[OD07] Waste management

Definition
The indicator shows the ratio between waste recovered and waste disposed of each year. The quantity and share of each recovery or disposal method are shown for municipal, hazardous and industrial waste.
The purpose of waste recovery is to divert a waste material from the waste stream, which results in a certain product with a potential economic or ecological benefit and it mainly refers to reuse and, material, biological and energy recovery. The latter implies the use of waste as fuel in a combustion plant or industrial furnace, or the use of waste to generate fuel. The recovery procedures are determined in Annex 5 of the Decree on the management of waste (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, nos. 34/08). Recovery does not include incineration of municipal and other waste by means of thermal treatment for the purpose of disposal.
Disposal of waste is the ultimate treatment of waste which cannot be recovered. Disposal methods include biological, thermal or chemo-physical treatment, incineration and landfilling. The procedures of waste disposal are outlined in Annex 6 of the Decree on the management of waste (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, nos. 34/08).
Charts
Waste Management Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2006
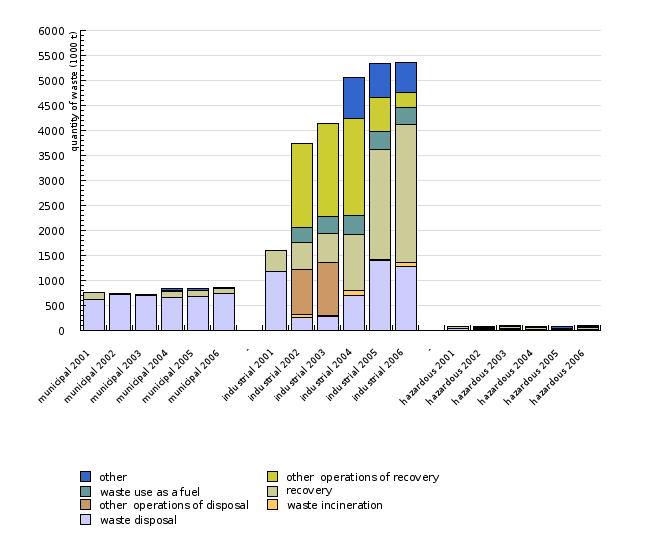
| municipal 2001 | municipal 2002 | municipal 2003 | municipal 2004 | municipal 2005 | municipal 2006 | - | industrial 2001 | industrial 2002 | industrial 2003 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| waste disposal | 1000 t | 620.8 | 712.8 | 693.5 | 667.7 | 672.3 | 731.8 | 1186.9 | 268.3 | 272 | |
| waste incineration | 1000 t | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 6.3 | 0 | 56.3 | 20.2 | |
| other operations of disposal | 1000 t | 0 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 894.1 | 1065.9 | |
| recovery | 1000 t | 141.4 | 7.1 | 11.3 | 112 | 129.1 | 96.8 | 421.9 | 536.2 | 583.1 | |
| waste use as a fuel | 1000 t | 0 | 4.5 | 1.6 | 14.3 | 2.2 | 0 | 0 | 313.1 | 332.2 | |
| other operations of recovery | 1000 t | 0 | 4.9 | 6.2 | 1.8 | 3.5 | 4 | 0 | 1663 | 1873.4 | |
| other | 1001 t | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36.8 | 36.3 | 26.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| total | 1000 t | 762.2 | 731.1 | 712.7 | 832.8 | 844.6 | 865.8 | 1608.8 | 3731 | 4146.8 | |
| industrial 2004 | industrial 2005 | industrial 2006 | - | hazardous 2001 | hazardous 2002 | hazardous 2003 | hazardous 2004 | hazardous 2005 | hazardous 2006 | ||
| waste disposal | 1000 t | 700.1 | 1390.5 | 1283.2 | 45.4 | 11.3 | 11.7 | 5.8 | 0.3 | 7.4 | |
| waste incineration | 1000 t | 105.6 | 19.5 | 82.6 | 0 | 12.5 | 15 | 11.6 | 13.5 | 13.7 | |
| other operations of disposal | 1000 t | 0 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 7 | 0 | 1.1 | 0 | |
| recovery | 1000 t | 1115.5 | 2202.1 | 2752.9 | 34.1 | 36.6 | 48.2 | 44.1 | 5.1 | 33.3 | |
| waste use as a fuel | 1000 t | 372.4 | 360.9 | 339.3 | 0 | 4.2 | 7.3 | 13.6 | 16.6 | 15 | |
| other operations of recovery | 1000 t | 1947 | 679.9 | 311.3 | 0 | 3.2 | 5.2 | 6.3 | 8 | 4.8 | |
| other | 1001 t | 827 | 682.6 | 589.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.7 | 39.8 | 16.7 | |
| total | 1000 t | 5067.6 | 5336.6 | 5358.7 | 79.5 | 75.9 | 94.5 | 83.1 | 84.4 | 90.9 |
Waste Management Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2006
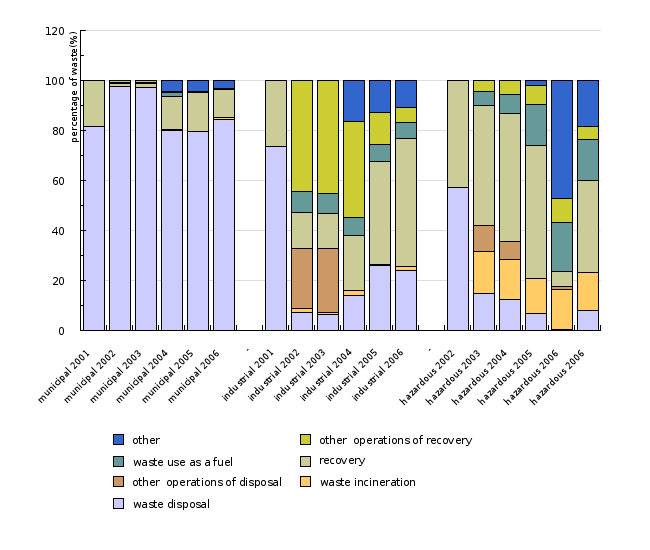
| municipal 2001 | municipal 2002 | municipal 2003 | municipal 2004 | municipal 2005 | municipal 2006 | - | industrial 2001 | industrial 2002 | industrial 2003 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| waste disposal | % | 81.4 | 97.5 | 97.3 | 80.2 | 79.6 | 84.5 | 73.8 | 7.2 | 6.6 | |
| waste incineration | % | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1.5 | 0.5 | ||||
| other operations of disposal | % | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 25.7 | |||
| recovery | % | 18.6 | 1 | 1.6 | 13.4 | 15.3 | 11.2 | 26.2 | 14.4 | 14.1 | |
| waste use as a fuel | % | 0.6 | 0.2 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 0 | 8.4 | 8 | |||
| other operations of recovery | % | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 44.6 | 45.2 | |||
| other | % | 4.4 | 4.3 | 3.1 | |||||||
| total | % | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| industrial 2004 | industrial 2005 | industrial 2006 | - | hazardous 2002 | hazardous 2003 | hazardous 2004 | hazardous 2005 | hazardous 2006 | hazardous 2006 | ||
| waste disposal | % | 13.8 | 26.1 | 23.9 | 57.1 | 14.9 | 12.4 | 7 | 0.4 | 8.1 | |
| waste incineration | % | 2.1 | 0.4 | 1.5 | 16.5 | 15.9 | 14 | 16 | 15.1 | ||
| other operations of disposal | % | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.5 | 7.4 | 0 | 1.3 | 0 | ||
| recovery | % | 22 | 41.3 | 51.4 | 42.9 | 48.2 | 51 | 53.1 | 6 | 36.6 | |
| waste use as a fuel | % | 7.3 | 6.8 | 6.3 | 5.6 | 7.8 | 16.4 | 19.7 | 16.5 | ||
| other operations of recovery | % | 38.4 | 12.7 | 5.8 | 4.3 | 5.5 | 7.6 | 9.5 | 5.3 | ||
| other | % | 16.3 | 12.8 | 11 | 2 | 47.2 | 18.4 | ||||
| total | % | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
Waste Management Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2006
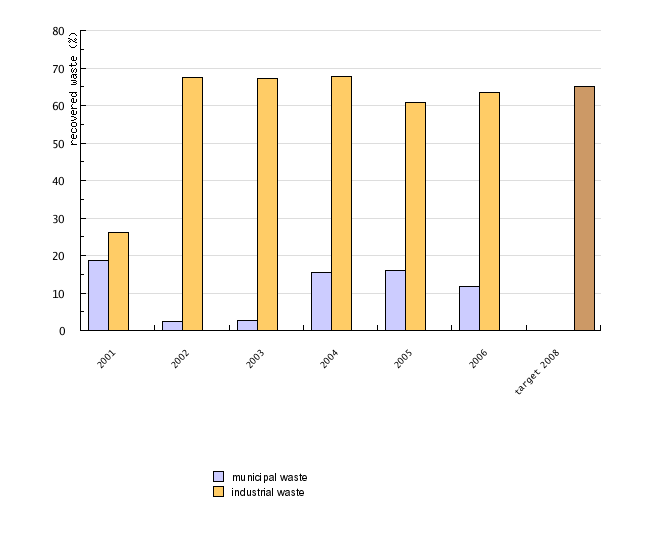
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | target 2008 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| municipal waste | % | 18.6 | 2.3 | 2.7 | 15.4 | 16 | 11.6 | |
| industrial waste | % | 26.2 | 67.3 | 67.2 | 67.8 | 60.8 | 63.5 | |
| 65 |
Waste Management Database, Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, 2006; Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Slovenia 2994, 2005
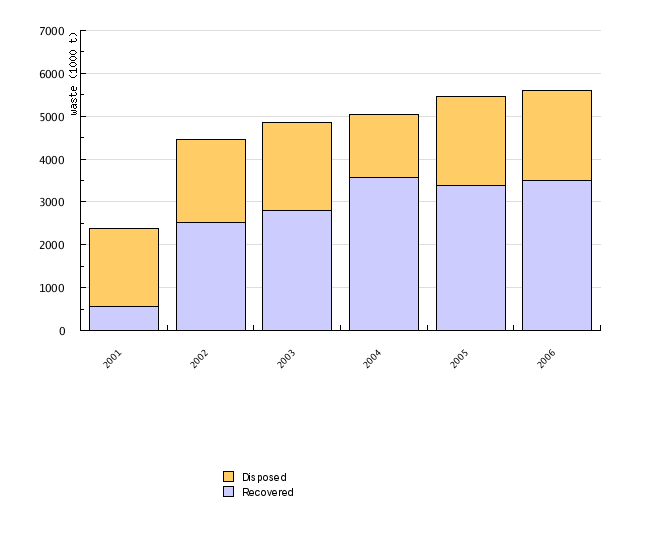
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovered | 1000 t | 563.3 | 2528.8 | 2807.7 | 3563 | 3377.7 | 3504.4 |
| Disposed | 1000 t | 1807.7 | 1933.2 | 2051.8 | 1473.6 | 2084.6 | 2103.9 |
Goals
To optimize the reuse and recovery of waste:
• treatment of at least 65% of all municipal waste prior to disposal and material utilization of at least 42% of it,
• treatment of at least 65% of industrial waste prior to disposal,
• further reduction of the quantities of hazardous waste at a rate of 5 – 10% annually.
Comment
Waste recovery has been steadily gaining ground. One of the reasons is the improved technical feasibility of recovery, allowing for both environmentally friendly and economical treatment. Recovery includes recycling, reuse and thermal treatment, where waste is used as an alternative source of energy. The environmental tax on landfilling serves as encouragement for further exploration of such options.
Another reason for increased recovery is related to the use of natural resources. In a consumer society, the useful life of a product is increasingly shorter; often, items are assembled from components which can only be replaced rather than repaired. It is therefore crucial that we maximize the level of reuse, recycling and recovery of waste to avoid excessive exploitation of natural resources. New environmental taxes on packaging, automobile tyres and waste electrical and electronic equipment further encourage the use of recyclable materials.
Though waste recovery is on the rise, absolute quantities of landfilled waste are not diminishing. We have not been able to cut the link between GDP growth and the increase of all types of waste. Furthermore, recovery is currently only suitable for specific types of waste. We will thus be facing quite a few challenges in the future before we shift the ratio between landfilled and recovered waste to the benefit of the latter.
The rising reuse, recycling and recovery of waste also contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gases.
Landfilling remains the most common method of municipal waste disposal in Slovenia. 85 % of municipal waste was landfilled in 2006. About 65% of industrial waste has been recovered annually since 2002. Waste disposed by means of other methods includes fly ash, which is used to backfill mine tunnels, and slag, which is used as construction material. The ratio for hazardous waste is similar to that of industrial waste - less than 40% of such waste is disposed of.
Methodology
Ministry of the Environment and Spatial Planning – Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia, database on the generation and management of all types of waste in the Republic of Slovenia.
The required reporting on waste is prescribed in the Environment Protection Act (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, no. 41/04, 20/06 and 70/08) and detailed in the Decree on waste management (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, nos. 34/08). Until 2008 in the Rules on the management of waste (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, nos. 84/98, 45/00, 20/01, 13/03). Provisions on municipal waste are given in the Order on the management of separately collected fractions in the public service of urban waste management (Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia, nos. 21/01 and 41/04). Municipal waste must be reported by local providers of public service of collection and transport of municipal and similar waste generated by production and service sectors and public municipal services. The Rules on the management of waste stipulate that reports on waste from industrial and other activities must be submitted by generators, collectors, recovery providers or disposers of non-hazardous and hazardous waste from the industry and other activities exceeding the prescribed quantity threshold (10 tonnes for non-hazardous waste and 5 tonnes for hazardous waste). Reports are submitted by March 31 for the previous year.