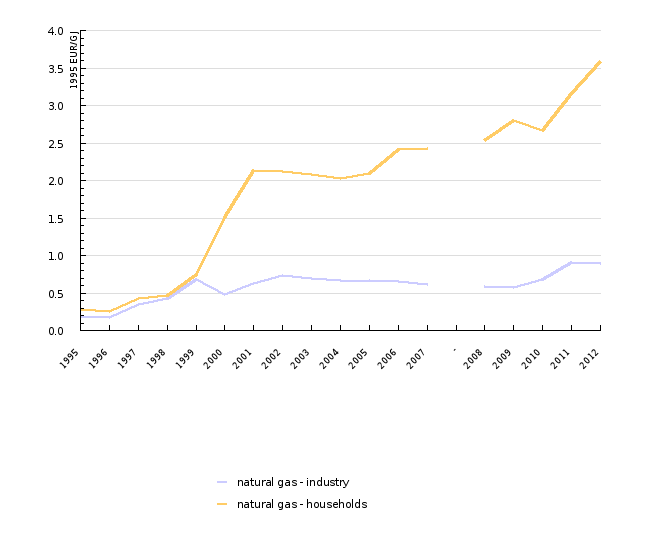
| 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| natural gas - industry | EUR/GJ | 0.189 | 0.17 | 0.352 | 0.425 | 0.68 | 0.474 | 0.627 | 0.733 | 0.694 | 0.671 |
| natural gas - households | EUR/GJ | 0.274 | 0.253 | 0.433 | 0.466 | 0.746 | 1.513 | 2.131 | 2.121 | 2.082 | 2.02 |
| 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | - | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | |||
| natural gas - industry | EUR/GJ | 0.661 | 0.647 | 0.617 | 0.593 | 0.575 | 0.679 | 0.905 | 0.899 | ||
| natural gas - households | EUR/GJ | 2.096 | 2.414 | 2.425 | 2.537 | 2.8 | 2.67 | 3.166 | 3.582 |
Statistical Office of the RS, 2012.
| 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel D2 - transport | EUR/l | 0.209 | 0.209 | 0.205 | 0.239 | 0.333 | 0.349 | 0.35 | 0.338 | 0.321 | 0.358 |
| Petrol NMB 95 - transport | EUR/l | 0.215 | 0.218 | 0.209 | 0.26 | 0.344 | 0.337 | 0.394 | 0.455 | 0.432 | 0.441 |
| Fuel oil - heating | EUR/l | 0.025 | 0.037 | 0.033 | 0.05 | 0.097 | 0.109 | 0.126 | 0.112 | 0.106 | 0.122 |
| 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | - | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | |||
| Diesel D2 - transport | EUR/l | 0.398 | 0.371 | 0.37 | 0.359 | 0.408 | 0.454 | 0.458 | 0.421 | ||
| Petrol NMB 95 - transport | EUR/l | 0.453 | 0.418 | 0.436 | 0.403 | 0.446 | 0.504 | 0.505 | 0.524 | ||
| Fuel oil - heating | EUR/l | 0.147 | 0.123 | 0.111 | 0.131 | 0.134 | 0.15 | 0.175 | 0.194 |
Statistical Office of the RS, 2012.
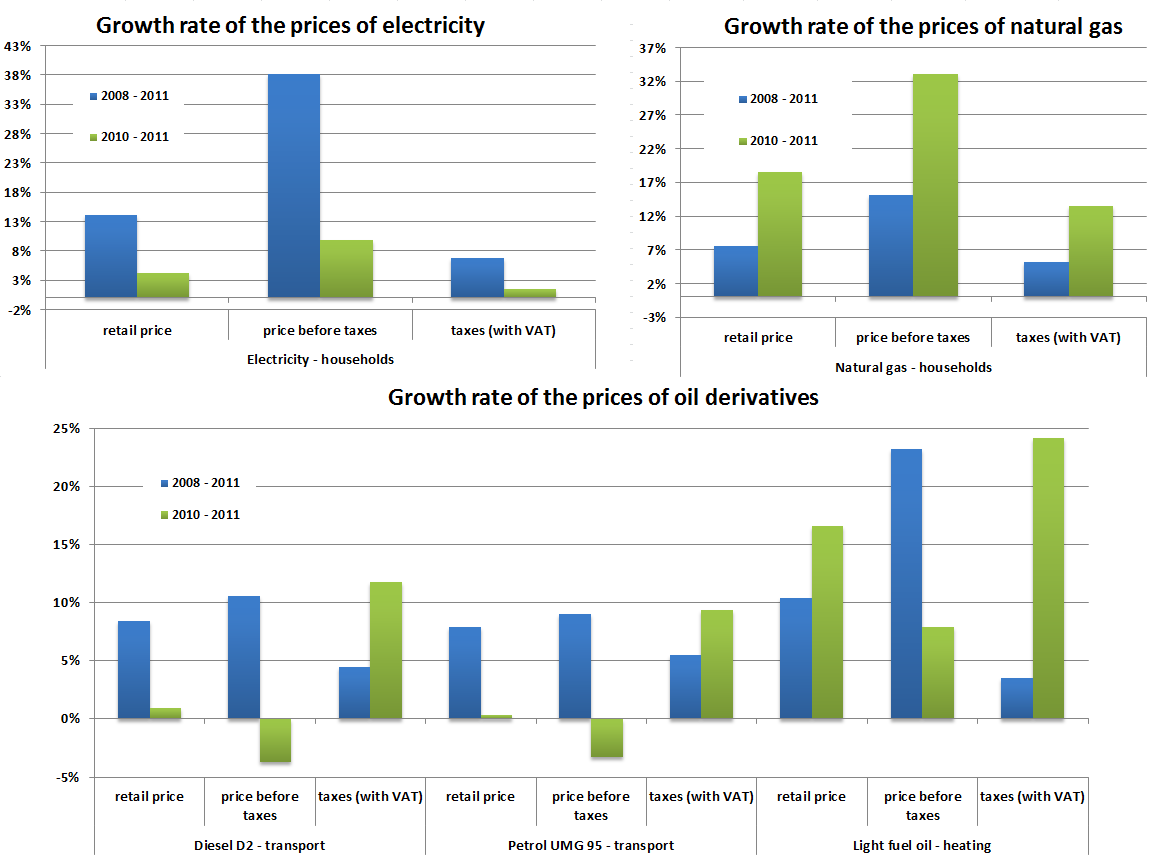
| 1995-2000 | 2000 - 2007 | 2008-2012 | 2011 - 2012 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electricity: households - retail price | % | 15.9 | -0.4 | 9.3 | -4.2 |
| Electricity: households - price before taxes | % | -100 | -0.4 | 18.5 | -25.1 |
| Electricity: households - taxes (with VAT) | % | 6.8 | 6.4 | ||
| Natural gas: households: retail price | % | 40.7 | 19.9 | 9 | 13.1 |
| Natural gas: households: price before taxes | % | 11.8 | 7 | 11 | -0.6 |
| Natural gas: households: taxes (with VAT) | % | 8.4 | 18.7 | ||
| Diesel D2: transport - retail price | % | 10.8 | 4.9 | 4 | -8 |
| Diesel D2: transport - price before taxes | % | 3.7 | -14.4 | ||
| Diesel D2: transport - taxes (with VAT) | % | -15 | -4.7 | 4.5 | 4.8 |
| Petrol NMB 95: transport - retail price | % | 9.4 | 6.1 | 6.8 | 3.6 |
| Petrol NMB 95: transport - price before taxes | % | 7.2 | 2 | ||
| Petrol NMB 95: transport - taxes (with VAT) | % | -16.7 | -4.5 | 5.9 | 7.2 |
| Fuel oil EL - retail price | % | 15.5 | 13.2 | 10.5 | 10.9 |
| Fuel oil EL - price before taxes | % | 16.8 | -0.6 | ||
| Fuel oil EL - taxes (with VAT) | % | 15.5 | 8.8 | 7.3 | 19.5 |
Statistical Office of the RS, 2012.
| Petrol NMB 95 - transport | Diesel D2 - transport | fuel oil - heating | natural gas - households | electricity - households | natural gas - industry | electricity - industry | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | % | 49.5 | 51.8 | 11.9 | 4.8 | 9.1 | 4.8 | 9.1 |
| 2000 | % | 62.4 | 60.1 | 33.8 | 23.3 | 16 | 8.3 | 0 |
| 2012 | % | 52.2 | 44.4 | 27.1 | 22.2 | 22.6 | 23.1 | 24.1 |
Eurostat, 2012.
| EU-27 | BE | BG | CZ | DK | DE | EE | IE | GR | ES | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| industry | % | 100 | 84 | 67.15 | 73.297 | 478.417 | 120.667 | 81 | 61.333 | 0 | 60.333 |
| households | % | 100 | 98.992 | 57.569 | 76.866 | 395.096 | 112.846 | 74.559 | 70.529 | 0 | 70.529 |
| FR | CY | LV | LT | LU | HU | MT | NL | AT | PL | ||
| industry | % | 76.333 | 86.4 | 87.37 | 0 | 128.12 | 136 | 133.333 | 71.75 | ||
| households | % | 73.804 | 76.474 | 61.937 | 0 | 77.647 | 203.778 | 137.28 | 61.338 | ||
| PT | RO | SI-11 | SK | FI | SE | UK | IT | ||||
| industry | % | 86.333 | 124.41 | 148.333 | 85.333 | 449.657 | 72.973 | 86.333 | |||
| households | % | 105.29 | 90.055 | 124.181 | 60.202 | 373.335 | 17.156 | 180.605 |
Eurostat, 2012.
| EU-27 | BE | BG | CZ | DK | DE | EE | IE | GR | ES | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| industry | % | 100 | 75.822 | 32.16 | 48.122 | 366.432 | 178.404 | 66.432 | 33.803 | 70.892 | 54.46 |
| households | % | 100 | 133.757 | 25.408 | 47.55 | 305.445 | 209.437 | 58.984 | 55.354 | 59.165 | 76.951 |
| FR | CY | LV | LT | LU | HU | MT | NL | AT | PL | ||
| industry | % | 59.155 | 95.305 | 50.939 | 53.756 | 14.085 | 68.779 | 18.779 | 67.606 | 87.793 | 54.93 |
| households | % | 73.684 | 80.399 | 43.376 | 39.564 | 41.379 | 66.788 | 15.426 | 98.185 | 98.367 | 56.624 |
| PT | RO | SI-12 | SK | FI | SE | UK | IT | ||||
| industry | % | 71.596 | 44.836 | 57.042 | 67.371 | 55.399 | 43.192 | 58.451 | 158.216 | ||
| households | % | 161.162 | 46.279 | 63.339 | 57.35 | 83.485 | 129.764 | 14.338 | 124.682 |
Eurostat, 2012; Oil Buletin, 2012.
| AT | BE | BG | CY | CZ | DE | DK | EE | ES | FI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMB | % | 96.566 | 113.396 | 72.109 | 67.433 | 93.021 | 116.495 | 117.333 | 81.656 | 83.542 | 117.77 |
| D2 | % | 101.557 | 103.088 | 80.732 | 77.903 | 100.146 | 107.949 | 106.751 | 94.475 | 84.438 | 114.533 |
| FR | GR | HU | IE | IT | LT | LU | LV | MT | NL | ||
| NMB | % | 110.432 | 127.548 | 85.741 | 109.55 | 127.769 | 85.284 | 81.541 | 86.464 | 87.611 | 128.815 |
| D2 | % | 101.563 | 108.175 | 99.71 | 114.794 | 134.453 | 80.717 | 74.76 | 90.446 | 89.454 | 101.132 |
| PL | PT | RO | SE | SI-12 | SK | UK | EU-27 | ||||
| NMB | % | 76.982 | 112.862 | 75.983 | 123.823 | 91.947 | 103.958 | 124.371 | 100 | ||
| D2 | % | 84.879 | 97.127 | 85.05 | 130.177 | 87.964 | 97.341 | 150.686 | 100 |
Goals
Specific objectives with regard to the taxation of energy products are set by the energy policy at the EU level together with the Directive (2003/96/EC) on the taxation of fuels and electricity. The Directive stipulates minimum levels of taxation of individual energy products, which are mandatory for all Member States. The main purpose of the Directive is to establish better competitiveness between energy products and eliminate the price disparities between Member States, which happened due to differences in the levels of taxation.
The Resolution on the National Energy Programme also indicates a »green tax reform«; however, the state is still waiting for its implementation.
Methodology
Data for Slovenia and other countries
Objectives summarised by: Resolucija o Nacionalnem energetskem programu (ReNEP)(Resolution on the National Energy Programme, Official Gazette of the RS, No. 57/04) in Directive (2003/96/EC) on the taxation of fuels and electricity.
Source database or source: The data on prices of energy products (prices before taxes, prices without VAT and prices with all taxes) are published by SORS on the SI-STAT Data Portal > Environment and natural resources > Energy > Prices of energy sources for all consumer groups.
Data administrator: Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia (Mojca Suvorov) and Eurostat.
Data acquisition date for the indicator: 5 December 2009.
Methodology and frequency of data collection for the indicator: The data for energy prices are published twice a year; namely, the prices in force on 1 January are published by SORS in the second week of March, and the prices of 1 July of the current year by SORS in the second week of September.
SORS has been collecting data since 1992 for electricity and since 1995 for natural gas. The prices of oil derivatives have been available since 1999; the data on prices and taxes before that year are available at Petrol.
The most representative consumer groups for industrial consumers of natural gas and electricity are I3 for consumers of natural gas and Id for consumers of electricity. For household consumers, the most representative consumer groups are D2 for consumers of natural gas and Dc for consumers of electricity.
Data processing methodology: The energy prices published by SORS are current prices. Since these are nominal categories, changes in prices do not reflect real changes. Real changes in prices and taxes are reflected only by real prices and taxes, which are calculated by the deflation of nominal prices with the GDP deflator, which is published by SORS for every previous year. The energy tax that is indicated in the data sheet is the real tax; deflators that converted nominal tax to the level of real tax of 1995 were used for the calculation. The real tax of 1995 was converted into EUR 1995 with the use of the average annual exchange rate of the Bank of Slovenia in 1995. Such a calculation enables better comparability of energy taxes in Slovenia with average taxes in the EU.
Real energy taxes are calculated as:
TRt = [(Rt*1/D1995,t)/er1995]
PR-real prices, P – current prices, D – deflator, er – exchange rate.
Geographical coverage: The EA-15 (Euro Area) is composed of: Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, and Slovenia. EA-16 = (From 1 January 2009 EA-15 + Slovakia). The EU-15 includes old EU Member States (Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, the United Kingdom). The EU-10 includes Member States that joined the EU in 2004 (Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Lithuania, Latvia, Malta, Poland, Slovenia, Slovakia). The EU-12 includes, besides the EU-10, Bulgaria and Romania. The EU-27 includes the EU-15 and EU-12, while the EU-25 includes the EU-15 and EU-10.
Information concerning data quality:
- Advantages and disadvantages: The source of basic data for the entire time series for electricity and natural gas is SORS, which enables a more efficient and consistent analysis of individual sectors; only for fuel tax before 1999, it was necessary to obtain data from the largest fuel dealer in Slovenia (Petrol).
- Relevance, accuracy, robustness, uncertainty:
Reliability of the indicator (archive data): The data reflect the prices by individual consumer groups that were in force on the first day of January and July.
Uncertainty of the indicator (scenarios/projections): Scenarios and projections are not available.
- Overall assessment (1 = no major comments, 3 = data to be considered with reservation):
Relevance: 1
Accuracy: 2
Completeness over time: 1
Completeness over space: 1
Other sources and literature:
- Directive 2003/96/EC of restructuring the Community framework for the taxation of energy products and electricity.
- Ministry of the Economy, 2007. Letni energetski pregled za leto 2005 (Annual energy review for 2005).