[KM29] Food self – sufficiency

Key message

Slovenia is a net importer of food, as it does not cover its demand for agricultural products (cereals, potatoes, vegetables, fruit, pig meat and honey) with domestic production. The long-term trend shows that the self-sufficiency rate for most animal products (milk, eggs, beef and poultry) is higher and more stable, with the exception of pig meat and honey, where the rate of self-sufficiency is decreasing. Oppositely, the self-sufficiency rate for most crops is lower (potatoes, vegetables and fruit) and fluctuates over the years (harvests and yields), with only the self-sufficiency rate for cereals increasing in the long term.
Definition
The indicator shows the rate of food self-sufficiency for the following agricultural products: meat, eggs, cereals, potatoes, vegetables, fruit, milk and honey. Food self-sufficiency shows to what point domestic production is able to meet total demand or domestic consumption (consumption for feed, food and industrial consumption) for individual agricultural products. The self-sufficiency rate is calculated only for individual agricultural products and not as the aggregated food self-sufficiency.
The indicator shows self-sufficiency rate for individual agricultural products, the per capita consumption of agricultural products and a comparison of self-sufficiency rate for cereals among the EU countries (EU–18).
Charts
SORS, calculations by Agricultural Institute of Slovenia
Data: 10.06.2020
* Temporary data
| Meat, total [%] | Eggs [%] | Cereals [%] | Potatoes [%] | Vegetables [%] | Fruit [%] | Milk, total [%] | Honey [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 91.58 | 95.42 | 48.02 | 83.34 | 47.15 | 66.04 | 113.23 | 111.65 |
| 2001 | 99.59 | 97.67 | 46.07 | 78.50 | 39.36 | 54.60 | 116.51 | 104.51 |
| 2002 | 97.07 | 96.73 | 62.82 | 85.05 | 42.08 | 59.49 | 115.21 | 105.15 |
| 2003 | 97.27 | 103.95 | 37.62 | 64.46 | 37.22 | 55.60 | 115.58 | 97.37 |
| 2004 | 91.86 | 102.91 | 63.25 | 86.05 | 43.32 | 58.17 | 113.83 | 102.17 |
| 2005 | 88.35 | 94.46 | 60.03 | 74.10 | 44.95 | 48.83 | 113.39 | 75 |
| 2006 | 88.08 | 96.81 | 50.05 | 59.81 | 38.64 | 52.46 | 120.18 | 80.94 |
| 2007 | 92.51 | 95.08 | 53.58 | 70.37 | 33.78 | 48.99 | 120.29 | 77.89 |
| 2008 | 90.95 | 95.35 | 63.54 | 57.45 | 36.01 | 37.71 | 114.56 | 81.44 |
| 2009 | 82.64 | 93.07 | 56.62 | 62.80 | 37.43 | 38.46 | 113.81 | 85.27 |
| 2010 | 84.21 | 92.69 | 56.55 | 62.89 | 30.13 | 46.69 | 116.35 | 73.89 |
| 2011 | 84.74 | 96.22 | 71.09 | 62.97 | 36.51 | 46.48 | 119.75 | 85.17 |
| 2012 | 83.41 | 92.23 | 70.23 | 55.09 | 34.04 | 37.15 | 117.43 | 51.24 |
| 2013 | 81.88 | 91.44 | 54.73 | 46.41 | 33.25 | 42.90 | 118.21 | 82.19 |
| 2014 | 79.79 | 90.43 | 76.57 | 67.46 | 37.83 | 41.94 | 120.25 | 20 |
| 2015 | 73.94 | 93.06 | 72.05 | 58.84 | 39.56 | 47.04 | 125.09 | 70.69 |
| 2016 | 76.37 | 94.78 | 74.12 | 54.94 | 41.71 | 31.83 | 131.75 | 59.09 |
| 2017 | 81.49 | 90.43 | 63.11 | 49.87 | 38.48 | 14.53 | 134.30 | 44.69 |
| 2018 | 80.64 | 95.60 | 69.07 | 48.45 | 40.91 | 47.19 | 128.70 | 79.19 |
| 2019* | 80.92 | 95.09 | 74.12 | 45.37 | 43.70 | 29.55 | 127.50 | 40.88 |
SORS, calculations by Agricultural Institute of Slovenia
Data: 10.06.2020
* Temporary data
| Beef and veal [%] | Pig meat [%] | Poultry meat [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 95.89 | 76.62 | 109.80 |
| 2001 | 119.06 | 80.72 | 113.26 |
| 2002 | 116.95 | 77.77 | 110.37 |
| 2003 | 106.68 | 86.50 | 114.44 |
| 2004 | 96.47 | 79.92 | 115.13 |
| 2005 | 93.37 | 69.53 | 112.36 |
| 2006 | 101.45 | 69.67 | 108.22 |
| 2007 | 101.28 | 73.63 | 113.74 |
| 2008 | 103.06 | 70.23 | 112.92 |
| 2009 | 98.06 | 54.81 | 109.14 |
| 2010 | 106 | 52.26 | 112.18 |
| 2011 | 109.69 | 49.50 | 113.33 |
| 2012 | 111.50 | 46.48 | 109.28 |
| 2013 | 107.44 | 39.63 | 117.35 |
| 2014 | 106.33 | 38.95 | 111.36 |
| 2015 | 98.62 | 34.56 | 103.08 |
| 2016 | 107.69 | 34.48 | 106.71 |
| 2017 | 110.48 | 38 | 109.36 |
| 2018 | 109.47 | 37.62 | 109.49 |
| 2019* | 103.06 | 39.83 | 109.88 |
SORS, calculations by Agricultural Institute of Slovenia
Data: 10.06.2020
* Temporary data
| Meat, total (carcass weight equivalent) [kg] | Eggs [kg] | Cereals [kg] | Potatoes [kg] | Vegetables [kg] | Fruit [kg] | Milk, total (raw milk equivalent) [kg] | Honey [kg] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 88.51 | 10.81 | 129.76 | 90.15 | 78.54 | 104.49 | 231.42 | 1.04 |
| 2001 | 93.04 | 10.11 | 135.19 | 79.57 | 73.39 | 79.12 | 227.89 | 1.22 |
| 2002 | 87.99 | 9.61 | 126.23 | 79.84 | 78.70 | 114.89 | 234.58 | 1.17 |
| 2003 | 99.17 | 6.85 | 123.62 | 72.45 | 81.52 | 100.10 | 228.68 | 0.95 |
| 2004 | 98.58 | 6.23 | 119.45 | 75.77 | 88.97 | 128.25 | 235.76 | 1.15 |
| 2005 | 97.30 | 6.51 | 123.99 | 76.82 | 91.26 | 125.07 | 235.33 | 1.10 |
| 2006 | 94.21 | 7.03 | 125.49 | 78.90 | 95.57 | 124.44 | 218.93 | 1.38 |
| 2007 | 94.66 | 8.91 | 123.92 | 81.35 | 90.29 | 131.73 | 223.64 | 0.94 |
| 2008 | 96.64 | 10.03 | 119.23 | 77.49 | 100.97 | 151.69 | 234.03 | 0.96 |
| 2009 | 94.14 | 10.23 | 108.73 | 72 | 103.24 | 148.45 | 229.97 | 1.10 |
| 2010 | 93.70 | 10.15 | 121.05 | 70.31 | 91.81 | 135.22 | 223.74 | 1.10 |
| 2011 | 89.53 | 10.12 | 118.06 | 66.43 | 97.09 | 129.30 | 218.91 | 1.41 |
| 2012 | 88.15 | 9.08 | 115.44 | 63.27 | 95.33 | 112.98 | 225.86 | 0.98 |
| 2013 | 82.24 | 10.27 | 112.29 | 59.41 | 98.29 | 129.39 | 218.59 | 1.42 |
| 2014 | 84.99 | 9.78 | 119.27 | 62.37 | 103.92 | 131.06 | 219.87 | 1.14 |
| 2015 | 88.32 | 11.06 | 120.89 | 68.25 | 109.88 | 134.23 | 218.68 | 1.41 |
| 2016 | 94.22 | 10.67 | 121.41 | 68.51 | 113.41 | 122.69 | 213.25 | 1.07 |
| 2017 | 93.08 | 11.52 | 120.97 | 68 | 113.97 | 121.62 | 209.89 | 0.87 |
| 2018 | 92.60 | 10.85 | 123.30 | 66.49 | 111.41 | 152.48 | 215.54 | 1.07 |
| 2019* | 90.82 | 11.66 | 118.24 | 63.71 | 123.21 | 128.85 | 213.76 | 0.76 |
SORS, calculations by Agricultural Institute of Slovenia
Data: 10.06.2020
* Temporary data
| Beef and veal [kg] | Pigmeat [kg] | Poultrymeat [kg] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 20.55 | 38.12 | 24.76 |
| 2001 | 20.23 | 41.29 | 26.05 |
| 2002 | 19.16 | 39.86 | 24.11 |
| 2003 | 23.55 | 42.43 | 24.90 |
| 2004 | 23.38 | 44.60 | 23.07 |
| 2005 | 23.61 | 44.15 | 24.66 |
| 2006 | 20.72 | 45.17 | 23.04 |
| 2007 | 21.07 | 42.05 | 26.05 |
| 2008 | 21.32 | 43.15 | 26.65 |
| 2009 | 20.49 | 40.51 | 28.06 |
| 2010 | 19.94 | 41.55 | 27.72 |
| 2011 | 19.82 | 39.55 | 26.22 |
| 2012 | 18.93 | 37.68 | 27.74 |
| 2013 | 18.57 | 35.54 | 24.76 |
| 2014 | 18.06 | 36.82 | 26.99 |
| 2015 | 18.99 | 37.02 | 28.88 |
| 2016 | 19.96 | 40.75 | 29.99 |
| 2017 | 20.77 | 37.62 | 31.08 |
| 2018 | 19.84 | 37.85 | 31.23 |
| 2019* | 20.01 | 36.70 | 30.81 |
EUROSTAT, calculations by Agricultural Institute of Slovenia
Data: 15.04.2020
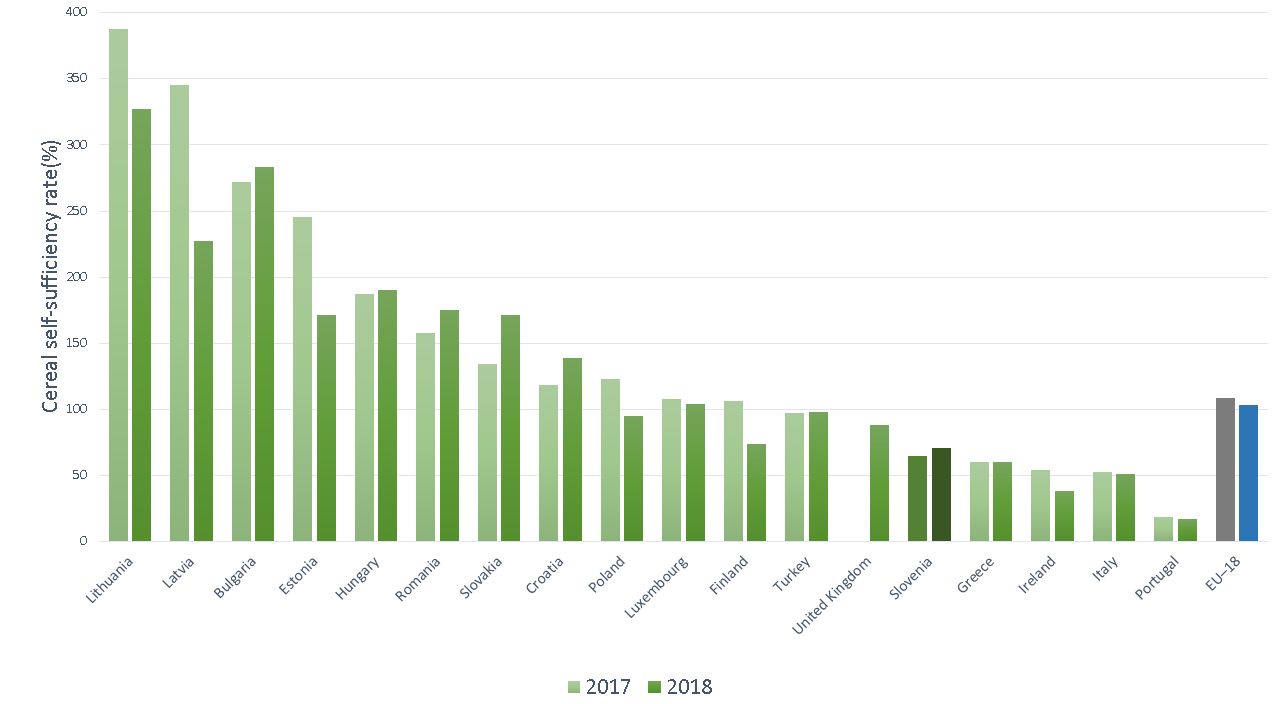
| Lithuania [%] | Latvia [%] | Bulgaria [%] | Estonia [%] | Hungary [%] | Romania [%] | Slovakia [%] | Croatia [%] | Poland [%] | Luxembourg [%] | Finland [%] | Turkey [%] | United Kingdom [%] | Slovenia [%] | Greece [%] | Ireland [%] | Italy [%] | Portugal [%] | EU–18 [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 387.08 | 345.43 | 271.50 | 245.47 | 186.85 | 157.43 | 134.21 | 118.55 | 122.47 | 107.55 | 106.00 | 97.21 | 64.71 | 59.81 | 54.08 | 52.68 | 18.27 | 108.94 | |
| 2018 | 326.91 | 227.49 | 283.09 | 171.40 | 190.17 | 174.67 | 170.84 | 138.42 | 95.13 | 103.60 | 73.66 | 97.97 | 88.29 | 70.61 | 59.80 | 38.42 | 51.30 | 16.71 | 103.54 |
Goals
- Increase the self-sufficiency rate for vegetables to 50 % by 2020.
- Increase the self-sufficiency rate for pig meat to 70 % by 2020.
- Increase the self-sufficiency rate for the following commodities, commodity groups and processed products by 2020: wheat, fodder cereals, legumes, oilseeds, potatoes, vegetables (fresh and processed), pig meat, cheese, curd cheese and honey.
- To achieve an adequate food self-sufficiency rate and ensure food security in the country.
- Ensure food security through the stable production of safe, high-quality and consumer-friendly food.
Comment
The food self-sufficiency rate indicates the level of country’s self-sufficiency in terms of providing sufficient quantities of food, which is very important from the point of view of food security and access to food for the Slovenian population. Global megatrends show that the quality and quantity of the food produced and the increasing dependence on the global market could be affected in the future by increasing climate change. Slovenia is a net importer of food, as it does not cover its demand for agricultural products with domestic production. In Slovenia, the self-sufficiency rate is higher in livestock production and lower in crop production, the lowest rates of self-sufficiency are in fruit, vegetables and potatoes. The self-sufficiency rate in crop production fluctuates over the years due to poor or rich harvests (total yields), which are also strongly influenced by extreme weather conditions such as droughts, frosts, hail and floods.
Self-sufficiency rate for agricultural products and the per capita consumption of agricultural products are compared between the periods before EU accession (2000–2003), post-accession period (2004–2013) and the period of recent years (2014–2018). Prior to EU accession, Slovenia was self-sufficient in milk and almost 100 % self-sufficient in eggs and meat. In the post-accession period (2004–2013), the self-sufficiency rate in meat, potatoes and fruit decreased, while self-sufficiency rate for cereals increased. The self-sufficiency rate for potatoes and fruit was lower due to lower production and the effects of extreme weather conditions. The meat self-sufficiency rate was lower due to the substantial decrease in production of pig meat due to weak competitiveness, slow structural change and price pressure (cheaper imports of foreign pig meat). A year after Slovenia's accession to the EU, the reform of the EU sugar market was adopted. As a result, the only sugar factory in Slovenia was closed and since then no sugar has been produced in Slovenia. Before the reform, the sugar self-sufficiency rate was on average 50 %. In recent years (2014–2018), Slovenia has been self-sufficient in milk, beef and poultry. The largest deficit was in fruit, vegetables, potatoes and pig meat. Compared to the pre-accession period (2000–2003), the milk and cereals self-sufficiency rates increased, while the meat, potatoes and fruit self-sufficiency rates decreased. The pig meat and honey self-sufficiency rates decreased the most, for more than a half, while the vegetables and eggs self-sufficiency rates remained at a similar level.
The per capita consumption of agricultural products fluctuates over the years. Compared to the pre-accession period (2000–2003), in the period 2014–2018, on average 42 % more vegetables (+32 kg) and 33 % more fruit (+33 kg) were consumed per capita. The consumption of eggs and poultry also increased (+1 kg and +5 kg per capita). Oppositely, potato consumption decreased the most (–14 kg per capita), while consumption of cereals, milk, beef and poultry decreased only slightly.
Strategy for the implementation of the Resolution on strategic orientations for the development of Slovene agriculture and food industry until 2020 (from year 2014) defined goals of achieving self-sufficiency rate of 50 % for vegetables and 70 % for pig meat by the end of 2020, but the current situation does not come close to these goals. The self-sufficiency rate for vegetables is slowly increasing, but has not yet reached the 50 % rate, while the self-sufficiency rate for pig meat has not reached 40 % rate in the most recent years. These goals have not been achieved by 2020
The rate of food self-sufficiency also influences the country's carbon footprint. A lower rate of self-sufficiency requires higher food imports, which increases the carbon footprint. Oppositely, greater self-sufficiency has a positive impact on food security and contributes to the greenhouse gas reduction goals (Operational Program for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by 2020), such as ensuring that greenhouse gas emissions by 2020 do not increase by more than 4% compared to 2005 and maintaining greenhouse gas emissions while increasing Slovenia's food self-sufficiency and ensuring food security. For the time being, the emissions movement in the agricultural sector remains in line with the goals.
On average, the EU countries (EU–18) are self-sufficient with cereals (2017: 109 %, 2018: 104 % self-sufficiency rate). The highest self-sufficiency rates for cereals are found in Lithuania (327 %), Bulgaria (283 %), Latvia (227 %), Hungary (190 %), Romania (175 %), Estonia and Slovakia (both 171 %). Slovenia is at the bottom third of the EU–18 by the rate of self-sufficiency for cereals (ranked 14th in 2018; 71 %). Low self-sufficiency rates are also found in Greece (2018: 60 %), Italy (2018: 51 %), Ireland (2018: 38 %) and Portugal (2018: 17 %).
Methodology
- EUROSTAT. 2018. Crop balances handbook, 2018 edition.
- Gale Š. 2014. Nekaj ščepcev podatkov o hrani. Ljubljana, Statistični urad Republike Slovenije. https://www.stat.si/StatWeb/News/Index/4872
- Kožar M., Pintar M., Volk T. 2014. Slovenian agri-food sector – A decade after the EU accession. V: 14th EEA International Congress, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 26-29 aug. 2014. https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/187278
- Operativni program ukrepov zmanjšanja emisij toplogrednih plinov do leta 2020 https://www.gov.si/teme/zmanjsanje-emisij-toplogrednih-plinov/
- Poročilo o stanju kmetijstva, živilstva, gozdarstva in ribištva, Kmetijski inštitut Slovenije https://www.kis.si/Porocila_o_stanju_v_kmetijstvu_OEK/
- Resolucija: »Naša hrana, podeželje in naravni viri po 2021«. http://www.pisrs.si/Pis.web/pregledPredpisa?id=RESO125
- STATISTICAL OFFICE OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES, EUROSTAT. 1998. Working party »CROP PRODUCTS STATISTICS« of the Agricultural Statistics Committee EEA. Handbook to compile supply balance sheet: general information, concepts, Luxemburg.
- Strategija za izvajanje resolucije o strateških usmeritvah razvoja slovenskega kmetijstva in živilstva do leta 2020. http://vrs-3.vlada.si/mandat13/vladnagradiva.nsf/bf16d7c913264dcac1256efa002c1c6e/7695b7f27056870cc1257cf400295ee4/$FILE/STRATEGIJA_12_6_2014.pdf
- Vpliv globalnih megatrendov na stanje okolja v Sloveniji, MOP ARSO 2019.
http://nfp-si.eionet.europa.eu:8980/Public/irc/eionet-circle/javna/library?l=/cooperation_eeasodelovan/sloveniji_2017-2018/konno_poroilo&vm=detailed&sb=Title