[KM33] Coverage of food imports by food exports

Key message

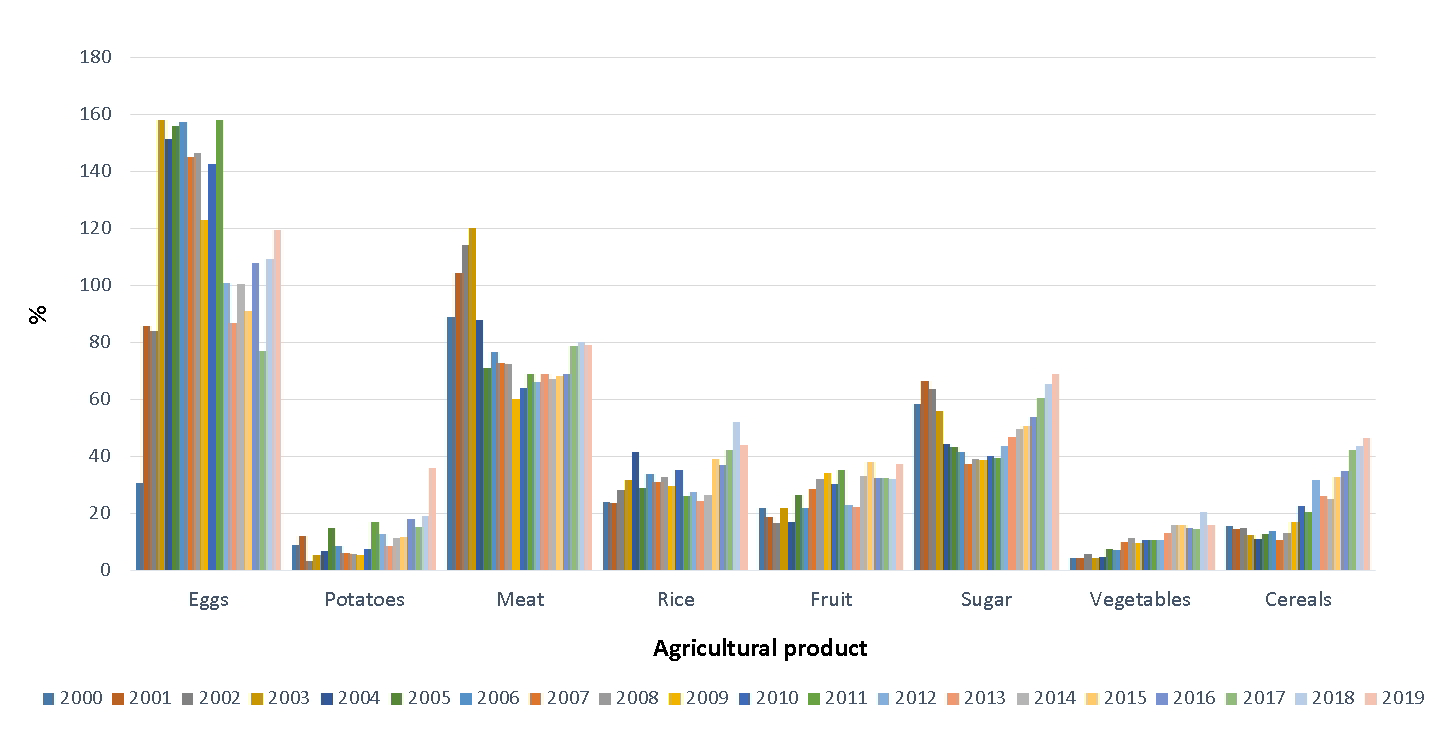
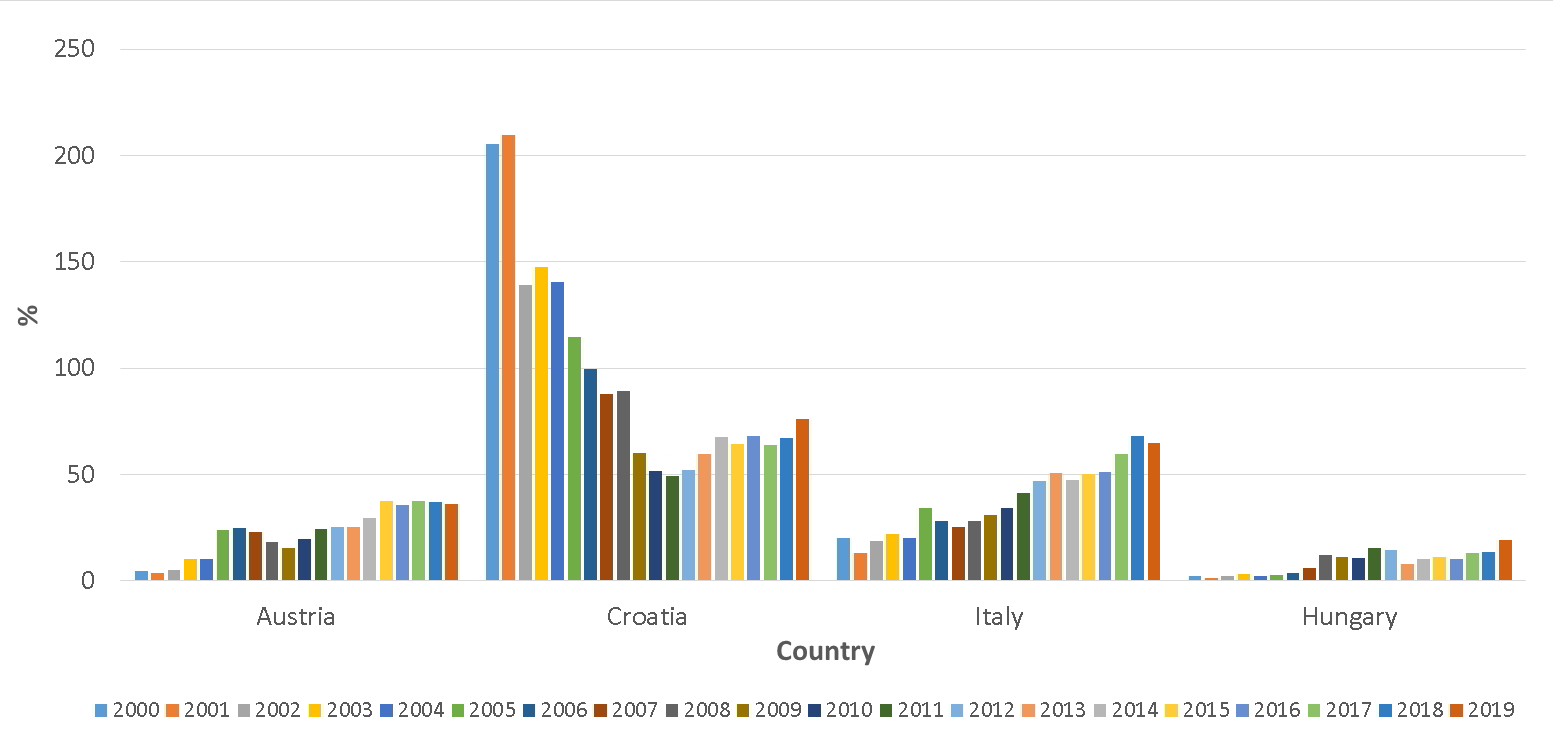
Slovenia is a net importer of food, as the value of food imports exceeds the value of exports. In recent years, food exports cover about 50% of imports. In the long run, the coverage of food imports by exports increases slightly. After Slovenia's accession to the EU, the value of food imports and exports increased significantly. Exports in value terms increased mainly at the expense of unprocessed agricultural products, while imports increased at the expense of processed products. Majority, i.e. more than half of the total value of food imports and exports in the recent years (2014–2019), is accounted for by the neighbouring countries (Austria, Croatia, Italy and Hungary). The highest index of coverage of food imports by exports is recorded for sugar, meat and eggs, and the lowest for vegetables, potatoes and fruit.
Definition
The indicator shows the coverage of food imports by exports. The indicator defines food as a set of the following agricultural products: cereals, meat, eggs, potatoes, vegetables, fruit, sugar and rice. The trade balance shows the flows of goods, in our case agricultural products or products derived from them, imported to or exported from Slovenia. Certain agricultural products are not produced in Slovenia (e.g. rice and sugar), but they can be added to products that are later exported, so they are included in the food balances. The trade balance is considered favourable when the value of food exports exceeds the value of imports, and unfavourable when the value of food imports exceeds the value of exports.
The indicator shows the coverage of food imports by exports (%), the coverage of imports of individual agricultural products by exports, the coverage of food imports by exports with neighbouring countries and a comparison of the share of coverage among EU–28 members.
Charts
SURS, calculations KIS
Data 08.09.2020
| Coverage of food imports by food exports [%] | |
|---|---|
| 2000 | 40.91 |
| 2001 | 44.27 |
| 2002 | 44.07 |
| 2003 | 41.30 |
| 2004 | 34.34 |
| 2005 | 36.30 |
| 2006 | 35.91 |
| 2007 | 33.51 |
| 2008 | 36.25 |
| 2009 | 35.45 |
| 2010 | 37.08 |
| 2011 | 38.16 |
| 2012 | 39.58 |
| 2013 | 39.80 |
| 2014 | 42.55 |
| 2015 | 45.34 |
| 2016 | 46.22 |
| 2017 | 50.93 |
| 2018 | 54.08 |
| 2019 | 56.04 |
SURS, calculations KIS
Data: 08.09.2020
| Eggs [%] | Potatoes [%] | Meat [%] | Rice [%] | Fruit [%] | Sugar [%] | Vegetables [%] | Cereals [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 30.82 | 8.97 | 88.97 | 24.22 | 21.98 | 58.31 | 4.50 | 15.60 |
| 2001 | 85.64 | 12.06 | 104.25 | 23.55 | 18.80 | 66.62 | 4.25 | 14.59 |
| 2002 | 83.87 | 3.33 | 114.10 | 28.09 | 16.65 | 63.57 | 5.67 | 15.05 |
| 2003 | 158.05 | 5.37 | 119.99 | 31.82 | 22.12 | 55.90 | 4.26 | 12.32 |
| 2004 | 151.28 | 6.94 | 87.77 | 41.58 | 16.91 | 44.31 | 4.65 | 11.08 |
| 2005 | 155.80 | 14.99 | 70.90 | 29.01 | 26.52 | 43.23 | 7.58 | 12.72 |
| 2006 | 157.24 | 8.46 | 76.57 | 33.87 | 21.92 | 41.60 | 7.05 | 13.76 |
| 2007 | 144.89 | 6.25 | 72.87 | 30.97 | 28.64 | 37.47 | 10.00 | 10.60 |
| 2008 | 146.48 | 5.80 | 72.47 | 32.99 | 32.25 | 39.13 | 11.50 | 13.26 |
| 2009 | 122.83 | 5.41 | 60.16 | 29.57 | 34.39 | 38.60 | 9.60 | 17.07 |
| 2010 | 142.66 | 7.54 | 64.04 | 35.16 | 30.33 | 40.10 | 10.78 | 22.50 |
| 2011 | 157.92 | 17.04 | 68.76 | 26.00 | 35.44 | 39.42 | 10.79 | 20.67 |
| 2012 | 100.94 | 12.95 | 66.03 | 27.52 | 23.00 | 43.62 | 10.86 | 31.82 |
| 2013 | 86.83 | 8.73 | 68.87 | 24.28 | 22.26 | 46.80 | 13.05 | 26.31 |
| 2014 | 100.63 | 11.40 | 67.01 | 26.45 | 33.10 | 49.59 | 15.98 | 25.26 |
| 2015 | 91.11 | 11.89 | 68.15 | 39.25 | 37.91 | 50.58 | 15.81 | 32.87 |
| 2016 | 107.85 | 17.98 | 68.81 | 36.99 | 32.52 | 54.01 | 15.10 | 34.85 |
| 2017 | 76.82 | 15.30 | 78.62 | 42.12 | 32.49 | 60.50 | 14.68 | 42.18 |
| 2018 | 109.15 | 18.98 | 79.99 | 51.96 | 32.00 | 65.58 | 20.63 | 43.55 |
| 2019 | 119.30 | 36.10 | 79 | 44 | 37.28 | 69 | 16 | 46.41 |
SURS, calculations KIS
Data: 08.09.2020
| Austria [%] | Croatia [%] | Italy [%] | Hungary [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 4.62 | 205.24 | 20.27 | 2.31 |
| 2001 | 3.61 | 209.59 | 13.16 | 1.29 |
| 2002 | 5.12 | 139.30 | 18.59 | 2.27 |
| 2003 | 10.10 | 147.67 | 21.94 | 3.11 |
| 2004 | 10.55 | 140.33 | 20.20 | 2.49 |
| 2005 | 23.90 | 114.65 | 34.31 | 2.58 |
| 2006 | 25.01 | 99.65 | 28.12 | 3.90 |
| 2007 | 23.07 | 87.67 | 25.30 | 6.00 |
| 2008 | 18.32 | 89.39 | 28.05 | 12.10 |
| 2009 | 15.47 | 60.29 | 30.82 | 11.11 |
| 2010 | 19.75 | 51.56 | 34.36 | 10.85 |
| 2011 | 24.32 | 49.36 | 41.43 | 15.50 |
| 2012 | 25.37 | 52.26 | 47.16 | 14.68 |
| 2013 | 25.45 | 59.80 | 50.66 | 8.03 |
| 2014 | 29.53 | 67.51 | 47.37 | 10.42 |
| 2015 | 37.58 | 64.42 | 50.17 | 11.19 |
| 2016 | 35.50 | 68.32 | 51.38 | 10.30 |
| 2017 | 37.38 | 63.84 | 59.80 | 13.29 |
| 2018 | 36.89 | 67.39 | 68.02 | 13.75 |
| 2019 | 36 | 76 | 65 | 19.08 |
EUROSTAT
Data: 12.10.2020
| Hungary [%] | Netherlands [%] | Denmark [%] | Ireland [%] | Bulgaria [%] | Poland [%] | France [%] | Spain [%] | Lithuania [%] | Belgium [%] | Austria [%] | Italy [%] | Germany [%] | Czechia [%] | Latvia [%] | Estonia [%] | Greece [%] | Slovakia [%] | Romania [%] | Croatia [%] | Slovenia [%] | Sweden [%] | Portugal [%] | Luxembourg [%] | United Kingdom [%] | Finland [%] | Malta [%] | Cyprus [%] | EU-28 [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 221.88 | 175.90 | 189.13 | 197.24 | 140.85 | 83.63 | 133.22 | 111.81 | 77.93 | 112.50 | 77.95 | 72.72 | 67.46 | 73.63 | 26.98 | 51.65 | 68.46 | 51.97 | 36.22 | 59.30 | 50.98 | 48.25 | 37.29 | 47.31 | 55.26 | 40.63 | 22.54 | 27.77 | 97.95 |
| 2001 | 226.22 | 169.91 | 192.36 | 171.21 | 124.92 | 88.96 | 125.27 | 111.80 | 89.93 | 113.03 | 81.01 | 74.83 | 69.88 | 71.58 | 39.30 | 65.59 | 72.63 | 52.69 | 35.84 | 55.40 | 51.67 | 49.55 | 35.80 | 50.24 | 49.75 | 43.31 | 22.34 | 28.73 | 96.54 |
| 2002 | 205.83 | 175.36 | 183.21 | 165.79 | 148.75 | 91.14 | 128.50 | 112.72 | 87.57 | 109.56 | 83.10 | 76.70 | 70.97 | 65.21 | 42.86 | 61.35 | 61.53 | 56.43 | 36.98 | 55.84 | 53.68 | 49.01 | 39.56 | 50.79 | 49.60 | 42.66 | 35.00 | 29.41 | 97.07 |
| 2003 | 191.79 | 171.86 | 178.07 | 170.95 | 131.19 | 112.55 | 128.09 | 114.91 | 98.90 | 110.35 | 89.65 | 73.53 | 71.72 | 63.27 | 41.09 | 57.25 | 60.53 | 62.85 | 32.43 | 61.10 | 52.17 | 50.57 | 40.34 | 48.52 | 49.49 | 39.56 | 28.97 | 31.43 | 96.95 |
| 2004 | 154.49 | 173.58 | 172.21 | 172.20 | 130.85 | 119.00 | 125.64 | 108.65 | 100.06 | 111.48 | 91.11 | 71.86 | 74.75 | 65.23 | 45.83 | 59.37 | 53.13 | 66.60 | 34.27 | 50.54 | 41.35 | 51.73 | 40.98 | 43.77 | 46.01 | 38.67 | 32.57 | 33.95 | 95.67 |
| 2005 | 136.67 | 175.02 | 168.57 | 161.29 | 141.99 | 130.46 | 127.19 | 103.10 | 113.91 | 113.03 | 96.28 | 73.63 | 77.56 | 75.92 | 62.38 | 65.20 | 63.68 | 69.16 | 33.30 | 57.80 | 46.26 | 52.97 | 44.54 | 46.61 | 43.79 | 37.20 | 33.41 | 31.31 | 96.27 |
| 2006 | 136.36 | 174.54 | 163.32 | 163.65 | 116.93 | 132.32 | 132.99 | 106.28 | 109.47 | 113.42 | 98.84 | 73.71 | 77.24 | 70.50 | 63.38 | 70.98 | 64.18 | 77.67 | 35.22 | 64.47 | 52.98 | 52.78 | 46.95 | 45.67 | 42.58 | 39.46 | 35.77 | 27.74 | 96.69 |
| 2007 | 152.06 | 168.15 | 156.82 | 151.55 | 91.51 | 125.05 | 125.41 | 102.37 | 120.55 | 110.91 | 94.20 | 75.84 | 79.31 | 74.94 | 70.07 | 68.86 | 58.40 | 73.04 | 33.62 | 60.98 | 54.35 | 51.85 | 48.58 | 44.83 | 42.86 | 41.90 | 36.33 | 26.43 | 95.21 |
| 2008 | 149.60 | 157.57 | 150.90 | 137.73 | 107.98 | 113.74 | 122.98 | 104.82 | 109.34 | 108.68 | 93.69 | 78.30 | 82.28 | 81.79 | 76.82 | 70.51 | 60.28 | 69.09 | 49.81 | 54.05 | 56.13 | 52.25 | 50.99 | 45.65 | 42.95 | 38.73 | 34.35 | 23.12 | 95.25 |
| 2009 | 150.60 | 161.71 | 156.93 | 130.47 | 115.08 | 123.68 | 114.13 | 109.46 | 120.08 | 111.51 | 89.55 | 77.89 | 82.34 | 76.08 | 78.76 | 72.51 | 62.75 | 68.50 | 58.65 | 60.60 | 53.75 | 52.00 | 52.47 | 46.05 | 43.52 | 33.44 | 18.16 | 22.37 | 95.38 |
| 2010 | 156.82 | 162.63 | 160.66 | 140.11 | 137.82 | 123.67 | 120.56 | 114.24 | 121.82 | 111.18 | 90.39 | 79.00 | 82.65 | 75.28 | 87.99 | 83.17 | 68.76 | 68.65 | 79.39 | 62.20 | 60.57 | 55.01 | 53.51 | 47.83 | 46.02 | 34.22 | 31.72 | 22.31 | 97.92 |
| 2011 | 161.00 | 151.58 | 156.51 | 142.69 | 146.78 | 120.56 | 126.73 | 114.45 | 120.49 | 107.40 | 91.40 | 78.01 | 82.01 | 76.81 | 86.89 | 81.63 | 69.86 | 77.64 | 90.43 | 60.58 | 58.28 | 52.98 | 55.03 | 50.24 | 48.45 | 37.39 | 29.39 | 25.11 | 97.93 |
| 2012 | 179.87 | 148.79 | 153.69 | 137.07 | 141.17 | 131.99 | 126.25 | 123.47 | 130.05 | 109.42 | 90.65 | 83.51 | 83.96 | 85.72 | 108.90 | 88.20 | 77.45 | 89.81 | 84.35 | 62.68 | 63.57 | 55.02 | 59.71 | 48.86 | 47.31 | 35.23 | 34.94 | 24.63 | 99.97 |
| 2013 | 177.98 | 151.47 | 152.33 | 137.38 | 166.75 | 142.75 | 123.54 | 130.97 | 126.33 | 109.48 | 91.43 | 85.44 | 86.17 | 87.00 | 101.21 | 84.26 | 78.82 | 81.59 | 106.80 | 56.06 | 61.68 | 56.40 | 61.74 | 47.93 | 46.32 | 33.59 | 38.26 | 31.22 | 101.67 |
| 2014 | 164.49 | 154.61 | 149.39 | 142.43 | 150.30 | 144.58 | 118.63 | 132.21 | 125.52 | 108.37 | 91.35 | 85.25 | 86.01 | 90.17 | 99.25 | 83.65 | 76.58 | 71.39 | 108.94 | 57.84 | 61.39 | 56.38 | 67.68 | 50.83 | 47.50 | 32.91 | 38.38 | 28.83 | 101.34 |
| 2015 | 162.31 | 144.27 | 144.77 | 140.55 | 138.28 | 148.64 | 118.30 | 131.54 | 125.00 | 113.26 | 90.98 | 89.11 | 83.81 | 91.24 | 100.34 | 81.26 | 86.60 | 72.00 | 97.78 | 63.80 | 63.39 | 56.23 | 66.82 | 52.14 | 45.72 | 30.65 | 42.57 | 29.22 | 99.99 |
| 2016 | 154.17 | 150.11 | 147.85 | 143.34 | 145.55 | 140.75 | 111.27 | 135.10 | 128.88 | 111.42 | 91.45 | 92.11 | 82.88 | 89.73 | 97.34 | 75.37 | 87.77 | 68.13 | 90.91 | 70.38 | 64.93 | 57.32 | 65.83 | 47.91 | 46.82 | 29.50 | 42.29 | 32.72 | 100.40 |
| 2017 | 158.48 | 148.27 | 149.44 | 149.93 | 133.09 | 144.21 | 109.71 | 133.12 | 128.47 | 111.76 | 93.30 | 94.70 | 81.40 | 85.75 | 99.35 | 77.07 | 82.73 | 66.41 | 86.30 | 68.67 | 66.73 | 56.98 | 64.73 | 49.36 | 46.83 | 30.58 | 41.13 | 33.20 | 100.42 |
| 2018 | 148.20 | 147.28 | 140.96 | 138.01 | 132.65 | 148.39 | 112.16 | 131.87 | 126.69 | 112.85 | 94.83 | 97.91 | 80.17 | 81.71 | 95.75 | 75.00 | 87.40 | 62.76 | 85.17 | 71.51 | 69.99 | 56.99 | 64.52 | 49.86 | 47.16 | 29.29 | 49.88 | 35.16 | 100.39 |
| 2019 | 147.73 | 147.95 | 142.63 | 145.11 | 129.69 | 149.30 | 113.50 | 137.82 | 130.09 | 116.46 | 96.70 | 101.57 | 80.74 | 80.67 | 102.88 | 84.22 | 83.11 | 60.94 | 85.46 | 65.89 | 70.70 | 58.58 | 64.90 | 48.38 | 47.84 | 32.94 | 38.68 | 36.58 | 102.01 |
Goals
- To achieve an adequate food self-sufficiency rate and ensure food security in the country.
- Ensure food security through the stable production of safe, high-quality and consumer-friendly food.
Comment
The indicator shows the relationship between the value of food imports and exports and is important from the perspective of monitoring food security and affordable access to food in Slovenia. If the coverage of food imports by exports is less than 100 %, the balance is negative and in terms of value, more food is imported than exported. The aim is to export as much food as possible in terms of value and to improve the coverage ratio. The coverage depends on several factors: rate of self-sufficiency in agricultural products, poor or rich harvests (total yields), extreme weather conditions, domestic consumption, different food trends, etc. Global megatrends show that climate changes in the future may influence food production in Slovenia and increase the dependence on food from the world market, which may also worsen the coverage of food imports by exports (at the expense of higher food imports) and affect food prices in Slovenia.
The indicator of coverage of food imports by exports has been analysed for whole period 2000–2019; but we compare the following period: period before EU accession (2000–2003), post-accession period (2004–2013) and the period of the most recent years (2014–2019). In terms of value, Slovenia was a net importer of food in all three periods mentioned above. In the period before EU accession (2000–2003), the coverage of food imports by exports was on average 43 %. In the post-accession period (2004–2013), the coverage decreased to 37 %. The lowest coverage was in years 2004 and 2007 (both 34 %). The reduction in coverage after EU accession was influenced by several factors. Both food imports and food exports increased in terms of value, with the exception that exports of raw materials or unprocessed agricultural products increased significantly, while imports of processed products (with higher value added) also increased. Since 2007, the coverage has been increasing, and was on average 49 % in the period of recent years (2014– 2019).
Most of the food value trade is with the EU member countries. In the period of recent years (2014–2019), 91 % of total food imports were from EU–28, while 73 % of total food exports were shipped to the EU–28. Just over 50 % of the value of food imports and exports are with neighbouring countries (Austria, Croatia, Italy and Hungary). Before Slovenia's accession to the EU, most of the trade was with the countries of the former Yugoslavia. After the EU accession, food trade has shifted to the EU countries. The coverage of food imports by exports is the highest in trade with Croatia; in the period before EU accession (2000–2003) it was on average 175 %, but then it declined after EU accession. In the period of recent years (2014–2019), the coverage of food imports by exports with neighbouring countries has been the lowest in terms of value in trade with Hungary (13 %) and Austria (35 %), higher with Italy (57 %) and Croatia (68 %). In general, the coverage with neighbouring countries increased during this period.
In terms of value, Slovenia is a net importer of most agricultural products. A trade surplus in value exists only for eggs, which represent a very small share of the total value of imports and exports (less than 1 %). In terms of value, the most traded were sugar, meat, cereals and fruit in the most recent years (2014–2019). Before the EU accession (2000–2003), sugar imports were covered by exports on average of 61 %. After the EU accession, when the only sugar factory in Slovenia was closed and sugar exports declined, the coverage also decreased significantly, to 41 %. In recent years, coverage for sugar has slowly increased due to the increase of exports of products with added sugar and is approaching the level at the beginning of the whole analysed period (2000–2019). Coverage of meat imports by exports was the highest in the pre-accession period (2000–2003), averaging 107 %. In the post-accession period, when the borders were opened and imports of cheaper meat from abroad increased, this share fell sharply (from 120 % in 2003 to 88 % in 2004). Since then, the coverage has been between 60 % and 80 %. The coverage of imports by exports is low for other agricultural products; the lowest for potatoes and vegetables, where it does not exceed 20% in most years. The coverage of rice exports by imports is slightly higher, ranging between 26 % and 54 % in the last years (2014–2019). In general, the share of coverage for all agricultural products except eggs and meat has increased during the whole analysed period. On average, the share of coverage has increased the most for cereals and fruit (from 14 % and 20 % in the period before EU accession to 38 % and 34 % in the period of recent years), while the share of coverage has decreased the most for meat (from 107 % in the pre-accession period to 74 % in the period of recent years).
In contrast to Slovenia, the other EU countries (EU–28) are on average net exporters of agricultural products (agricultural and food products). Over the long period (2000–2019), the coverage of agri-food imports by exports was 98 % on average, whereas over the shorter period (2017–2019) it was 101 %. Among the EU–28, Hungary (167 %), the Netherlands (161 %), Denmark (160 %) and Ireland (152 %) have the highest average coverage over the period 2000–2019. Slovenia is in the bottom third of the EU–28 (average for the period 2000–2019: 58 %). On average over the period 2000–2019, the coverage rate is lower than in Slovenia in Sweden (54 %), Portugal (53 %), Luxembourg (48 %), United Kingdom (47 %), Finland (36 %), Malta (34 %) and Cyprus (29 %).